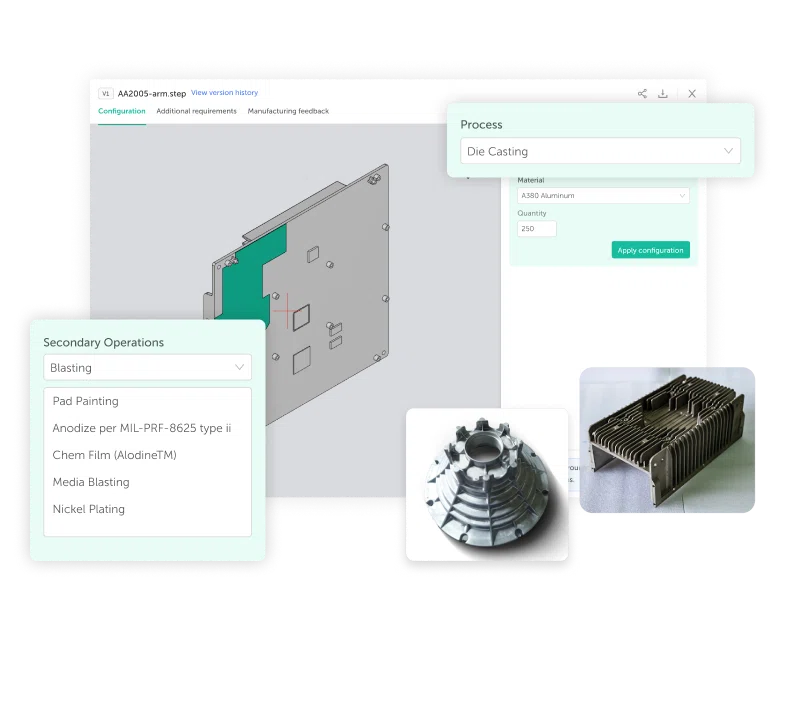
Your Trusted Zinc Die Casting Supplier
Looking for durable and precise zinc die cast parts? IEC MOULD provides professional Zinc Die Casting services with excellent surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and fast production turnaround. We support projects of all sizes, delivering high-performance castings tailored to your needs.

±0.01mm
Tolearance
20+
Years Experience
20 Day
Die Casting Samples Delivered
Certifications
ISO 9001 & IATF 16949
China Zinc Die Casting Manufacturer and Supplier
IEC MOULD is a trusted Zinc Die Casting manufacturer and supplier, specializing in high-strength, precision-engineered components. Leveraging our in-house mold workshop, advanced zinc die casting lines, CNC machining center, and surface finishing capabilities, we deliver full-process manufacturing—from design and prototyping to finished assemblies. We produce components with:
- Tight Tolerances: Ensuring perfect fit and reliable assembly performance.
- Durable Zinc Alloys: High strength, corrosion resistance, and wear performance.
- Complex Geometries & Excellent Surface Finish: Reducing post-processing needs.
- Fast Turnaround: Supporting both small-scale prototypes and large-volume production.
Backed by ISO 9001 & IATF 16949 certifications, rigorous quality control, and advanced testing equipment, IEC MOULD guarantees consistent quality, cost-effective manufacturing, and on-time delivery for global customers. Partner with IEC MOULD for reliable, high-performance zinc die cast components engineered to meet your most demanding applications.
