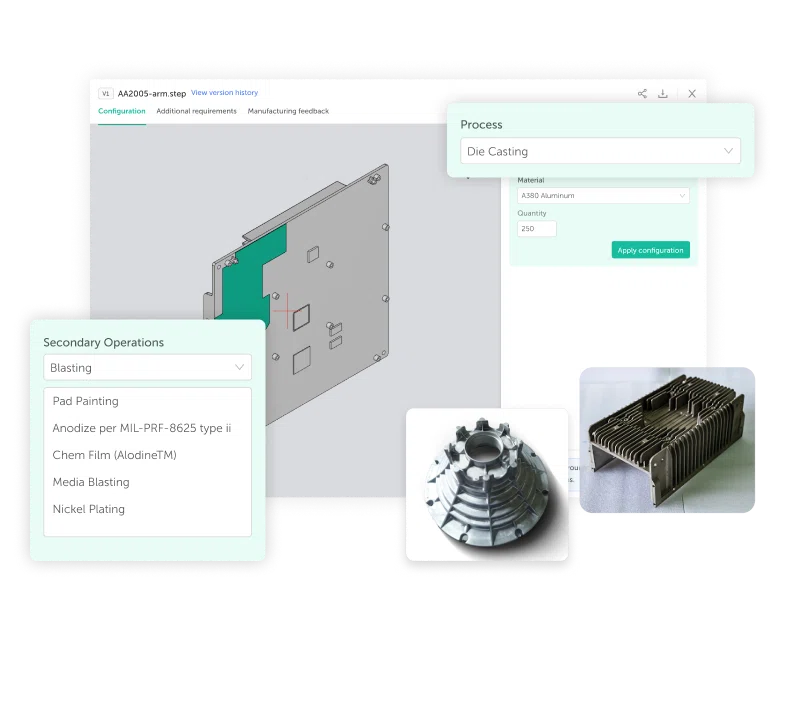
High Pressure Die Casting Manufacturer
Advanced Die Casting & Machining Capabilities
Standard Tooling Options aHelp Save Your Initial Investment
One-Stop Service – Mold Design, Die Casting, CNC, Surface Treatment
Support Low to High Volume Production — Starting from 100pcs
±0.01mm
Tolearance
20+
Years Experience
20 Day
Die Casting Samples Delivered
Certifications
ISO 9001 & IATF 16949
China High Pressure Die Casting Manufacturers and Suppliers
IEC MOULD is a trusted High Pressure Die Casting manufacturer and supplier with decades of experience in mold design, die casting production, CNC machining, and post-processing. We operate our own tooling workshop and die casting production lines, enabling us to provide one-stop solutions from concept to finished parts.
Our services are widely used in automotive, electronics, industrial machinery, home appliances, and medical devices. With ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certifications, advanced inspection equipment, and a professional engineering team, we ensure that every customer receives reliable, precise, and cost-effective solutions.
