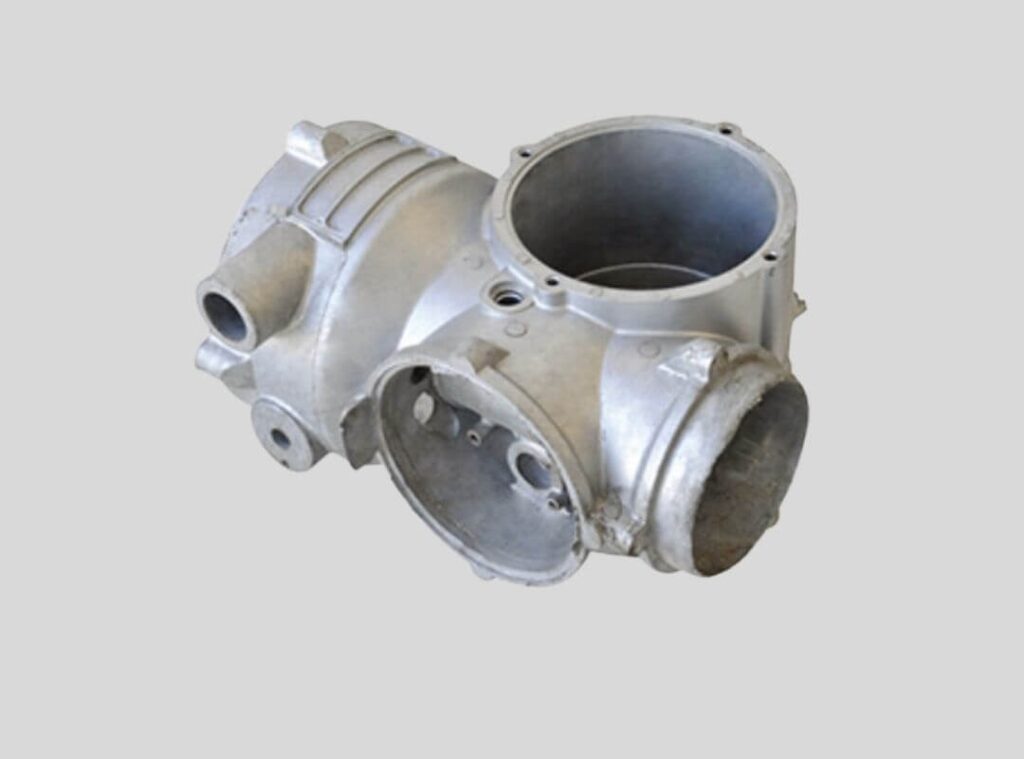
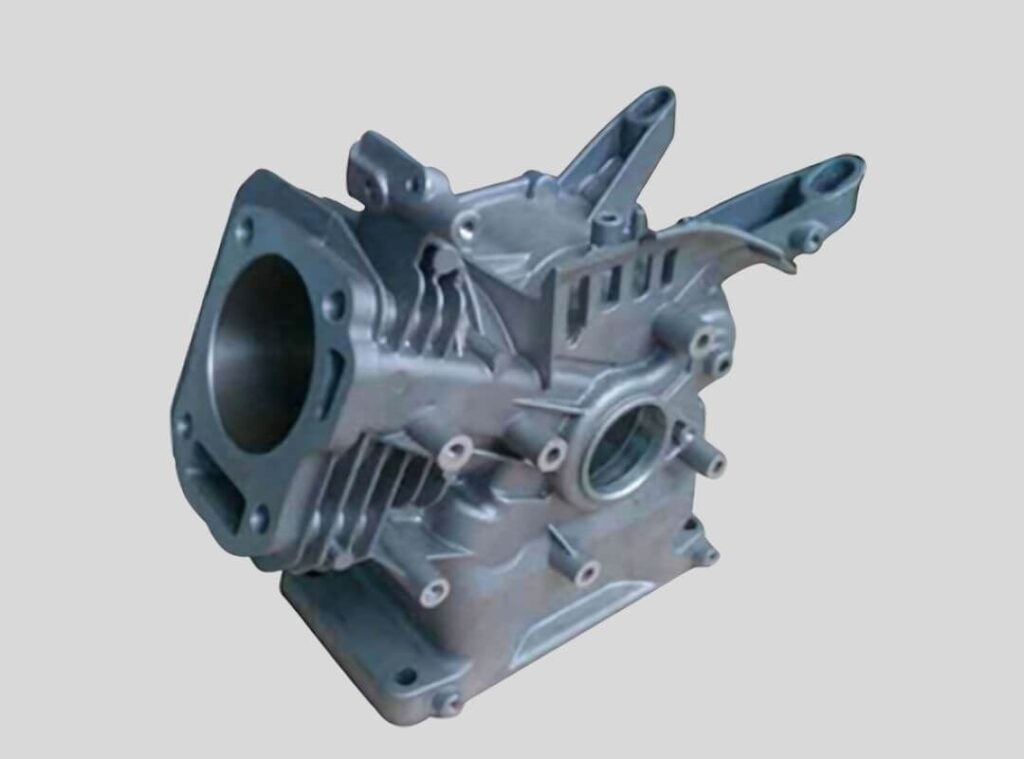
Hot Chamber Die Casting Manufacturer
Ultra-Fast Cycle Times – Shorten project timelines with injection speeds up to 15 cycles/min
Tight Dimensional Control – Achieve ±0.05 mm accuracy for perfect fit and interchangeability.
- Defect-Minimized Casting – Reduce porosity, shrinkage, and surface defects for zero-rework production.