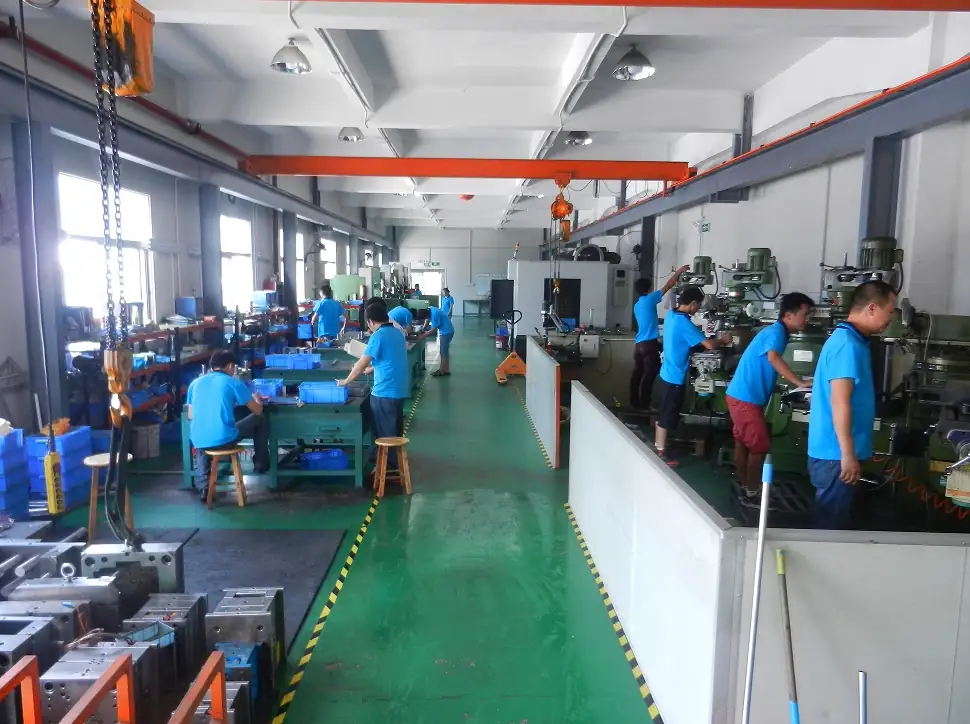
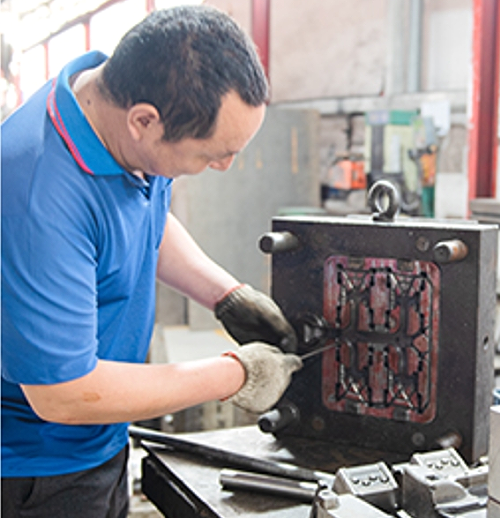
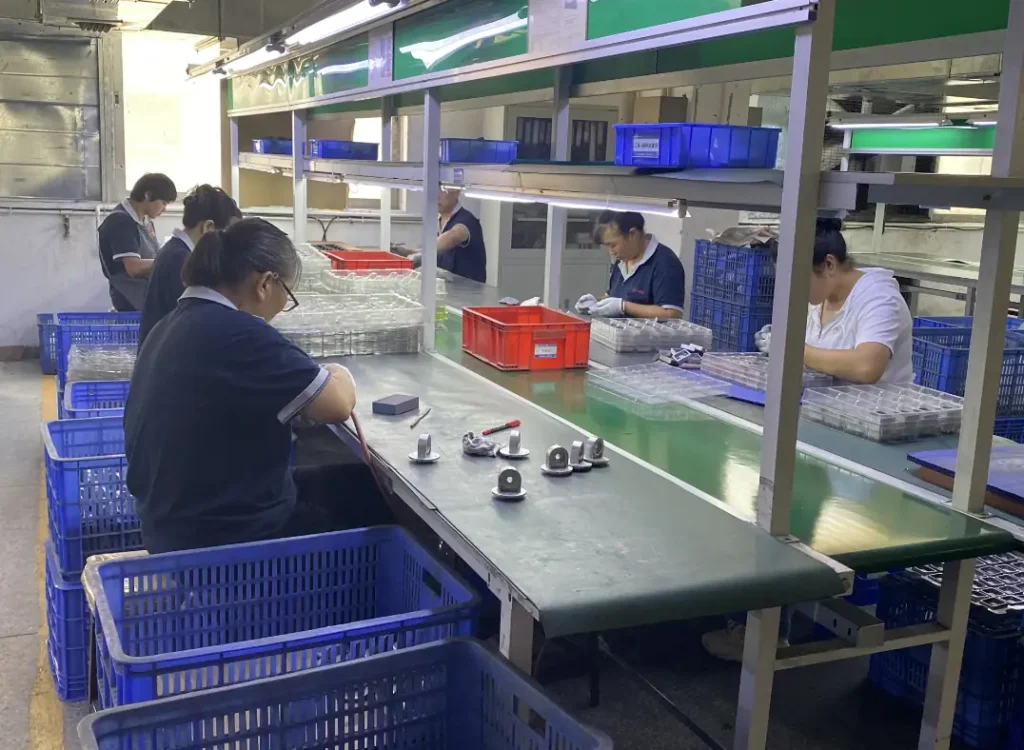





Our Zinc Die Casting Services
We deliver complete zinc die casting solutions that ensure precision, strength, and production efficiency from design to final assembly:
- Custom Zinc Component Manufacturing – Expertly crafted zinc parts with intricate details, thin walls, and tight tolerances for reliable assembly performance.
- Design & Engineering Support – Comprehensive DFM reviews, mold flow simulation, and material optimization to enhance casting quality and process efficiency.
- Tooling & Mold Production – Precision-built die tools with optimized gating and venting systems for consistent filling and long tool life.
- High-Precision Machining – Multi-axis CNC machining, drilling, and threading to achieve perfect dimensional accuracy and assembly readiness.
- Surface Treatment & Finishing – Electroplating, powder coating, polishing, and painting for enhanced appearance and corrosion protection.
- Assembly Integration – Mechanical assembly, insert installation, and sealing functions for turnkey zinc component delivery.
- Quality Assurance & Inspection – Dimensional checks, X-ray inspection, hardness testing, corrosion resistance evaluation, and full traceability reporting.