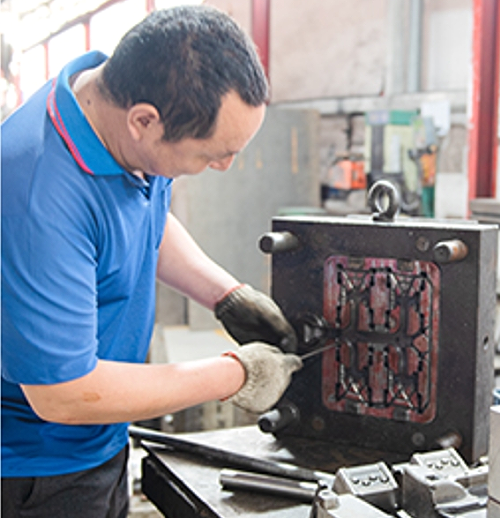
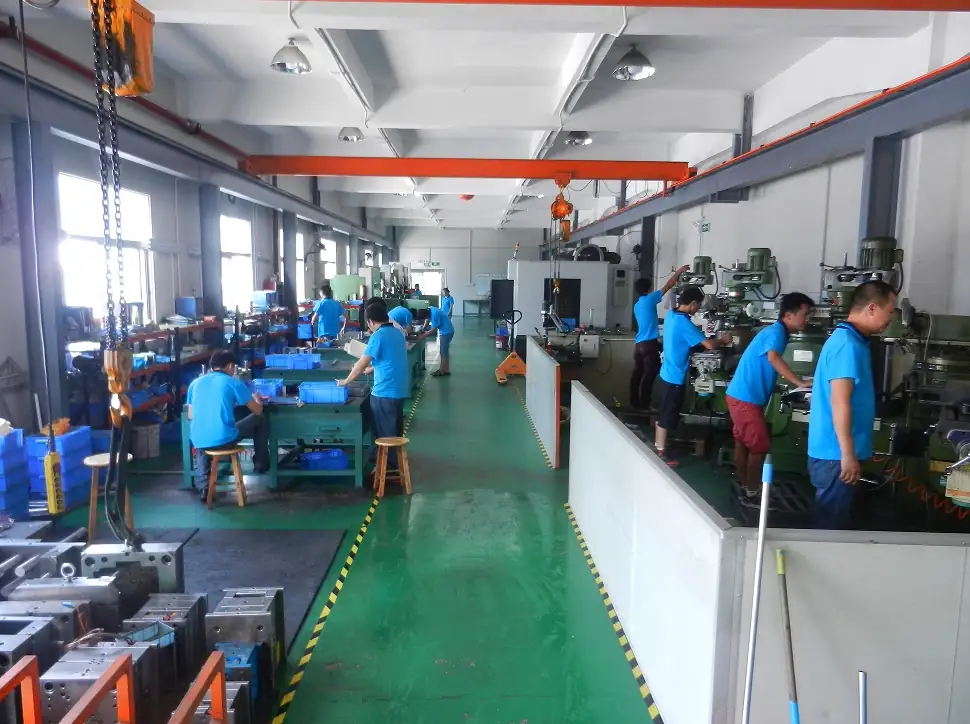
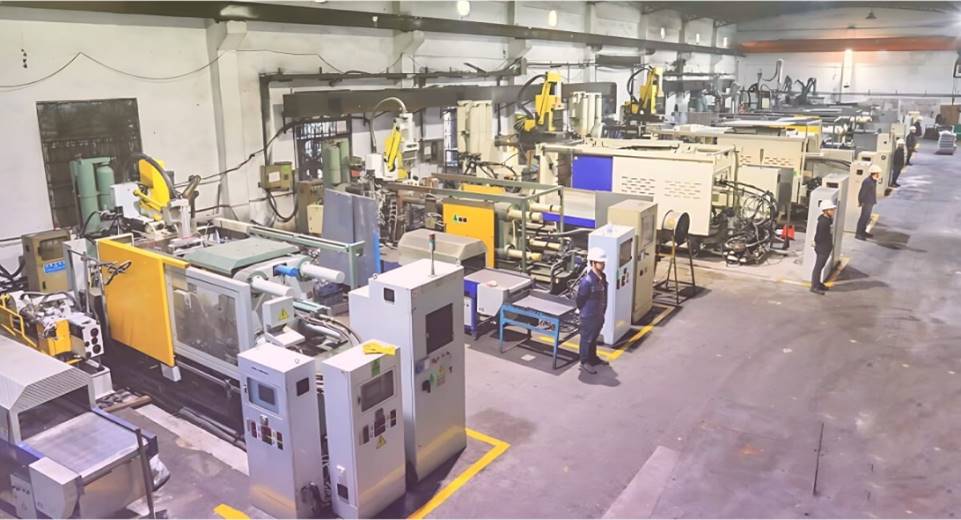





Our High Pressure Die Casting Services
We offer comprehensive High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) services to meet different project requirements:
- Custom High Pressure Die Casting – Aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys
- DFM & Moldflow Analysis – Optimize part design and reduce defects
- Mold Design & Manufacturing – High-quality tooling for mass production
- CNC Machining – Precision finishing for tight tolerances
- Surface Treatments – Anodizing, painting, plating, powder coating, etc.
- Assembly Services – Delivering complete ready-to-use components
- Quality Inspection – CMM, X-ray, leak testing, hardness testing, and more
With IEC MOULD, you don’t need multiple suppliers. We design, cast, machine, finish, and assemble – all under one roof.