- Cost-Efficient for High Volumes – Lower per-unit cost while ensuring consistent, repeatable quality
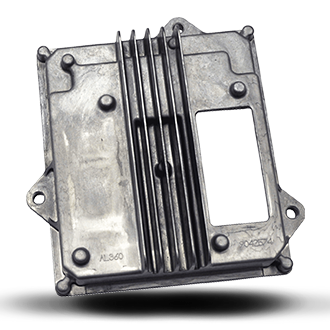
±0.01mm
Tolearance
20+
Years Experience
20 Day
Die Casting Samples Delivered
Certifications
ISO 9001 & IATF 16949
China Hot Chamber Die Casting Manufacturer and Supplier
IEC MOULD specializes in Hot Chamber Die Casting, offering a fast, reliable, and cost-effective solution for zinc, magnesium, and lead parts. Our in-house tooling and production lines allow us to deliver from prototype to finished component without compromising quality or precision.
Hot Chamber Die Casting is particularly suited for small, detailed, and high-volume parts, making it a preferred choice for industries such as automotive, electronics, consumer appliances, and industrial machinery.
Equipped with ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certifications, advanced inspection tools, and a skilled engineering team, IEC MOULD ensures consistent quality, short lead times, and optimized manufacturing costs, helping our clients bring their designs to market faster and more efficiently.
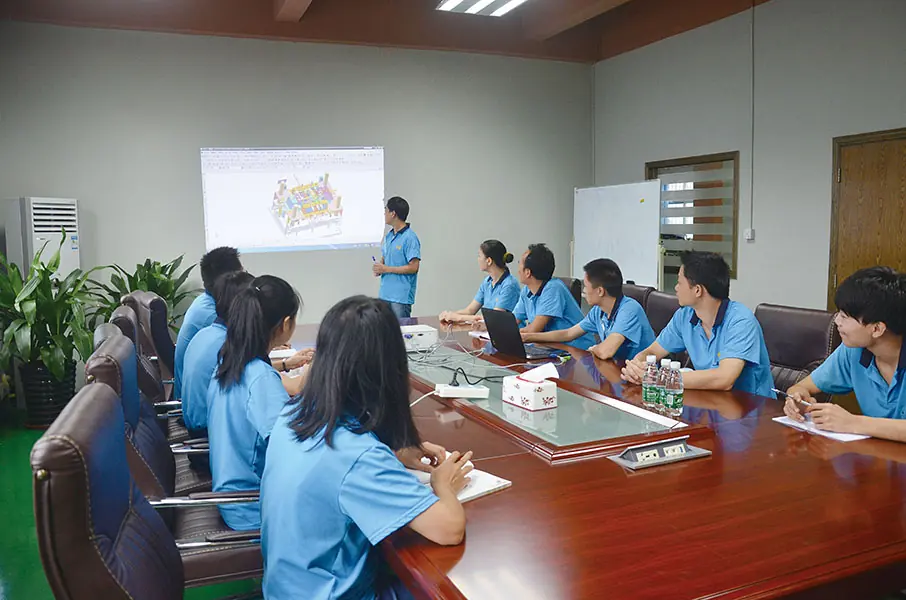
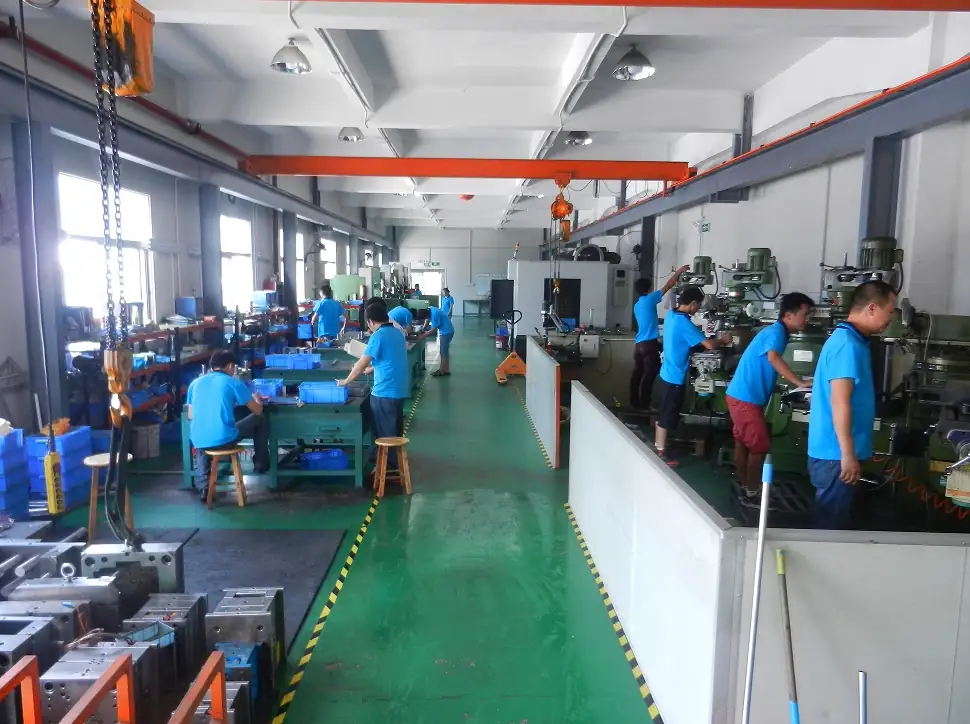
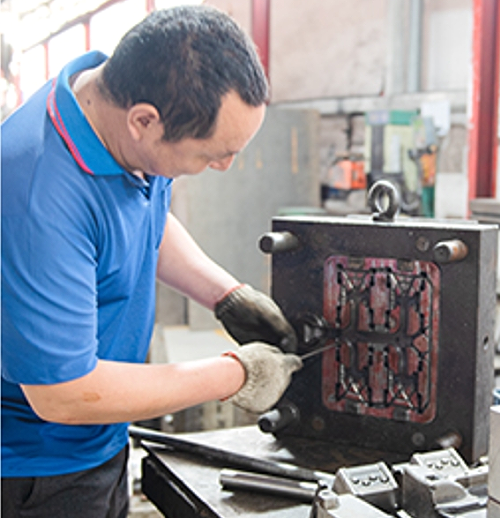
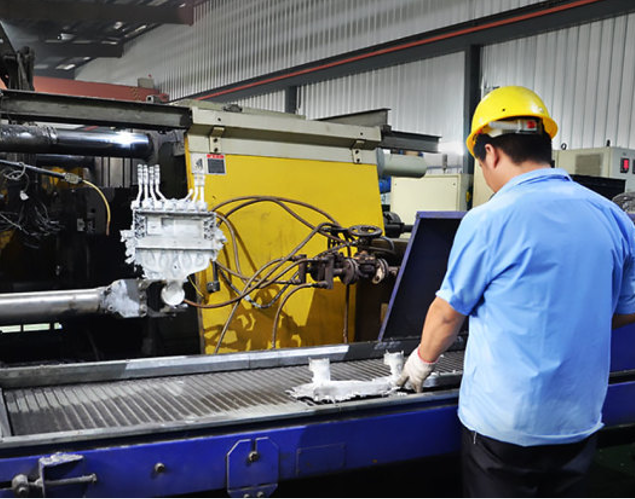





Our Hot Chamber Die Casting Services
We offer specialized Hot Chamber Die Casting (HCDC) services designed for low-melting-point alloys and high-volume precision components:
- Custom Hot Chamber Die Casting – Ideal for zinc, magnesium, and lead alloys with fast cycle times and superior surface finish
- Rapid Tooling & Mold Design – In-house design and mold manufacturing ensure shorter lead times and cost efficiency
- High-Speed Production – Integrated hot chamber systems enable continuous, repeatable casting for mass production
- Precision Machining – CNC finishing and dimensional control for detailed and intricate components
- Surface Finishing Options – Polishing, electroplating, chromating, and painting to enhance both performance and appearance
- Assembly & Integration – Streamlined processes to deliver fully finished, ready-to-install parts
- Quality Assurance – Comprehensive testing including dimensional checks, coating inspection, and functionality verification