With IEC MOULD, you gain more than a zinc die casting supplier—you gain a dependable manufacturing partner focused on quality, efficiency, and technical excellence. We combine engineering expertise with modern production control to ensure every component meets your functional and aesthetic expectations.
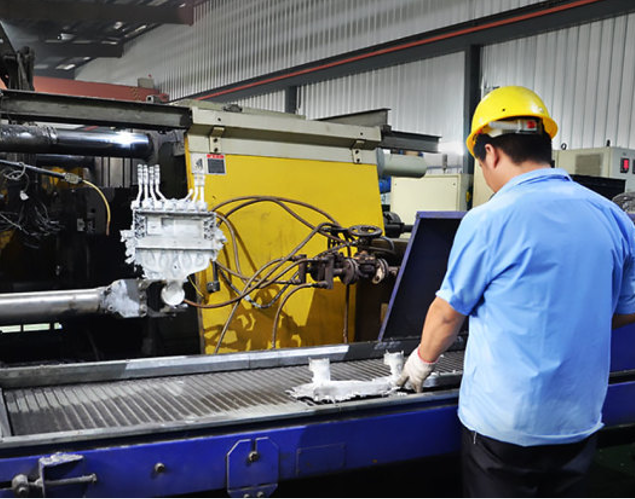
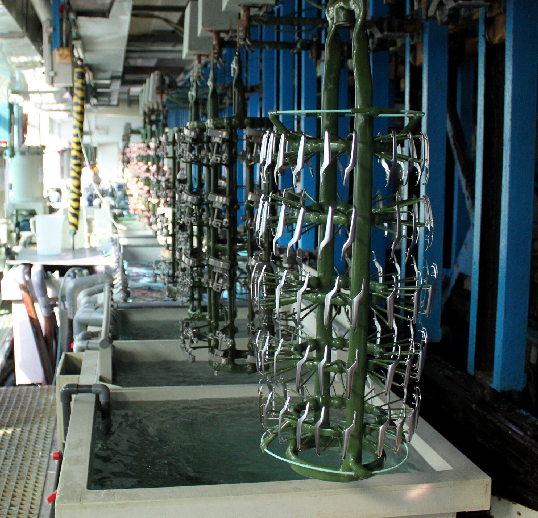
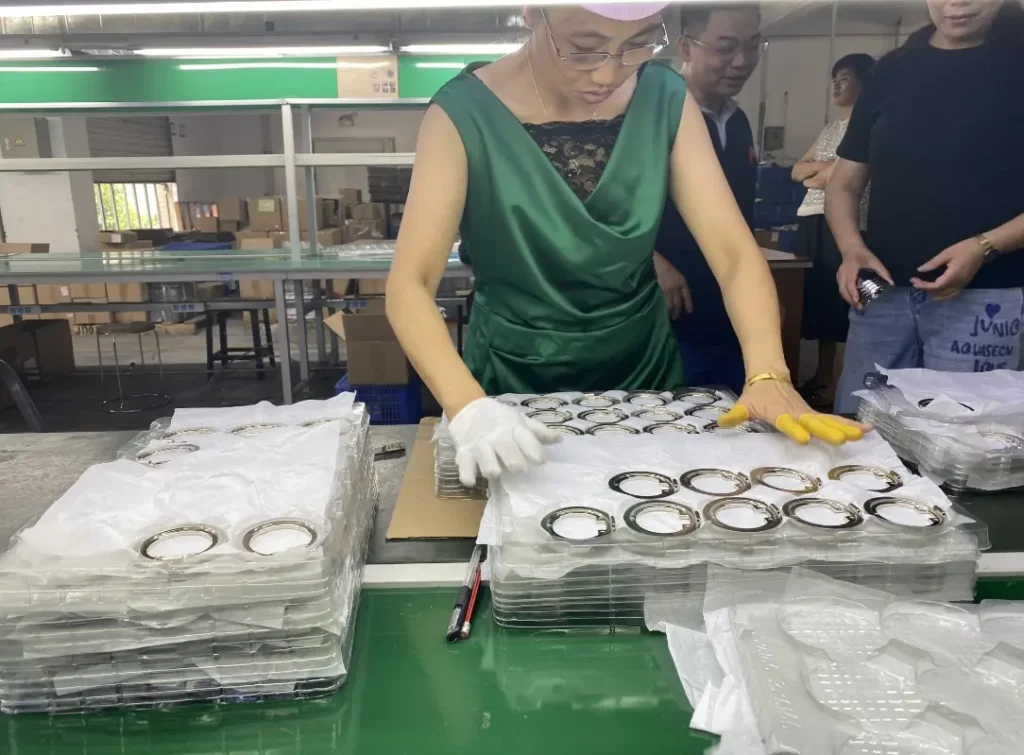
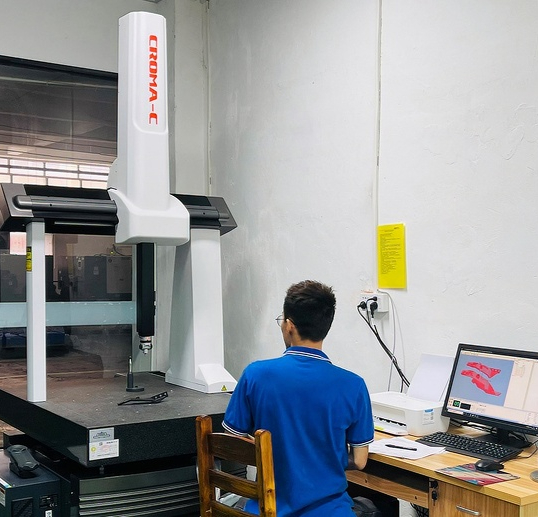




IEC Mould's Zinc Pressure Die Casting Capabilities
| Details | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy for Zinc Components | Zinc die cast parts can achieve exceptional precision with dimensional tolerances of ±0.01 mm, and up to ±0.005 mm after CNC finishing—ideal for intricate assemblies and high-precision functional components. |
| Minimum Zinc Wall Thickness | Standard thin-wall sections range between 0.6–1.0 mm, depending on part geometry and mold design. Zinc’s excellent fluidity allows thinner, more detailed structures compared to aluminum. |
| Uniform Wall Structure Requirement | To maintain optimal filling and avoid distortion, zinc castings are typically designed with a 1:1.5 to 1:2 wall thickness ratio between adjoining sections. |
| Fine Details, Threads & Inserts | Small holes (≥1.0 mm), fine threads, and insert features can be cast directly with high accuracy, minimizing or eliminating secondary machining. |