IEC Mould's high Pressure Die Casting Capabilities
| Details | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Tolerance | High Pressure Die Casting parts can reach accuracy up to ±0.01mm with secondary machining, ensuring reliable precision for complex applications. |
| Minimum Wall Thickness | In High Pressure Die Casting, the recommended minimum wall thickness is 1.5mm for aluminum alloys and as thin as 0.8mm for zinc alloys. |
| Wall Thickness Ratio | To maintain casting stability, High Pressure Die Casting parts should follow a 1:3 wall thickness ratio to avoid uneven filling. |
| Hole Diameter | For High Pressure Die Casting molds, round holes smaller than 3mm require secondary drilling. Threaded holes and external threads are typically achieved through machining after casting. |
| Draft Angle | A minimum draft angle of 0.5° is required in High Pressure Die Casting to ensure smooth part ejection and reduce mold wear. |
| Maximum Die Life (Cycles) | – Zinc High Pressure Die Casting molds: up to 1,000,000 cycles – Aluminum & Magnesium High Pressure Die Casting molds: approximately 100,000 cycles |
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | Standard production MOQ for High Pressure Die Casting is 100 pieces, ideal for medium to large-scale manufacturing. |
| Lead Time | Typical lead time for High Pressure Die Casting projects is 20–25 days, depending on mold design and part complexity. |
High Pressure Die Casting Parts We Manufactured
Whether you need small precision components or large structural parts, our High pressure die casting (HPDC) expertise ensures that we can handle your project efficiently.
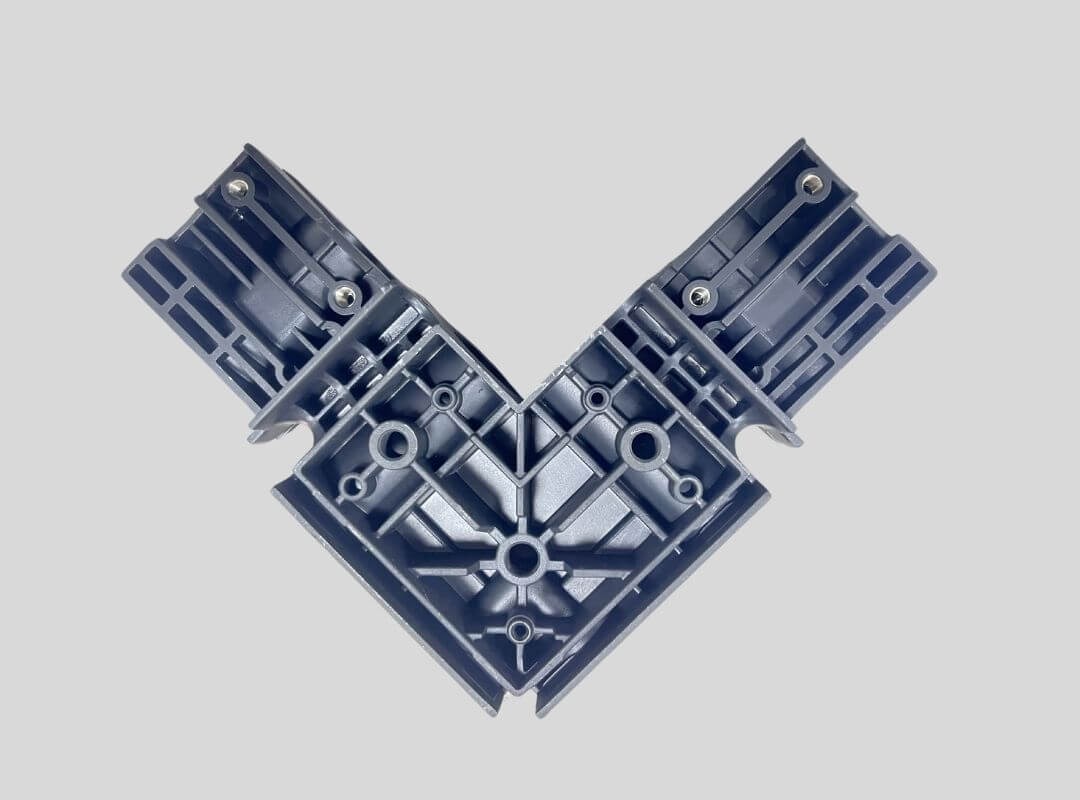
Electronics Part
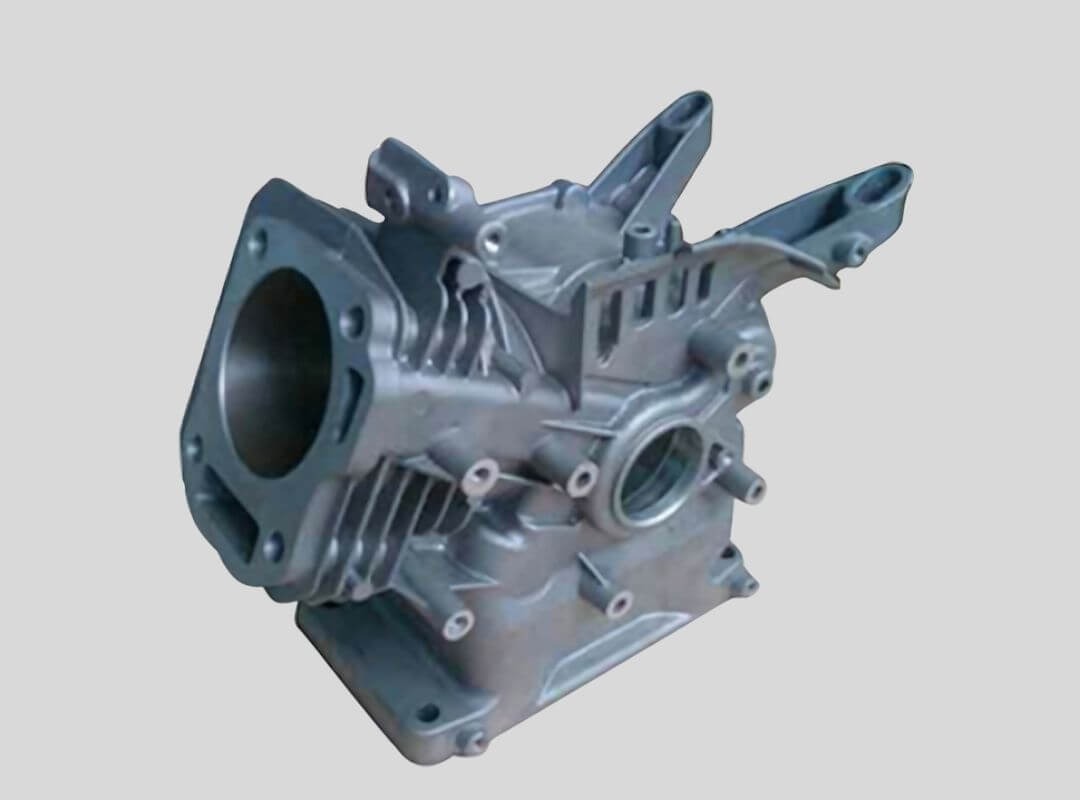

Automotive Part
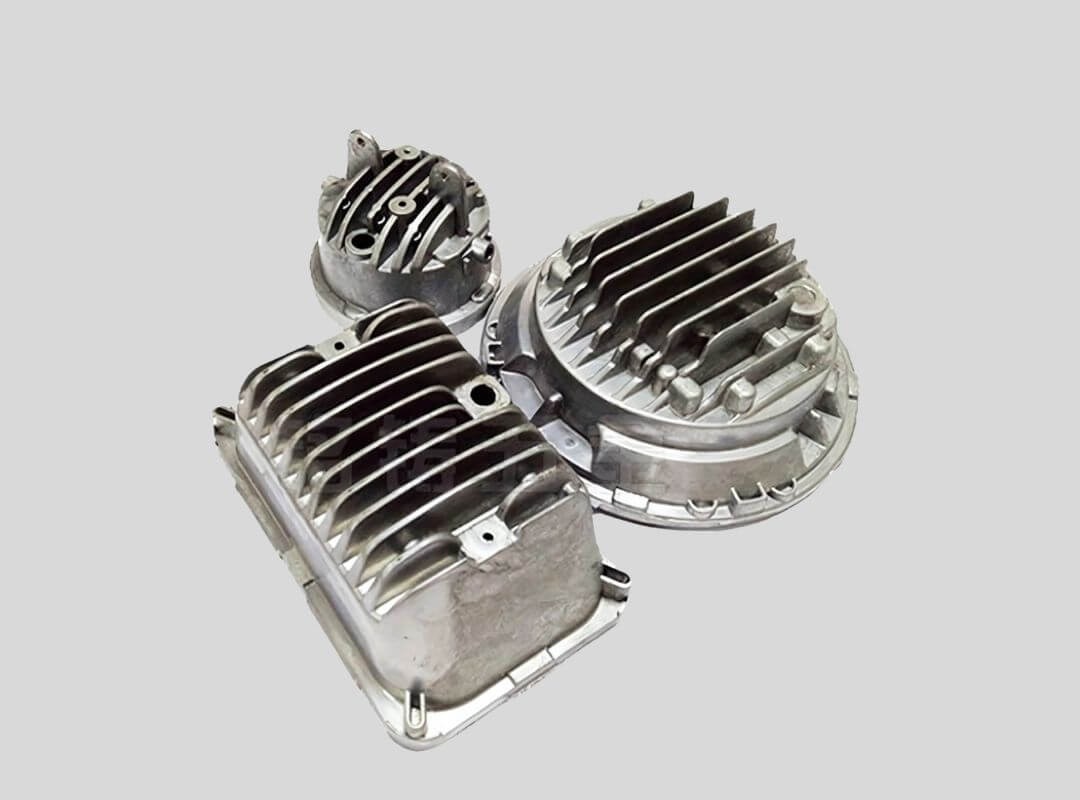

Home Appliances Part
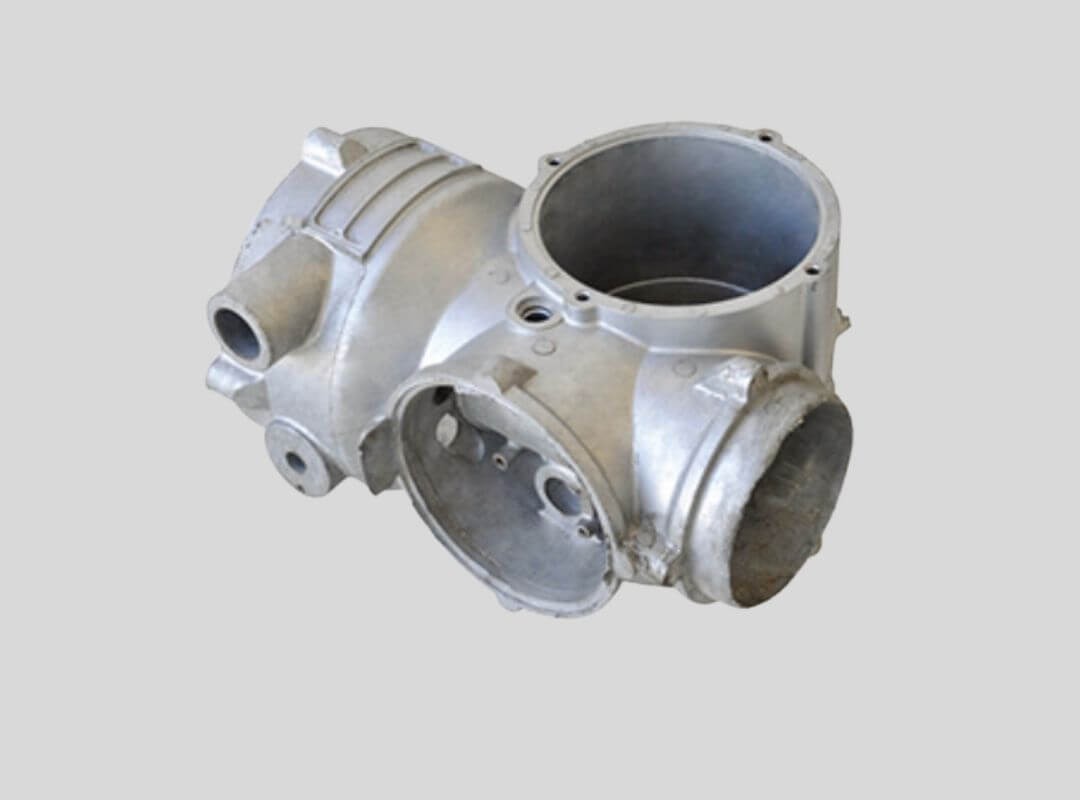

Industrial Machinery Part
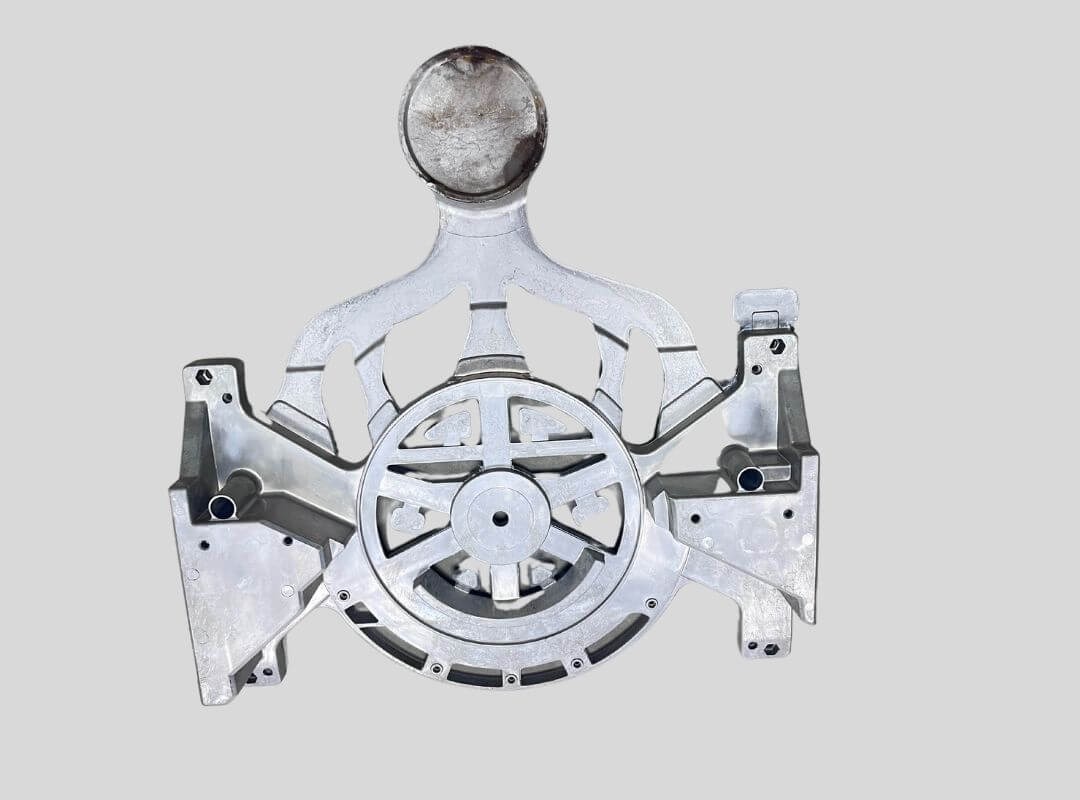

Medical Devices Part
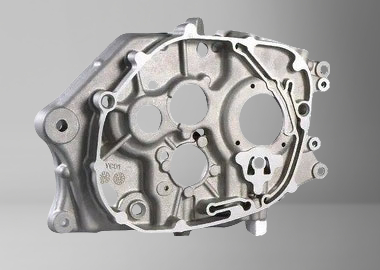