With IEC MOULD, you benefit from a faster, cleaner, and more efficient casting process. We combine tooling expertise, rapid production, and strict quality control to deliver precision parts that meet your exact specifications – all from one trusted partner.
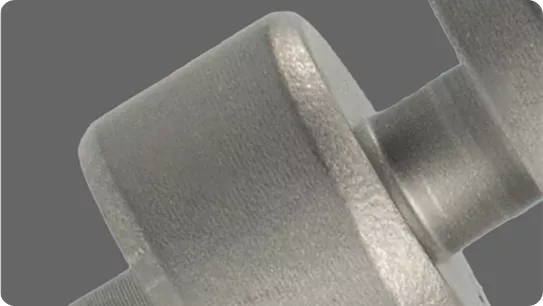



IEC Mould's Hot Chamber Die Casting Capabilities
| Details | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Tolerance | Hot Chamber Die Casting parts can achieve precision up to ±0.005mm with secondary machining, suitable for small, intricate components requiring exceptional dimensional stability. |
| Minimum Wall Thickness | In Hot Chamber Die Casting, the recommended minimum wall thickness is as thin as 0.5mm for zinc alloys and 0.8mm for magnesium alloys, depending on part geometry and flow design. |
| Wall Thickness Ratio | For optimal filling and cooling, Hot Chamber Die Casting typically follows a 1:2 wall thickness ratio, ensuring uniform structure and minimizing porosity. |
| Hole Diameter | Holes smaller than 1.5mm are not recommended to cast directly and should be drilled or machined afterward. Threaded and fine-tolerance holes are finished through CNC machining. |
| Draft Angle | A minimum draft angle of 0.25°–0.5° is recommended in Hot Chamber Die Casting to allow smooth ejection while maintaining surface quality. |
| Maximum Die Life (Cycles) | – Zinc Hot Chamber molds: up to 1,000,000–1,200,000 cycles – Magnesium Hot Chamber molds: approximately 150,000–200,000 cycles |
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | Standard MOQ for Hot Chamber Die Casting is 500 pieces, making it ideal for mass production of small, detailed components. |
| Lead Time | Typical lead time for Hot Chamber Die Casting projects is 15–20 days, depending on tooling complexity and part design. |
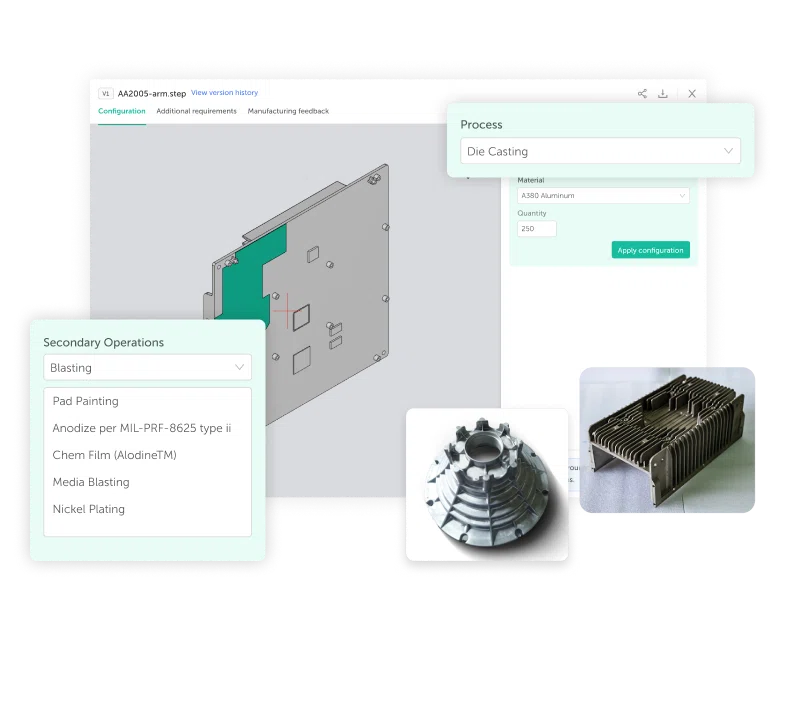
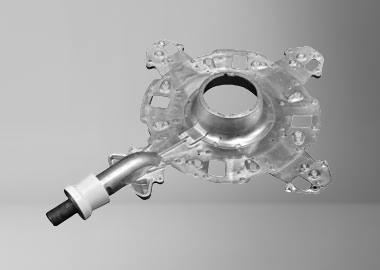
Hot Chamber Die Casting Parts We Manufactured
Whether you need small precision parts or intricate thin-wall components, IEC MOULD’s Hot Chamber Die Casting (HCDC) solutions deliver fast cycle times, excellent surface finish, and stable quality — helping you achieve reliable, high-volume production with confidence.