| Draft Angle for Zinc Ejection | Typical draft angle: 0.5°–1° due to zinc’s superior flow and low shrinkage characteristics. Smaller angles are possible for cosmetic or high-fit areas. |
| Mold Durability for Zinc Alloy | Zinc die casting molds generally reach 500,000–1,000,000 cycles, thanks to lower melting temperatures and reduced thermal fatigue compared to aluminum tooling. |
| Surface Finish Quality | As-cast surfaces typically achieve Ra 0.8–1.6 µm, suitable for direct plating, painting, or decorative finishing without heavy polishing. |
| Minimum Production Volume | Flexible production capability starting from 500 pcs, ideal for precision prototypes, pilot runs, and full-scale mass production. |
| Production Schedule / Lead Time | Mold fabrication and first article sampling: 15–25 days, depending on part complexity, surface finish, and machining requirements. Zinc’s fast solidification supports shorter production cycles. |
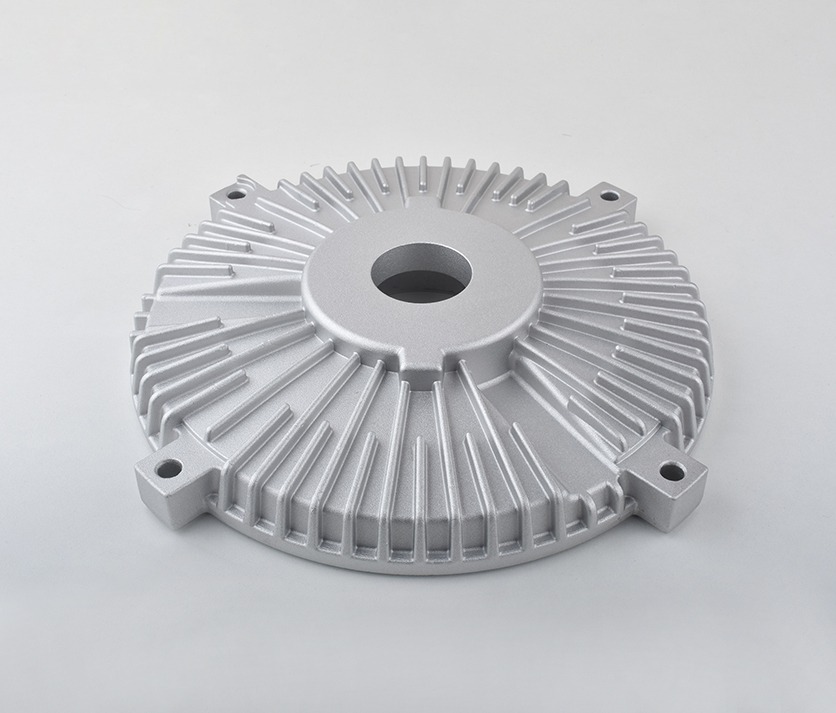
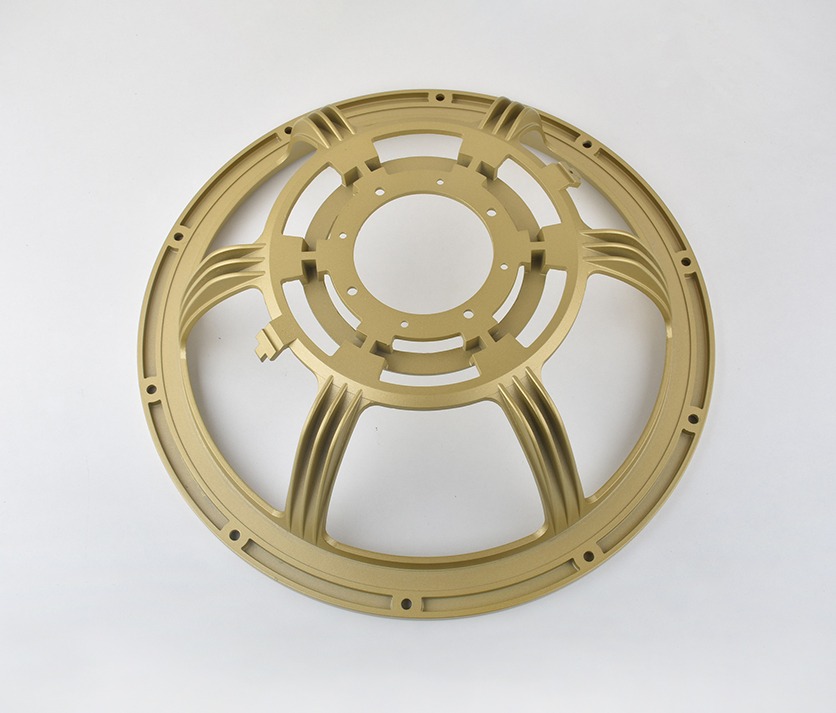
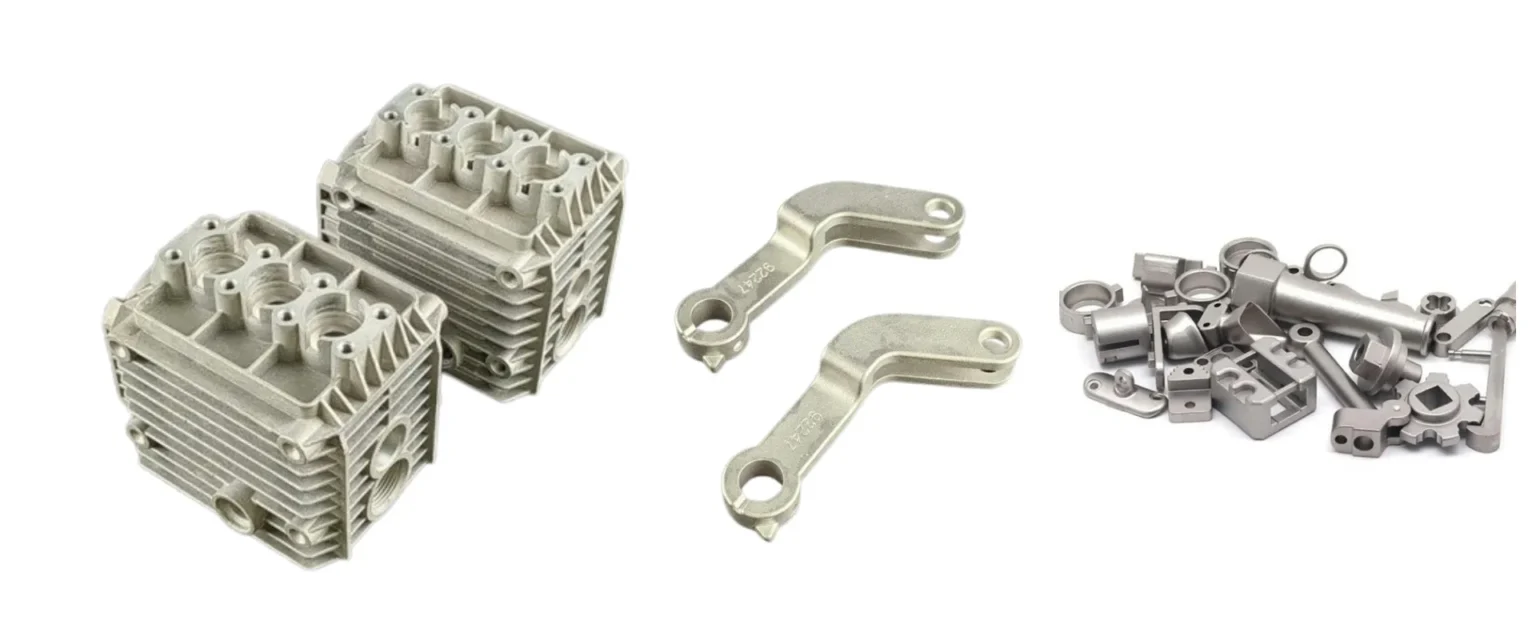
Zinc Die Casting Parts We Manufactured
These zinc die cast components highlight our capability to handle complex geometries, thin-wall designs, and premium surface finishes — from functional mechanical parts to decorative housings. Each part reflects our commitment to high precision, strength, and consistent quality in zinc die casting manufacturing.