Engineering Part
High Pressure Die Casting materials we used
| Material | Key Features | Typical Applications | Why It Fits High Pressure Die Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys (ADC12, A380, A383, A360) | Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance, high thermal and electrical conductivity, good mechanical strength | Automotive engine blocks, gearbox housings, electronic enclosures, lighting components, consumer products | Perfect for thin-walled, complex designs that require strength, durability, and heat dissipation in high volumes |
| Zinc Alloys (Zamak 3, Zamak 5, ZA-8, ZA-27) | Superior dimensional accuracy, excellent surface finish, high ductility, low melting point for faster cycle times | Precision gears, connector housings, decorative hardware, consumer electronics | Ideal for small to medium parts requiring tight tolerances, intricate details, and cost-efficient mass production |
| Magnesium Alloys (AZ91D, AM60B, AM50) | Ultra-lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent machinability, good damping properties | Steering wheels, seat frames, aerospace interior structures, handheld devices | Enables weight reduction without sacrificing performance, making it valuable for automotive and aerospace industries |
| Copper Alloys (Brass, Bronze, Cu-based alloys) | High strength, superior corrosion resistance, excellent wear resistance, good thermal conductivity | Plumbing fittings, heat exchangers, electrical components, marine hardware | Suitable for demanding applications where strength, conductivity, and corrosion resistance are critical |
| Specialized Aluminum-Silicon Alloys (Al-Si series) | Excellent wear resistance, low thermal expansion, good fluidity for complex molds | Cylinder heads, transmission cases, high-performance automotive and industrial parts | Allows production of highly complex, durable, and heat-resistant components under mass production conditions |
Why Choose IEC MOULD for your high pressure die casting project?