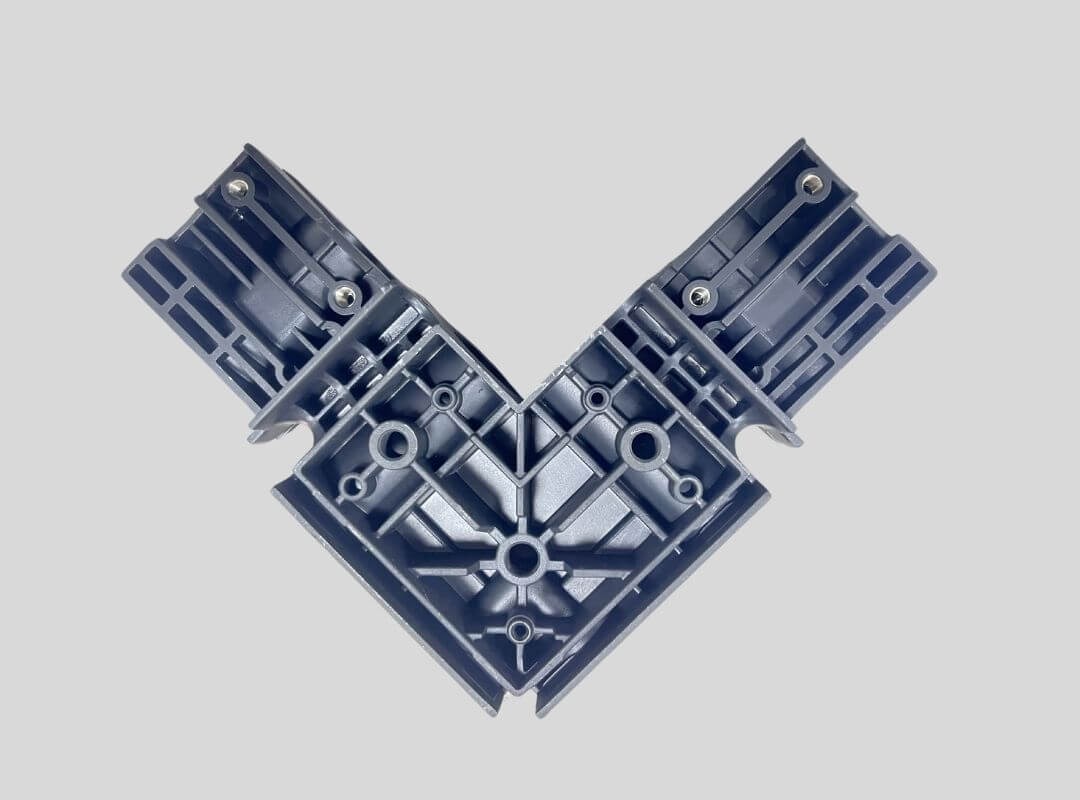
Electronics Part

Automotive Part

Home Appliances Part
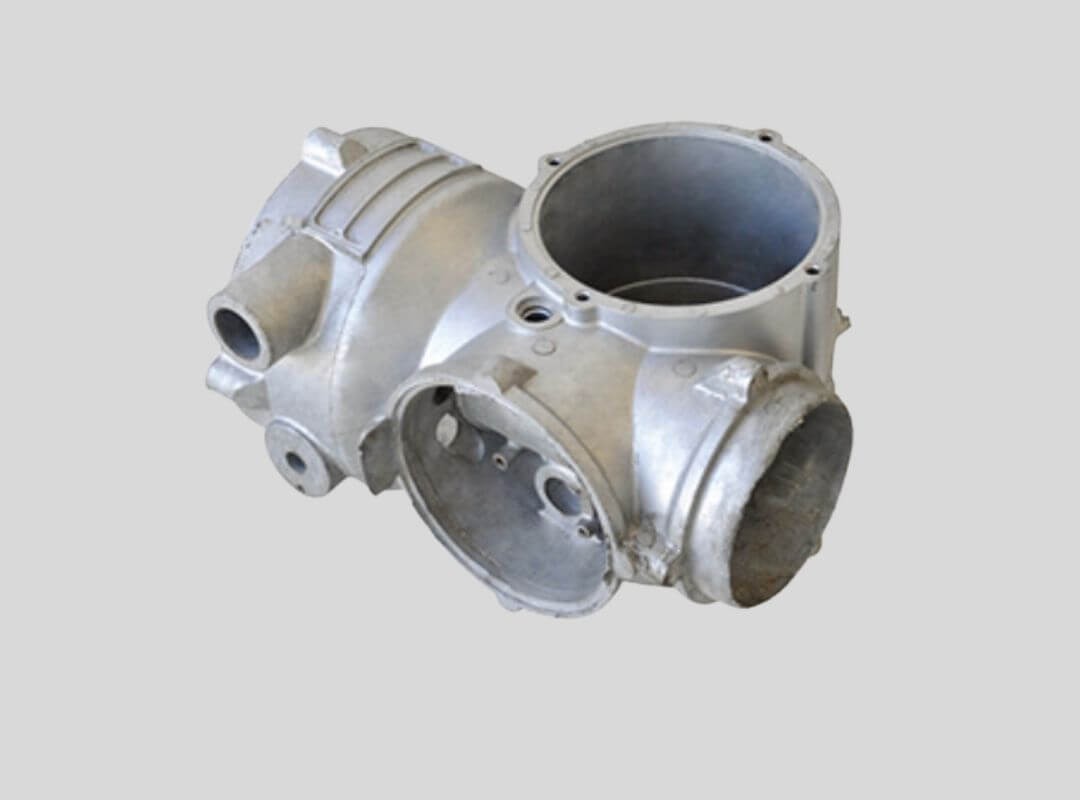

Industrial Machinery Part
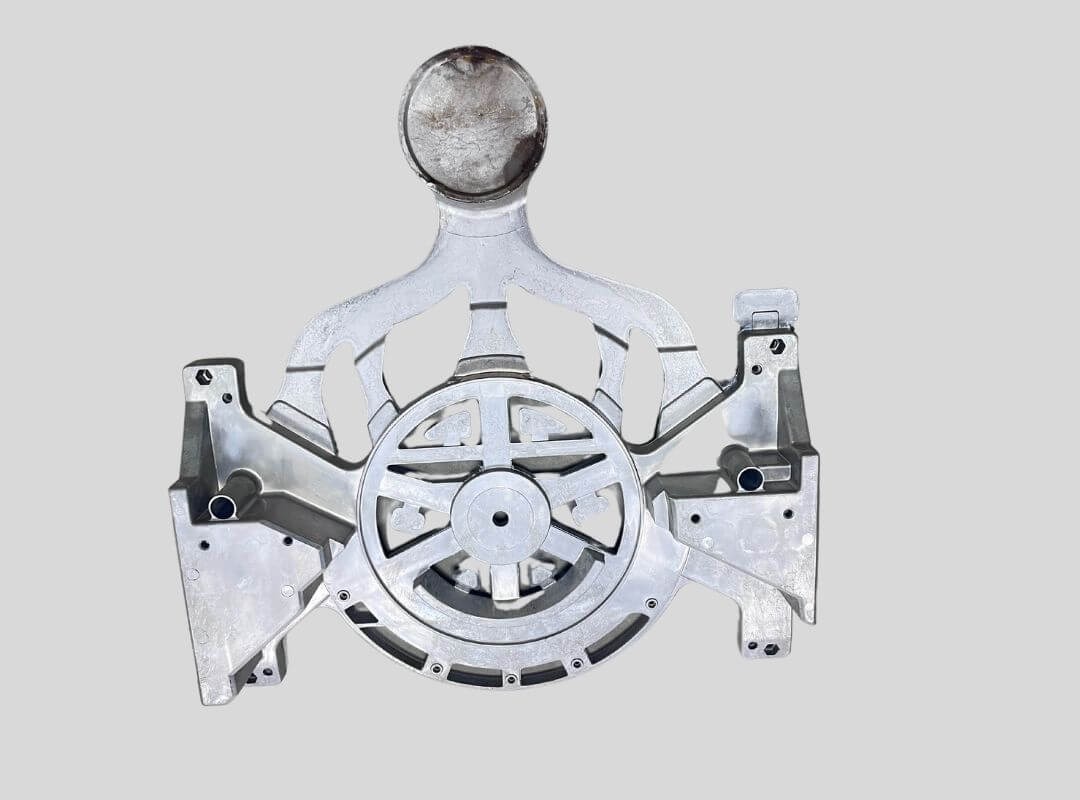

Medical Devices Part
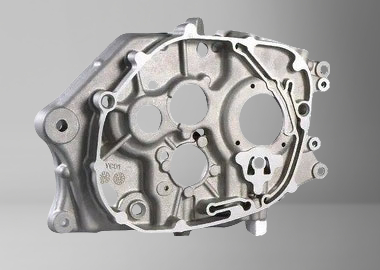
Engineering Part
Hot Chamber Die Casting materials we used
| Material | Key Features | Typical Applications | Why It Fits Hot Chamber Die Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zinc Alloys (Zamak 2, Zamak 3, Zamak 5, ZA-8) | Low melting point, excellent fluidity, superior dimensional accuracy, high impact strength, and smooth surface finish | Electrical connectors, precision gears, decorative hardware, consumer electronics housings | Ideal for high-volume production of small, intricate parts with tight tolerances and fine surface details |
| Magnesium Alloys (AZ91D, AM60A, AM50A) | Extremely lightweight, excellent strength-to-weight ratio, good corrosion resistance, and fast solidification | Automotive interior parts, handheld device housings, power tools, and small mechanical components | Enables rapid-cycle manufacturing of lightweight components with excellent mechanical performance |
| Lead-Based Alloys (Pb-Sn, Pb-Sb series) | Excellent castability, low melting temperature, and good radiation shielding properties | Electrical terminals, balance weights, radiation shielding parts | Perfect for specialty applications where density and formability are more critical than strength |
| Tin Alloys (Sn-Zn, Sn-Bi) | Outstanding fluidity, bright surface finish, excellent corrosion resistance, and easy plating | Decorative parts, miniature components, electrical contacts, and small mechanical fittings | Suitable for very fine and detailed components requiring high surface aesthetics and smoothness |
| Zinc-Aluminum Alloys (ZA-12, ZA-27) | High strength, good wear resistance, and better creep resistance than standard zinc alloys | Industrial fittings, bearing housings, small structural brackets | Provides improved mechanical properties for applications needing strength beyond standard Zamak alloys |
Why Choose IEC MOULD for your hot chamber die casting project?
- Feature: Integrated in-house capabilities covering tooling design, hot chamber die casting, precision machining, and surface finishing.