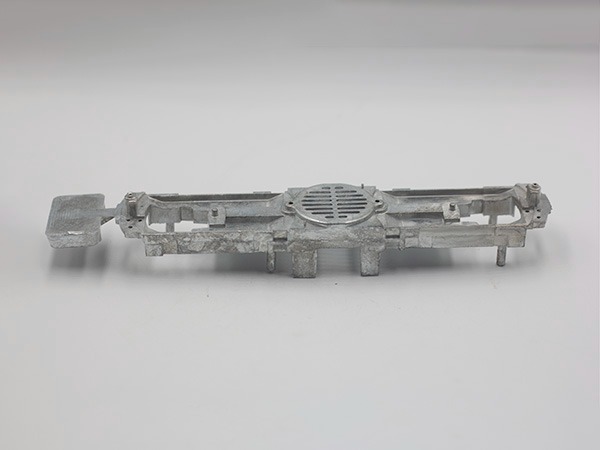
Electronics Part
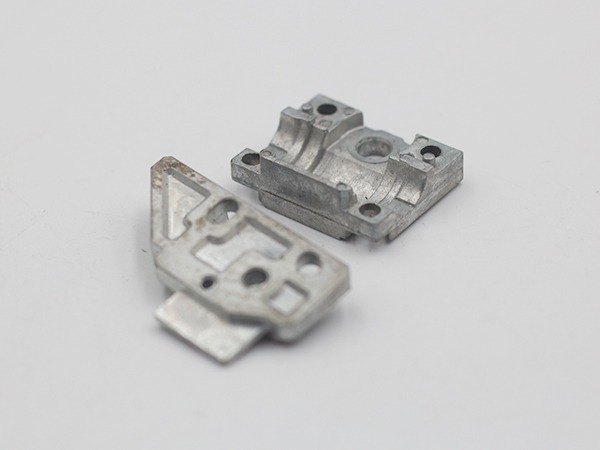

Automotive Part
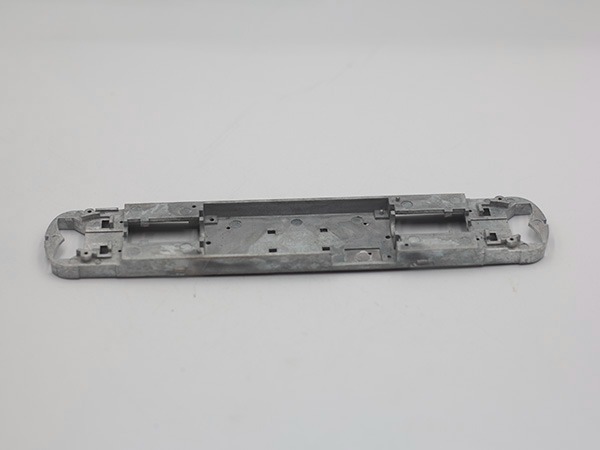

Home Appliances Part
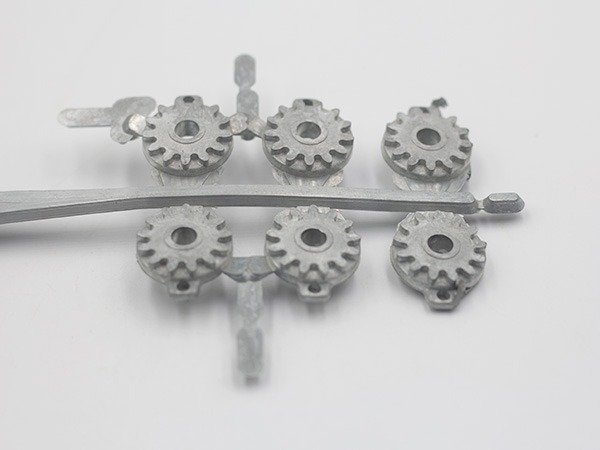

Industrial Machinery Part
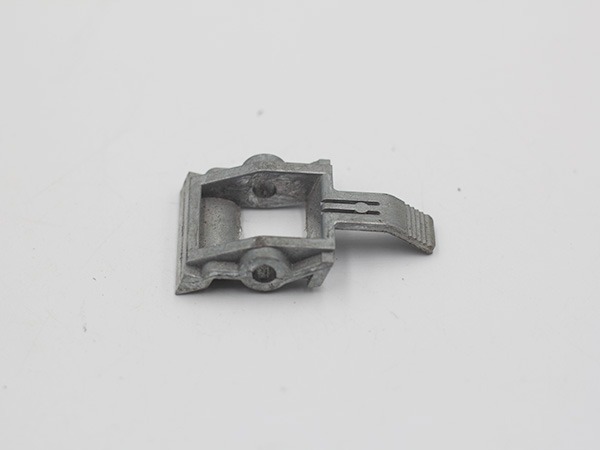

Medical Devices Part
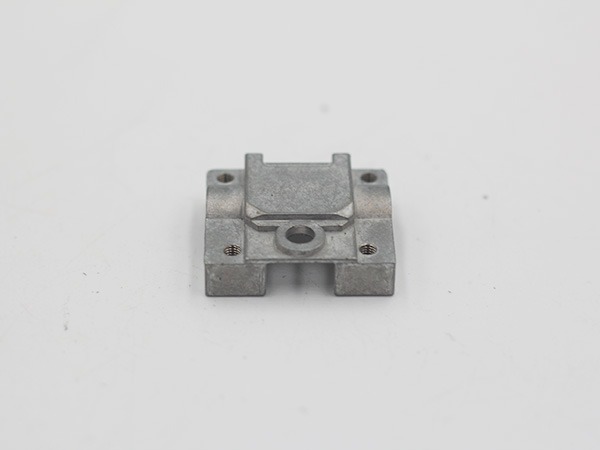

Engineering Part
Zinc Die Casting Alloys and Materials We Use
Selecting the right zinc alloy is essential to achieving the desired balance between mechanical performance, surface quality, and production cost. IEC MOULD’s engineering team evaluates each project’s function, environment, and volume requirement to recommend the most suitable material.
| Alloy Grade | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications | Why It Excels in Zinc Die Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zamak 3 (ZnAl4) | The most commonly used zinc alloy; excellent dimensional stability, good strength and ductility, superior surface finish, and easy castability. | Electrical housings, connectors, small mechanical components, decorative parts | Provides excellent balance of strength, surface quality, and economic production — ideal for high-volume precision parts. |
| Zamak 5 (ZnAl4Cu1) | Higher strength and hardness than Zamak 3, with slightly reduced ductility; improved creep resistance and wear resistance. | Automotive lock parts, gears, brackets, and structural inserts | Best for mechanical strength and wear applications while maintaining good castability. |
| Zamak 2 (ZnAl4Cu3) | Highest strength and hardness among standard Zamak alloys; excellent fatigue resistance but limited ductility; suitable for long-term load-bearing parts. | Industrial fittings, bearing housings, precision mechanisms, and heavy-duty hardware | Ideal when exceptional durability and mechanical performance are required. |
| ZA-8 (ZnAl8Cu1) | Higher aluminum content provides better strength and temperature resistance; can be hot-chamber or cold-chamber cast. | Connector shells, levers, handles, electronic enclosures | Combines aluminum’s rigidity with zinc’s fine surface finish, perfect for parts requiring structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. |
| ZA-12 / ZA-27 (High-performance Zinc-Aluminum alloys) | Very high tensile strength, stiffness, and wear resistance; used when aluminum or brass replacement is desired. | Gear housings, structural frames, and mechanical linkages | Excellent choice for semi-structural components requiring high mechanical performance and dimensional precision. |
Why Choose IEC MOULD for your Zinc die casting parts?
