5 Key Zinc Die Casting Applications in Modern Manufacturing
Zinc die casting is an essential manufacturing process that involves injecting molten zinc alloy into a mold to produce complex, durable parts. Thanks to its versatility, strength, and cost-effectiveness, zinc die casting has become one of the most widely used techniques in various industries, ranging from automotive to electronics. In this article, we’ll dive into the key applications of zinc die casting, explore the advantages and disadvantages of zinc alloys, and discuss the most commonly used materials in this process
Key Industries for Zinc Die Casting Applications
Zinc die casting serves a crucial role in many industries due to its excellent properties, such as high corrosion resistance, dimensional stability, and ease of mass production. The following sectors are among the biggest adopters of zinc die casting applications:

Automotive Industry
The automotive sector is one of the largest consumers of zinc die casting products. Zinc alloys are widely used for manufacturing parts such as transmission cases, engine brackets, door handles, and more. These parts benefit from zinc’s strength and durability while keeping the overall weight of the vehicle low.
Consumer Electronics
Zinc die casting applications are found in consumer electronics like mobile phones, laptops, and other handheld devices. Zinc components, such as enclosures and connectors, offer both structural integrity and aesthetic appeal, making them ideal for the design of modern electronic devices.


Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, zinc die casting is used for producing lightweight yet strong components that need to withstand high-stress conditions. Parts like brackets, housings, and connectors made from zinc alloys contribute to the performance and longevity of aircraft
Construction and Hardware
Zinc die casting is also applied in the production of various construction components and hardware items, such as locks, faucets, and electrical connectors. The material’s ability to resist corrosion makes it especially valuable for outdoor and marine applications
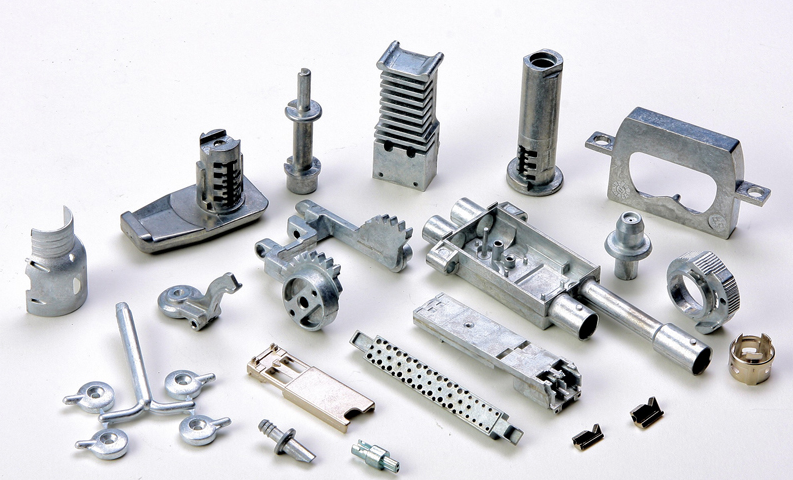