- Advantage: Seamless coordination and process control ensure high efficiency, consistent quality, and shorter production cycles.
- Benefit: You gain faster turnaround, reduced costs, and stable product quality — all from a single, experienced manufacturing partner.
- Evidence: Backed by ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certifications, advanced CMM and optical inspection systems, and trusted by global customers in automotive, electronics, and consumer industries.
Choosing IEC MOULD means partnering with a manufacturer that understands precision engineering, production speed, and quality assurance — delivering the reliability your project deserves.

Hot Chamber Die Casting Frequently Questions & Answers
What tolerances can be achieved with Hot Chamber Die Casting?
Dimensional tolerances can reach ±0.05 mm for critical features. Consistency is high due to controlled filling and solidification, reducing scrap rates.
How is quality controlled in Hot Chamber Die Casting?
- Mold temperature monitoring to prevent defects.
- Process parameter control (pressure, injection speed, fill time).
- Non-destructive testing (X-ray, CMM inspection) for internal defects and dimensional accuracy.
What are common defects and how are they prevented?
- Porosity: Controlled by vacuum assist and degassing.
- Cold shuts: Prevented by optimizing gate design and fill speed.
- Flash: Minimized with correct clamping force and die alignment.
What is the production speed and efficiency?
Typical cycle times are 15–30 seconds, enabling thousands of parts per day.
For procurement: This supports short lead times and cost-efficient large batches.
What post-processing options are available for hot chamber die casting?
- Surface finishing: Plating, powder coating, painting, polishing.
- Machining: CNC drilling, tapping, milling for precision fits.
- Assembly: Direct integration into sub-assemblies to save handling time.
How to select the right Hot Chamber Die Casting supplier?
- Proven ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 certification.
- In-house tooling, casting, machining, and finishing capability.
- Transparent QC documentation (CP, FAI, PPAP).
- Experience in your industry (automotive, electronics, consumer goods).
What is the typical wall thickness for Hot Chamber Die Casting?
Wall thickness can be as thin as 0.5 mm for small parts, with excellent consistency and minimal defects.
Other Die Casting Technologies You May Looking for
What is Hot Chamber Die Casting?
Hot Chamber Die Casting is a high-speed die casting process in which the injection system is submerged in a pool of molten metal, allowing molten alloy to be drawn directly into the injection chamber and forced into the die under high pressure. This integrated design minimizes metal handling, shortens cycle times, and enables production rates of up to 15 cycles per minute.
Unlike Cold Chamber Die Casting, where molten metal is ladled into the shot chamber for each cycle, Hot Chamber Die Casting offers faster production and better energy efficiency for low melting point alloys such as zinc, magnesium, and certain lead-based alloys. The process produces parts with excellent surface finish, tight dimensional tolerances (±0.05 mm), and minimal porosity, often eliminating the need for secondary machining.
Because of its speed, precision, and cost-effectiveness, Hot Chamber Die Casting is widely used for automotive components, electronic housings, consumer product parts, and industrial equipment requiring high accuracy, thin walls, and complex geometries.
Why Choose Hot Chamber Die Casting?
- Ultra-Fast Cycle Times – The Hot Chamber Die Casting process enables extremely short injection and solidification cycles, making it ideal for high-volume production of small, detailed components.
- Exceptional Dimensional Accuracy – With precise process control, HCDC achieves tolerances up to ±0.01mm, ensuring repeatable precision across every production run.
- Superior Surface Finish – Due to the clean molten metal feed system and smooth mold flow, parts feature a high-quality surface with minimal need for secondary finishing.
- Optimized for Low-Melting-Point Alloys – Perfectly suited for zinc, magnesium, and lead alloys, HCDC delivers excellent fluidity and fine detail replication, ideal for miniature and intricate parts.
How Hot Chamber Die Casting Works?
Hot Chamber Die Casting (HCDC) is a high-speed, high-precision casting process in which molten metal is injected directly into a reusable steel die using a submerged injection system. Unlike cold chamber die casting, HCDC allows extremely fast cycle times and excellent surface quality for low-melting-point alloys such as zinc and magnesium. Here is a step-by-step breakdown of how Hot Chamber Die Casting works:
Step 1: Mold Preparation and Preheating
- Clean and preheat the steel die to 150–250°C.
- Reduces thermal shock and prevents cracking.
- Improves metal flow, surface finish, and dimensional stability.
Step 3: Metal Injection via Submerged System
- Submerged “gooseneck” draws molten metal into the cylinder.
- Injects metal rapidly into the die cavity.
- Minimizes turbulence and ensures complete filling of thin walls.
Step 5: Solidification Under Pressure
- Cool the part while maintaining pressure.
- Prevents shrinkage and ensures dimensional accuracy.
- Controls mechanical properties for consistent strength.
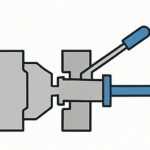
Step 7: Trimming & Flash Removal
- Remove flash, runners, and gates.
- Bring parts closer to net shape.
- Reduce manual finishing and secondary operations.
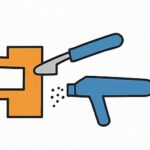
Step 2: Molten Metal Preparation
- Melt zinc or magnesium alloy in the integrated furnace.
- Maintain controlled temperature to prevent oxidation.
- Ensure consistent fluidity for precise injection.
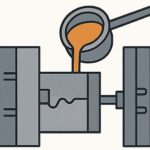
Step 4: High-Pressure Filling of Die Cavity
- Force molten metal under high pressure into the die.
- Captures intricate mold details with tight tolerances.
- Reduces porosity and ensures excellent surface finish.
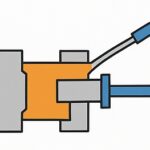
Step 6. Die Opening & Part Ejection
- Open the die and eject the solidified part.
- Inspect for visible defects.
- Clean and lubricate die for the next cycle.