IEC MOULD is a trusted partner for high-quality zinc die casting solutions, delivering precision, durability, and efficiency for a wide range of industries. Here’s why leading engineers and procurement teams rely on us:
- Engineering Expertise: Full support from design and DFM to mold optimization for precise, manufacturable parts.
- Advanced Casting: Precision molds and modern zinc die casting lines for complex, thin-wall components with excellent surface finish.
- Integrated Manufacturing: In-house alloy selection, casting, CNC machining, finishing, and assembly for consistent quality.
- Quality Assurance: Dimensional checks, hardness tests, X-ray inspection, and surface evaluation ensure every part meets specs.
- Cost & Scalability: Efficient processes support prototypes, small runs, and high-volume production.
- Global Compliance: ISO 9001 & IATF 16949 certified for reliable, standard-compliant components.
Partnering with IEC MOULD means working with a single-source supplier who delivers high-performance, precision-engineered zinc die casting parts on time and within budget — every time.
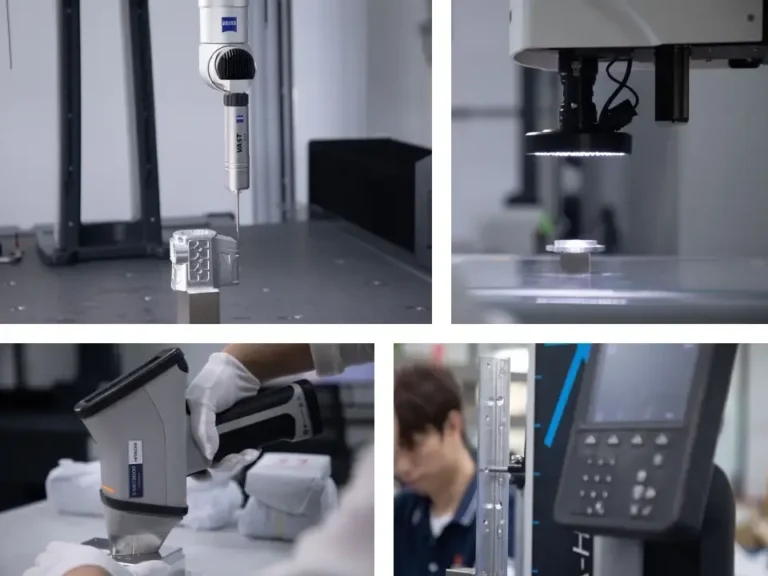

Zinc Die Casting Frequently Questions & Answers
How does zinc die casting reduce costs?
Zinc has a low melting point, which extends die life and reduces energy consumption. Combined with shorter cycle times and less machining, zinc die casting achieves a lower cost per unit, especially in mass production.
Can zinc die cast parts be surface finished?
Yes. Zinc components can undergo plating, painting, powder coating, chromating, and polishing, achieving both functional protection (corrosion resistance, wear resistance) and premium aesthetics.
What is the maximum size of parts that can be made with zinc die casting?
Zinc die casting is best suited for small to medium-sized parts (from a few grams to several kilograms). For larger components, aluminum or magnesium might be more suitable, but zinc excels in precision small-scale production.
What tolerances can be achieved with zinc die casting?
Zinc die casting can achieve very tight tolerances — often ±0.02 mm for small features — making it ideal for precision components such as gears, connectors, and housings.
Is zinc environmentally friendly?
Yes. Zinc is 100% recyclable without losing its properties, and its long tool life reduces waste. Combined with efficient energy use, zinc die casting is a sustainable choice for high-volume manufacturing.
How long is the tool life for zinc die casting molds?
Zinc’s low melting point and smooth flow help extend mold life. Typical tool life can range from 200,000 to 1,000,000 shots, depending on alloy, complexity, and surface treatment.
How does IEC MOULD ensure the quality of zinc die casting parts?
We apply strict quality control at every stage, including mold validation, X-ray inspection, CMM measurement, mechanical property testing, leak and pressure testing, and surface inspection to guarantee high-precision, defect-free components.
Other Die Casting Metals Services You May Looking for
What is Zinc Die Casting?
Zinc die casting is a precision manufacturing process that transforms molten zinc into complex, durable metal components using high pressure. In simple terms, it’s like injecting liquid zinc into a steel mold — when it solidifies, you get a part with excellent strength, tight dimensional control, and a flawless surface finish.
But zinc die casting is far more than “just shaping metal.” It’s a process of balance — between strength and detail, speed and stability. Every shot requires perfect control of temperature, flow, pressure, and cooling to achieve smooth surfaces, fine details, and consistent dimensions. When done right, it produces components that are strong, precise, and cost-efficient.
That’s why zinc die casting is widely used in automotive, electronics, hardware, telecommunications, and industrial equipment — industries that demand both performance and precision. Zinc’s unique properties allow for thin-wall designs, excellent wear resistance, and superior surface quality, making it perfect for both functional and aesthetic parts.
At IEC MOULD, we view zinc die casting as the art of turning engineering into reality. Our process starts with understanding your true priorities — tight tolerances, mechanical strength, surface appearance, or production efficiency — and transforming those needs into tangible results through advanced mold design, DFM expertise, and years of casting experience.
In essence, zinc die casting is not only about producing parts — it’s about delivering durable, detailed, and scalable solutions that connect innovation with precision manufacturing.
Why Choose Zinc Die Casting?
Zinc is one of the most versatile and precise die casting metals available. Known for its excellent strength, dimensional stability, and ability to reproduce fine details, zinc die casting is ideal for manufacturing complex, durable, and cost-effective components across various industries.
Key Benefits of Zinc Die Casting:
- Superior Dimensional Accuracy: Zinc’s low melting point and excellent fluidity enable extremely precise casting of thin walls, micro details, and intricate geometries.