Medical Devices
Zinc die casting applications extend to the medical field, where zinc alloys are used to produce medical equipment parts such as surgical instruments, prosthetics, and dental devices. The biocompatibility and strength of zinc alloys ensure that these parts can perform effectively while enduring harsh conditions.
Zinc Die Casting Advantages VS Disadvantages
Zinc die casting is widely used in modern manufacturing due to its excellent balance of precision, strength, and cost efficiency. However, like all die casting materials, zinc alloys offer specific advantages as well as certain limitations. Understanding these factors helps manufacturers determine whether zinc die casting applications are suitable for their design, performance, and production requirements.
Advantages of Zinc Die Casting
- Excellent Corrosion Resistance
Zinc alloys provide strong natural corrosion resistance, making zinc die casting applications ideal for outdoor, marine, and industrial environments where long-term durability is required. - High Dimensional Accuracy and Precision
Zinc die casting enables tight tolerances and superior dimensional stability, reducing the need for secondary machining and ensuring consistent part quality in mass production. - Cost-Effective for High-Volume Production
With relatively low material cost, long mold life, and high casting efficiency, zinc die casting is a cost-effective solution for large-scale manufacturing. - Good Mechanical Strength and Impact Resistance
Zinc alloys offer reliable strength, hardness, and impact resistance, making them suitable for functional and load-bearing components in automotive and hardware applications. - Excellent Castability for Complex Designs
The superior fluidity of molten zinc allows the production of thin walls, intricate geometries, and fine surface details with minimal post-processing.
Disadvantages of Zinc Die Casting
- Limited Performance at High Temperatures
Zinc alloys tend to soften at elevated temperatures, making zinc die casting less suitable for continuous high-temperature or extreme thermal environments. - Lower Strength Compared to Aluminum or Magnesium Alloys
While zinc alloys perform well in most applications, they generally offer lower tensile strength than aluminum or magnesium die casting materials under extreme loads. - Higher Density Than Lightweight Metals
For applications where weight reduction is critical, zinc alloys may be heavier than alternative die casting materials such as aluminum or magnesium. - Potential for Stress Cracking
Improper part design or excessive mechanical stress may increase the risk of stress cracking in zinc die cast components, especially in demanding operating conditions.
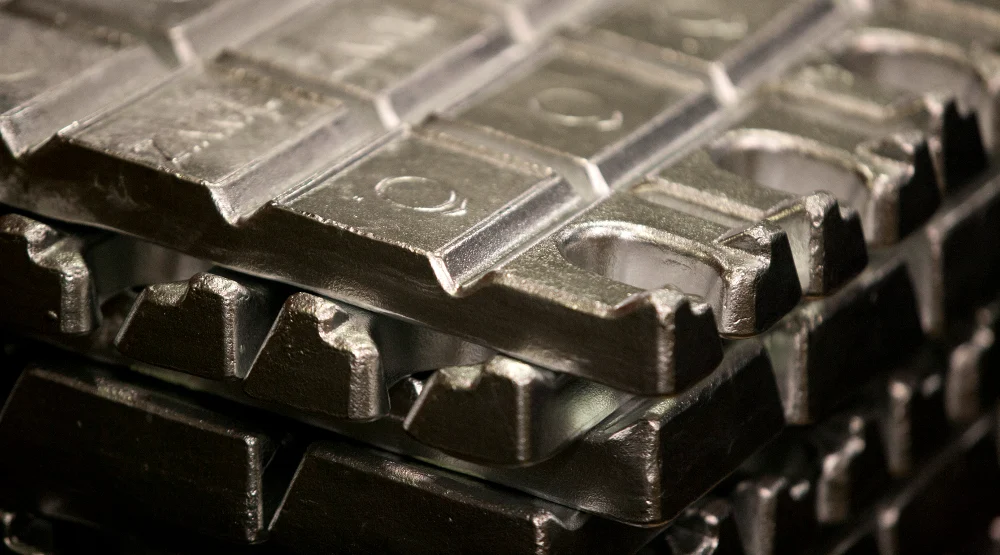
Commonly Used Zinc Alloys in Die Casting
There are several types of zinc alloys used in die casting, each offering different properties that cater to specific applications. The most common zinc die casting alloys include:

Zinc Alloy 3 (Zamak 3)
Zinc Alloy 3, also known as Zamak 3, is one of the most widely used alloys in the die casting industry. It contains approximately 95% zinc, with small amounts of aluminum, copper, and magnesium. Zamak 3 is known for its excellent mechanical properties, such as strength and hardness, making it suitable for a variety of applications in automotive, electronics, and hardware industries.
Zinc Alloy 5 (Zamak 5)
Zinc Alloy 5 is similar to Zamak 3 but contains higher amounts of aluminum (around 4-5%). This alloy offers improved strength, hardness, and better creep resistance at higher temperatures, making it ideal for applications in the automotive and industrial sectors.
Zinc Alloy 7 (Zamak 7)
Zinc Alloy 7 is an alloy with a higher copper content, which enhances its dimensional stability and improves its resistance to corrosion. This alloy is commonly used in applications requiring precise, high-quality components such as in the electrical and electronics industries.
Zinc Alloy 8 (Zamak 8)
Zinc Alloy 8 is a specialized alloy that features an improved composition for better wear resistance and higher strength. It is particularly suited for parts that undergo frequent mechanical wear, such as gears, bearings, and other high-performance applications.
Zinc Alloy 2 (Zamak 2)
Zinc Alloy 2 is the most robust among the zinc alloys and is used for parts that require enhanced strength and durability. It is commonly used in industrial applications where strength and wear resistance are critical.
Conclusion: Why Zinc Die Casting Is Essential for Modern Manufacturing
Zinc die casting offers a wide range of applications across various industries, thanks to its exceptional properties such as corrosion resistance, strength, and cost-effectiveness. From the automotive and electronics sectors to medical devices and aerospace, zinc die casting provides reliable solutions for the production of high-quality, precision components.
By understanding the advantages and limitations of zinc alloys, as well as the different types of alloys available, manufacturers can make informed decisions on the best materials for their projects. With the continued evolution of die casting technology, zinc alloys remain an integral part of modern manufacturing, meeting the demands of today’s fast-paced industries while delivering superior performance and value.
Whether you’re in the automotive, electronics, aerospace, or any other industry, zinc die casting applications can provide you with a reliable and cost-effective solution for your manufacturing needs.
Optimize Your Manufacturing with Zinc Die Casting
By choosing zinc die casting, you can benefit from durable, high-quality components at competitive prices. Contact us today to explore how our zinc die casting solutions can enhance your manufacturing processes and elevate your product quality.
IEC MOULD (China)
Location: China
Email: sherry@iec-mould.com
Tel: +86-0769-85336570
Website: www.iec-mould.com