- Feature: In-house tooling, die casting, CNC machining, and finishing
- Advantage: Full control over quality, lead time, and cost efficiency
- Benefit: You save time and reduce risks by working with a single trusted supplier
- Evidence: Certified by ISO 9001 & IATF 16949, equipped with CMM, X-ray inspection, and trusted by global automotive and electronics leaders
Choosing IEC MOULD means choosing a partner who understands engineering challenges, procurement goals, and strict quality standards.

High Pressure Die Casting Frequently Questions & Answers
What materials are best suited for High Pressure Die Casting?
HPDC is most commonly used with aluminum (e.g., A380, ADC12), zinc (Zamak 3, Zamak 5), and magnesium (AZ91D, AM60B) alloys. These metals have the right melting points and fluidity for high-pressure injection, allowing for thin-walled, complex geometries.
What are the typical tolerances achievable with HPDC?
HPDC can achieve tight dimensional tolerances, typically ±0.05–0.1 mm, depending on the size and complexity of the part. Proper tooling design, process control, and mold maintenance are key to maintaining these tolerances.
How does HPDC compare to Low Pressure or Gravity Die Casting?
HPDC is best for high-volume production of thin-walled parts with excellent surface finish and tight tolerances.
LPDC is used for larger parts requiring low porosity and strong mechanical properties, often in automotive structural parts.
Gravity Die Casting is more cost-effective for medium-volume runs with moderate complexity.
What is the maximum part size for High Pressure Die Casting?
HPDC is ideal for small to medium-sized parts. Typical part weights range from a few grams up to ~20 kg, though the maximum size depends on machine clamping force and mold design.
Are HPDC parts heat-treatable?
Most aluminum HPDC alloys are not heat-treatable because of trapped gas porosity. However, certain specialized alloys and vacuum die casting processes can produce parts suitable for heat treatment. Consult our engineers for material recommendations.
What surface finishes are available for HPDC components?
HPDC parts come with a smooth, high-quality as-cast finish. Additional surface finishes can be applied:
Powder coating or painting
Anodizing (for aluminum)
Plating (zinc, chrome, nickel)
Shot blasting or polishing
What quality assurance methods are used for HPDC parts?
We follow ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 standards and use:
CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) inspections, X-ray and ultrasonic testing for porosity, SPC (Statistical Process Control) during production, 100% traceability for every batch
Other Die Casting Technologies You May Looking for
What is High Pressure Die Casting?
High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) is a precision metal casting process where molten metal is injected into a steel mold at high pressure (1,000 to 1,500 bar). The process is ideal for producing complex, lightweight, and highly detailed components. HPDC is widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and industrial manufacturing for parts that require tight tolerances, superior surface finish, and high production volumes.
Why Choose HPDC?
Fast Production Cycles – HPDC offers rapid cycle times and is highly efficient for large batch production.
- Dimensional Precision – The process achieves tight tolerances (up to ±0.05mm) and is ideal for intricate parts.
- Smooth Surface Finish – Parts come out of the mold with minimal post-processing required.
- Complex Geometries – HPDC can handle thin-walled and complex shapes, making it versatile for various applications.
How High-Pressure Die Casting Works?
The High pressure Die Casting (HPDC) process involves multiple steps that work together to create highly precise metal parts.
Step 1: Preparation
The steel mold is prepped with a release agent to prevent sticking. The molds are designed for durability and precise control of temperature and cooling rates.
Step 3: Cooling and Solidification
Once the molten metal fills the cavity, it cools and solidifies rapidly. The speed of cooling is controlled to prevent defects like shrinkage or porosity, resulting in high-quality finished parts.
Step 2: Molten Metal Injection
Molten metal, typically aluminum, zinc, or magnesium alloys, is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The pressure ensures that the metal fills even the most intricate details of the mold.
Step 4: Ejection
The mold is opened after cooling, and the part is ejected using ejector pins. Secondary operations such as trimming, machining, or surface finishing may be required depending on part specifications.
Advantages of High Pressure Die Casting
Precision and Customization
Tight Dimensional Tolerances: HPDC allows for ±0.05 mm accuracy, ensuring that parts meet stringent specifications with minimal variation.
Complex Part Geometries: Ideal for producing intricate shapes and thin-walled designs that would be difficult or costly with other manufacturing methods.
Fast Prototyping & Low Cycle Time: The ability to produce parts rapidly makes HPDC an excellent choice for fast-tracking product development cycles and achieving quick market entry.