- Exceptional Strength & Toughness: Zinc alloys, such as Zamak and ZA series, provide higher impact strength and wear resistance than aluminum or magnesium.
- Outstanding Surface Finish: Produces smooth, high-quality surfaces suitable for plating, painting, or decorative finishing without extensive post-processing.
- Longer Tool Life: Lower casting temperature reduces mold wear, extending tool life up to three times longer than aluminum die casting.
- Cost Efficiency: Faster cycle times, minimal machining, and long mold lifespan make zinc die casting one of the most economical options for medium to high-volume production.
- Excellent Creep & Wear Resistance: Perfect for functional components such as gears, locks, and connectors that require mechanical durability over time.
- Recyclability: Zinc alloys are 100% recyclable with negligible property loss, supporting sustainable manufacturing.
🔧 Compared to Aluminum: Zinc delivers better detail precision, smoother finishes, and higher strength in small or thin-walled parts.
🔧 Compared to Magnesium: Zinc offers greater toughness, superior corrosion resistance, and more stable casting performance at lower production costs.
How Does Zinc Die Casting Process Works?
As a leading zinc die casting manufacturer, IEC Mould understand the importance of precision, alloy selection, and process control in producing high-quality zinc components. Whether you need intricate parts, thin-walled designs, or durable functional components, a well-managed zinc die casting process is essential for success.
Below, we outline the typical six-step zinc die casting workflow followed by every reliable foundry. This streamlined approach ensures precise filling, consistent part performance, and cost-effective scalability across automotive, consumer electronics, hardware, and industrial applications.
Step 1: Alloy Melting & Preparation
The process begins with melting zinc ingots or recycled zinc scrap in a controlled furnace. Alloying elements such as aluminum, copper, or magnesium may be added to improve strength, corrosion resistance, or surface finish properties.
- Engineer’s view: Consistent alloy composition ensures predictable mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy, and smooth flow for intricate designs.
- Procurement’s view: Efficient use of recycled zinc lowers material costs while supporting sustainable manufacturing.
- Quality control’s view: Proper temperature control and impurity removal prevent porosity, cracks, and weak spots in the final castings.

Step 2: Die & Mold Preparation
Before casting, the steel die (mold) is preheated and coated with a release agent. Preheating prevents thermal shock, while coatings extend mold life and improve surface quality.
- Engineer’s view: Optimized mold design with cooling channels supports thin-walled, complex geometries with tight tolerances.
- Procurement’s view: Well-maintained dies reduce downtime and maximize tooling lifespan, improving overall cost efficiency.
- Quality control’s view: Proper mold preparation minimizes surface defects such as flow marks, cold shuts, or blisters.
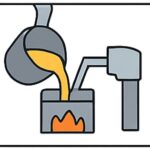
Step 3: High-Pressure Injection Casting
Molten zinc is injected into the die cavity under high pressure. Zinc’s low melting point and fluidity ensure complete cavity filling, even for intricate, thin-walled, or decorative components.
- Engineer’s view: High-pressure injection ensures superior repeatability, dimensional accuracy, and excellent surface finish across high-volume production.
- Procurement’s view: Rapid cycle times reduce per-unit costs and improve overall productivity.
- Quality control’s view: Stable pressure and temperature control minimize porosity and defects, ensuring reliability in functional and decorative applications.
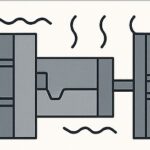
Step 4: Cooling & Solidification
The molten zinc solidifies rapidly inside the die, aided by integrated cooling channels that control shrinkage and maintain dimensional stability. Once solidified, the die opens and ejector pins release the finished component.
- Engineer’s view: Controlled cooling ensures dimensional accuracy, predictable mechanical performance, and stable surface quality for intricate or thin-walled parts.
- Procurement’s view: Efficient cooling reduces cycle times, enabling high-volume production without compromising quality.
- Quality control’s view: Monitoring solidification prevents internal stresses, cracks, or uneven microstructures, ensuring consistent part reliability.
Step 5: Trimming & Surface Finishing
Once the zinc part is ejected, excess material such as flash, gates, and runners is trimmed. Depending on functional or aesthetic requirements, components can undergo:
- CNC machining for tight tolerances
- Shot blasting or tumbling for smooth surfaces
- Electroplating, powder coating, or painting for durability and appearance
- Assembly of multiple die cast components into complete units
Step 6: Quality Inspection & Testing
Every batch of zinc die cast parts undergoes rigorous quality inspection to ensure compliance with customer and industry standards. Common testing methods include:
- X-ray or CT scanning for internal defects and porosity
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) for dimensional accuracy
- Mechanical property testing for tensile strength, hardness, and elongation
- Surface finish and plating quality checks
Advantages of Zinc Die Casting
Zinc Die Casting (ZDC) is highly valued for its exceptional precision, strength, and ability to reproduce fine details with minimal post-processing. It is particularly suitable for small-to-medium-sized components requiring complex geometries, superior surface finish, and long tooling life. Below are the key advantages of Zinc Die Casting.
| Advantage | For Engineers | For Procurement Teams | For Quality Control (QC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior Castability & Detail Reproduction | Enables production of intricate features, thin walls, and complex textures directly from the mold | Reduces the need for secondary machining and simplifies production flow | Maintains consistent geometry and surface precision across all batches |
| Exceptional Dimensional Stability | Provides excellent repeatability and dimensional control for high-precision parts | Reduces rework and scrap rates, improving overall cost efficiency | Simplifies measurement and ensures stable tolerance verification |
| High Strength & Toughness at Room Temperature | Offers excellent impact resistance and mechanical reliability for small components | Reduces risk of part failure and minimizes warranty returns | Ensures stable mechanical performance under physical testing |
| Excellent Surface Finish & Plating Capability | Delivers smooth surfaces ideal for decorative or protective finishes such as chrome or nickel plating | Enhances appearance and reduces finishing time | Easier to inspect for cosmetic and surface quality consistency |
| Low Melting Point, Longer Tool Life | Minimizes thermal stress on molds and improves tooling durability | Extends mold lifespan, reducing tooling amortization cost per part | Ensures stable dimensional accuracy throughout long production runs |
| High Production Efficiency | Fast solidification allows shorter cycle times and high-volume output | Provides cost-effective solutions for medium-to-large production quantities | Consistent process repeatability ensures reliable quality from batch to batch |
| Excellent Electrical Conductivity | Ideal for parts requiring electrical connection or shielding properties | Reduces need for secondary conductive coatings | Easy to measure and maintain conductivity during QC inspections |
| Fully Recyclable & Environmentally Friendly | Can be fully recycled without loss of performance | Supports sustainable sourcing and reduces environmental footprint | Consistent alloy quality supports stable quality verification standards |
Disadvantages of Zinc Die Casting
Zinc die casting offers outstanding precision, strength, and surface finish for small-to-medium parts. However, it also has certain design and production constraints that engineers and buyers should evaluate early in the project.