Step 8. CNC Machining, Finishing & Inspection
- Perform machining on critical surfaces as needed.
- Conduct X-ray, leak tests, CMM, and dimensional reports.
- Ensure all parts meet specifications and quality standards
Advantages of Hot Chamber Die Casting
| Advantage | For Engineers | For Procurement Teams | For Quality Control (QC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fast Cycle Times | Enables high-speed production with short shot-to-shot intervals, ideal for small precision components. | Increases throughput and reduces per-unit labor cost. | Shorter cycles make it easier to maintain consistent inspection schedules. |
| Excellent Surface Finish (Ra 1.6–3.2 μm) | Delivers near-net-shape parts with minimal finishing. | Reduces secondary operation costs and accelerates delivery. | Smooth surfaces allow easier detection of cosmetic and dimensional defects. |
| High Dimensional Accuracy (±0.05–0.1 mm) | Achieves precise tolerances for intricate geometries. | Reduces machining requirements, saving cost and lead time. | Improves repeatability in measurement and inspection. |
| Suitable for Low-Melting Alloys (Zinc, Magnesium) | Supports design of lightweight yet strong components. | Expands options for cost-effective material sourcing. | Consistent quality control across alloys with low melting points. |
| Reduced Metal Wastage | Optimized gating system reduces scrap and re-melting. | Lowers material costs and improves overall yield. | Less variation in part quality due to reduced metal rework. |
| Compact Machinery Footprint | Allows installation in smaller production spaces. | Reduces facility and infrastructure investment. | Simplifies QC logistics by minimizing handling distance. |
| Complex Thin-Wall Capability | Enables production of lightweight parts with fine features. | Reduces part weight and shipping costs. | Consistent inspection process for thin-wall tolerances. |
| Ideal for High-Volume Small Parts | Economical for producing millions of small, detailed parts. | Low cost per unit at scale. | Maintains stable quality metrics over large batch runs. |
Disadvantages of Hot Die Casting
| Disadvantage | For Engineers | For Procurement Teams | For Quality Control (QC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Limited to Low-Melting-Point Alloys | Cannot process high-melting alloys like aluminum or copper, restricting design options. | Limits supplier consolidation if other materials are needed. | Requires separate inspection standards for zinc and magnesium parts. |
| Tool Wear from Corrosive Alloys | Certain alloys (e.g., zinc with aluminum impurities) can accelerate die erosion. | Increases tooling replacement and maintenance costs. | Frequent tool changes may affect process stability and measurement consistency. |
| Smaller Part Size Capability | Best suited for small-to-medium components; not ideal for large castings. | May need to outsource large parts, increasing logistics cost. | More frequent setup changes increase QC workload for different part sizes. |
| Limited Injection Pressure | Lower injection pressure (compared to HPDC) can reduce density for some complex parts. | May affect part strength in load-bearing applications. | More variability in internal porosity and dimensional stability. |
| Potential for Trapped Air and Porosity | Rapid filling can trap air, causing minor voids. | Additional finishing or impregnation may be required. | Increases inspection time, especially for airtight or pressure-critical parts. |
| High Initial Tooling Cost | Complex molds and hot chamber systems require upfront investment. | Extends payback period for low-volume projects. | Early production runs may need more process validation. |
| Maintenance Complexity | Hot chamber systems operate under high thermal and mechanical stress. | Requires regular downtime and skilled technicians. | Temperature variations can impact dimensional control during production. |
How to Overcome Hot Chamber Die Casting Disadvantages
| Challenge | For Engineers | For Procurement Teams | For Quality Control (QC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Limited Alloy Compatibility (No Aluminum or Copper) | Choose optimized zinc and magnesium alloys (e.g., Zamak 5, AM60B) to balance strength and flowability. | Work with suppliers offering a range of zinc and magnesium alloys for flexibility in sourcing. | Maintain separate material testing and verification plans for each alloy system. |
| Lower Melting Temperature Alloys | Design components considering alloy strength limits and avoid high-temperature applications. | Evaluate total lifecycle cost — zinc alloys may offer savings in tooling and finishing despite lower heat resistance. | Implement tensile and hardness testing to ensure mechanical property consistency. |
| Tool Wear from High Injection Speeds | Utilize optimized gate design, PVD-coated shot sleeves, and proper lubrication systems. | Partner with suppliers using advanced die coatings and precision temperature control. | Monitor cavity wear and dimensional drift through regular SPC measurements. |
| Limited Part Size Capability | Redesign large components into multiple smaller sections suitable for hot chamber processing. | Optimize production mix — allocate small precision parts to hot chamber and larger ones to cold chamber casting. | Validate dimensional matching between multi-piece assemblies through CMM inspection. |
| Risk of Soldering (Metal Adhesion to Die) | Apply anti-solder coatings (e.g., nitride, ceramic) and maintain optimal die temperature balance. | Choose experienced suppliers who monitor die temperature and injection speed in real time. | Inspect surfaces after each production batch to detect and prevent solder adhesion early. |
| Cycle Time Variation Due to Temperature Fluctuations | Use closed-loop temperature control for molten metal and die cooling systems. | Request process capability data (Cp, Cpk) to evaluate supplier stability. | Implement temperature and pressure data logging for root-cause traceability. |
| Shorter Mold Life Compared to Cold Chamber | Select premium die steels (e.g., H13, 8407) and ensure consistent preheating before casting. | Track mold lifecycle costs to optimize replacement planning and ROI. | Apply regular dimensional audits to confirm part accuracy before and after tool refurbishment. |