At IEC Mould, these factors — such as thermal performance, component size, and creep resistance — are carefully considered during DFM and tooling design to ensure the most efficient and reliable casting solution.
| Disadvantage | For Engineers | For Procurement / QC Teams |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Heat Resistance | Zinc alloys lose strength at temperatures above 150°C, making them unsuitable for high-heat environments | Requires careful material selection or switching to aluminum for heat-exposed components |
| Heavier Density Compared to Aluminum or Magnesium | Higher part weight may restrict use in ultra-lightweight assemblies | Increases shipping and handling costs for bulk quantities |
| Creep Under Long-Term Load | Components under constant mechanical stress may deform over time | Requires additional validation and periodic dimensional checks during QC |
| Not Ideal for Large Components | Best suited for compact parts; very large mold cavities can reduce dimensional accuracy | Large tooling setups increase production cost and cycle time |
| Thick Section Porosity Risk | Slow cooling in thick areas may cause internal voids or sink marks | QC must apply X-ray or density testing for internal defect detection |
| Surface Oxidation During Storage | Without protective coating, unplated zinc may oxidize when exposed to humidity | Requires additional finishing or controlled storage conditions |
| Slightly Higher Alloy Cost per kg | Material cost is higher than aluminum on a per-weight basis | Impacts total cost if used for high-volume, low-margin products |
Zinc vs. Other Die Casting Metals
Zinc die casting offers engineers exceptional design freedom for small-to-medium components. Its unique material characteristics allow for thin-wall sections, intricate details, and functional features—such as threads, hinges, and bosses—directly molded into the part. This reduces the need for secondary machining and assembly, streamlining production while maintaining high precision.
Compared to other die casting metals, zinc provides a balanced combination of mechanical performance, manufacturability, and surface quality. Its moderate density delivers a solid, premium feel, while the alloy’s toughness and dimensional stability allow for reliable performance even in complex geometries. Designers can integrate multiple functions into a single component, optimizing part count, assembly complexity, and overall cost efficiency.
At IEC MOULD, we support this process with DFM analysis, mold-flow simulation, and alloy selection, ensuring that every part is engineered for repeatable precision, long-term reliability, and manufacturability. By understanding zinc’s advantages relative to aluminum, magnesium, and copper alloys, engineers can make informed material choices that best meet their performance, aesthetic, and cost requirements.
| Property | Zinc (Zn) | Aluminum (Al) | Magnesium (Mg) | Brass / Copper Alloys (Cu-Zn) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Moderate – heavier than aluminum, giving a dense and durable feel | Very light – ideal for large or weight-sensitive parts | Extremely light – best for portable and handheld components | Heavy – used where mass and stability are desired |
| Strength & Toughness | High – excellent impact resistance and wear strength for small mechanisms | High – strong but more brittle in thin sections | Moderate – good for light-duty applications | Very high – ideal for load-bearing or wear parts |
| Dimensional Precision | Excellent – achieves the highest accuracy and finest surface detail among die cast metals | Very good – suitable for most precision applications | Moderate – less stable during solidification | Good – stable but limited in complex thin-wall structures |
| Surface Finish | Superior – can be polished, plated, or coated without porosity issues | Good – can be anodized or painted for protection | Fair – typically requires coating for aesthetics | Excellent – naturally smooth and corrosion-resistant |
| Thermal Resistance | Limited – not suitable for high-temperature environments (>150°C) | Excellent – performs well under high heat | Moderate – good heat dissipation but lower melting point | Excellent – high heat tolerance and conductivity |
| Production Efficiency | Outstanding – low melting point allows rapid cycles and long mold life | High – efficient for medium to large parts | Moderate – slower due to oxidation control | Low – higher melting temperature increases tooling wear |
| Cost Efficiency | Excellent – minimal waste, long tool life, and short cycle times | High – good balance between performance and cost | Moderate – higher alloy and process costs | Lower – expensive raw material and energy use |
| Typical Applications | Precision gears, connectors, locks, hinges, decorative components, small enclosures | Structural housings, covers, engine parts, heat sinks | Portable casings, brackets, electronic housings | Plumbing parts, fittings, marine valves, decorative items |
Zinc Die Casting Part Applications Across Industries
Zinc die casting is widely used for components where design versatility, production efficiency, and cost-effectiveness are critical. Its low melting temperature, high mold repeatability, and ability to integrate multiple functions into a single part make it a preferred choice for industries that require reliable, ready-to-use parts at scale.
| Industry | Typical Components | Why Zinc Die Casting Fits |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Switch housings, connectors, control knobs | Allows compact designs with integrated features while keeping production costs low |
| Hardware & Locks | Hinges, latches, door handles | Durable and precise, reducing the need for secondary assembly or machining |
| Automotive Accessories | Decorative trims, small brackets, emblem parts | Combines dimensional accuracy with cost-efficient mass production |
| Industrial Equipment | Levers, small housings, precision gears | Supports consistent quality across medium-volume runs with minimal tool wear |
| Lighting & Fixtures | Lamp bases, mounting brackets | Smooth surfaces ready for plating or coating, reducing finishing steps |
| Medical Devices & Instruments | Control panels, clamps, small housings | High repeatability ensures each part meets tight tolerances without extra processing |
| Home Appliances | Handles, brackets, control components | Integrated features reduce assembly complexity and improve long-term reliability |
| Locks & Security Systems | Cylinder parts, bolt mechanisms | Maintains strength and wear resistance while enabling intricate part geometries |
| Consumer Hardware & DIY Products | Fasteners, brackets, tool components | Cost-effective production with reliable quality for mass-market products |
Ready to Start Your Zinc Die Casting project?
Our experienced engineers are here to guide you through zinc alloy selection, mold design, production optimization. Discover how advanced zinc die casting technologies can deliver high-precision, durable, and cost efficient components for your next zinc casting project.
- yoyo@iec-mould.com
- 86 13712993487
- 86 13712993487

*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.