| Potential Gas Entrapment in Thin Sections | Optimize venting layout and injection parameters using Moldflow or MagmaSoft simulation. | Prioritize suppliers that use vacuum-assisted hot chamber casting. | Conduct X-ray or helium leak testing to verify internal soundness and porosity control. |
Hot Chamber Die Casting vs Other Casting Methods
| Feature | Hot Chamber Die Casting (HCDC) | Cold Chamber Die Casting | Gravity Die Casting | Sand Casting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suitable Alloys |  Low-melting alloys (Zn, Mg, Pb) Low-melting alloys (Zn, Mg, Pb) |  High-melting alloys (Al, Cu, Brass) High-melting alloys (Al, Cu, Brass) |  Most non-ferrous alloys Most non-ferrous alloys |  Most metals Most metals |
| Filling Pressure | High (up to 1000+ bar) | High (up to 1500+ bar) | Gravity only | Gravity only |
| Porosity |  Moderate (lower than cold chamber) Moderate (lower than cold chamber) |  Moderate Moderate |  Moderate Moderate |  High High |
| Heat Treatment |  Often not applicable Often not applicable |  T5/T6 Possible T5/T6 Possible |  Yes Yes |  Yes Yes |
| Surface Finish |     (Smooth, Ra 1.6–3.2 μm) (Smooth, Ra 1.6–3.2 μm) |     |   |  |
| Dimensional Accuracy |     (±0.05–0.1 mm) (±0.05–0.1 mm) |     (±0.1 mm) (±0.1 mm) |   |  |
| Part Size Capability | Small to Medium | Medium to Large | Medium to Large | Large |
| Ideal for | Small, intricate, high-volume parts like connectors, gears, housings | Structural parts, housings, engine components | Simple to medium-complexity shapes | Large prototypes or low-volume production |
Hot Chamber Die Casting Part Applications Across Industries
Hot Chamber Die Casting is primarily used for small to medium-sized precision components that require excellent surface finish, dimensional consistency, and cost-effective high-volume production. Its compatibility with zinc, magnesium, and other low-melting alloys makes it ideal for detailed, thin-walled, and complex parts across multiple industries.
| Industry | Typical Components | Why Hot Chamber Die Casting Fits |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Connector housings, camera shells, switch components, charging ports | Perfect for small, intricate parts with tight tolerances and smooth finishes used in compact electronic devices. |
| Automotive & E-Mobility | Interior trim parts, key fob housings, seat adjuster gears, sensor brackets | Enables production of lightweight, detailed components at scale with consistent quality and minimal post-processing. |
| Home Appliances | Door handles, motor housings, decorative trims, heat sink covers | Offers fast, repeatable production of aesthetic components requiring excellent surface quality and dimensional precision. |
| Telecommunication & IT Hardware | Antenna brackets, connector casings, RF shields, micro enclosures | Provides precise, thin-wall structures essential for heat dissipation and electromagnetic shielding. |
| Lock & Hardware Industry | Door lock bodies, hinges, decorative fittings, gear mechanisms | Supports high-detail parts with tight mechanical fit and durable surface plating options. |
| Medical Devices & Instruments | Surgical handle components, pump housings, control knobs, precision fixtures | Ensures uniformity and smoothness required for hygienic and ergonomic medical-grade components. |
| Lighting & Electrical Equipment | LED housings, junction boxes, switchgear frames, electrical covers | Offers superior surface finish and repeatable accuracy for high-volume electrical components. |
| Toys & Leisure Products | Mechanical toy parts, action figure joints, precision gears | Enables efficient, low-cost mass production of small, durable, and detailed parts. |
| Precision Instruments & Optics | Calibration housings, adjustment wheels, optical mounts | Delivers dimensional stability and fine detailing for sensitive mechanical and optical assemblies. |
| Industrial Automation | Small gearbox casings, connector clamps, mounting brackets | Ideal for compact, high-tolerance parts used in automation modules and robotics. |
Common Technical Specifications – Hot Chamber Die Casting (HCDC)
Filling Pressure:
Hot chamber die casting typically operates at 10 to 35 MPa (100–350 bar) of injection pressure. The molten metal is drawn directly from the furnace into the shot chamber, enabling very fast injection speeds for small-to-medium parts.Cycle Time:
HCDC offers extremely short cycle times—often 8 to 30 seconds—due to its integrated furnace and minimal metal transfer distance. This makes it highly suitable for high-volume production runs.Alloy Selection:
Commonly used alloys include zinc alloys (Zamak 3, Zamak 5, Zamak 7), magnesium alloys (AZ91D, AM60B), and some low-melting-point copper alloys. These materials allow for fine details, thin walls, and excellent dimensional stability.Wall Thickness:
Hot chamber die casting can produce parts with walls as thin as 0.5–1.5 mm while maintaining excellent structural integrity and smooth surfaces, even in intricate designs.Tolerances:
Typical tolerances range from ±0.02 mm to ±0.08 mm, offering exceptional precision for electronics, hardware, and small mechanical components.
Common Challenges and Solutions – Hot Chamber Die Casting (HCDC)
Corrosion from Molten Metal Exposure:
The submerged injection components are constantly in contact with molten metal, leading to corrosion.
Solution: Use high-quality, corrosion-resistant steels and apply protective coatings to prolong component life.Alloy Limitations:
HCDC is unsuitable for high-melting-point metals like aluminum or brass.
Solution: Select alloys within the process’s melting range (zinc, magnesium, some copper alloys) or switch to cold chamber casting for high-melting-point materials.Flash Formation:
High-speed injection can force excess metal into parting lines, creating flash.
Solution: Maintain precise die alignment, ensure proper clamping force, and optimize injection pressure.Thermal Fatigue of Dies:
Continuous heating and cooling cycles can cause die cracking.
Solution: Use thermal management systems, preheat dies uniformly, and employ premium die steels.Porosity in Thin Sections:
Trapped gases in very thin or complex parts can create porosity.
Solution: Optimize venting, injection speed, and gating design to allow smooth metal flow and gas escape.
Get in touch with us
Contact our experts and we will provide you quotation, DFM, Moldflow for your High Die Casting Part.
- yoyo@iec-mould.com
- 86 13712993487
- 86 13712993487

*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.