Compatibility with Multiple Alloys: HPDC works with a variety of alloys like A380, ADC12, AZ91D, etc., giving engineers flexibility in material selection based on specific part requirements.
Quality Assurance and Control
High-Quality Finish: HPDC parts require minimal post-processing due to their smooth surface finish. This minimizes defects like scratches and dimensional variations.
Process Control: Tight process control ensures parts are produced with high precision. The use of X-ray inspection, CMM measurements, and ultrasonic testing guarantees quality consistency across production runs.
Porosity Prevention: By controlling injection speed, mold temperature, and pressure, HPDC minimizes internal defects like gas porosity and shrinkage that can affect part strength.
Cost Efficiency and Reliability
Cost-Effective for High Volumes: HPDC is ideal for large-scale production due to its short cycle times and material efficiency, making it a cost-effective option for high-volume runs.
Material Sourcing & Alternatives: HPDC works with multiple alloys like aluminum, magnesium, and zinc, giving procurement teams options for material selection based on cost, performance, and availability.
Supply Chain Reliability: Partnering with an experienced supplier ensures that high-quality parts are delivered on time, with the ability to scale production based on changing demand.
Disadvantages of High Pressure Die Casting
While High Pressure Die Casting is one of the most efficient and widely used manufacturing processes, it also comes with certain limitations. Understanding these disadvantages helps engineers, procurement managers, and quality teams make informed decisions.
High Initial Tooling Cost
High Pressure Die Casting requires precision steel molds and complex tooling. The upfront investment can be significant, making it less cost-effective for very low-volume production.
Not Ideal for Small Batches
Due to the high mold cost and setup time, High Pressure Die Casting is best suited for medium to large-scale production runs. Small-batch projects may find other casting methods more economical.
Limited Thickness Range
High Pressure Die Casting is excellent for thin-walled parts, but very thick walls are difficult to produce without defects such as porosity or shrinkage.
Secondary Machining Required
Although the process achieves high precision, features like small holes, threads, and fine details usually require secondary machining. This adds extra steps and cost.
Porosity Issues
Due to the high-speed injection of molten metal, gas entrapment can occur, leading to internal porosity. This can limit applications requiring high airtightness or heat treatment.
Mold Wear and Maintenance
High Pressure Die Casting molds operate under extreme pressure and temperature, which leads to faster wear compared to other casting processes. Regular maintenance and eventual replacement increase long-term costs.
Material Limitations
Not all metals are suitable for High Pressure Die Casting. The process is mainly used for aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys, while high-melting-point metals like steel are not feasible.
High Pressure Die Casting vs Other Die Casting Technologies
| Feature | High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) | Low Pressure Die Casting (LPDC) | Gravity Die Casting (Permanent Mold Casting) | Sand Casting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suitable Alloys | ✅ Aluminum, Zinc, Magnesium | ✅ Aluminum, Magnesium | ✅ Most non-ferrous alloys | ✅ Most metals |
| Filling Pressure | Very High (1000–2500+ bar) | Low (0.7–1.5 bar) | Gravity only | Gravity only |
| Porosity | ⚠️ Moderate (can be minimized with vacuum die casting) | ✅ Lower than HPDC | ✅ Low | ❌ High |
| Heat Treatment | ❌ Limited (not always suitable due to porosity) | ✅ T5/T6 Possible | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Surface Finish | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Smooth, Ra 1.6–3.2 μm) | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐ |
| Dimensional Accuracy | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (±0.05–0.1 mm) | ⭐⭐⭐ (±0.2 mm) | ⭐⭐ | ⭐ |
| Wall Thickness | Thin (as low as 1–1.5 mm) | Medium (≥3 mm) | Medium | Thick |
| Part Size Capability | Small to Large (depends on press size) | Medium to Large | Medium to Large | Large |
| Production Speed | ⏩ Very Fast (short cycle times) | ⏩ Moderate | ⏩ Slow | ⏩ Very Slow |
| Tooling Cost | 💰 High | 💰 Medium | 💰 Medium | 💰 Low |
| Ideal for | Complex, thin-walled, high-volume automotive, aerospace, and electronics parts | Structural automotive wheels, chassis parts | Medium-complexity parts, lower volume | Large prototypes, low-volume casting |
High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) Applications
High Pressure Die Casting is used across various industries, thanks to its ability to produce lightweight, strong, and complex components.
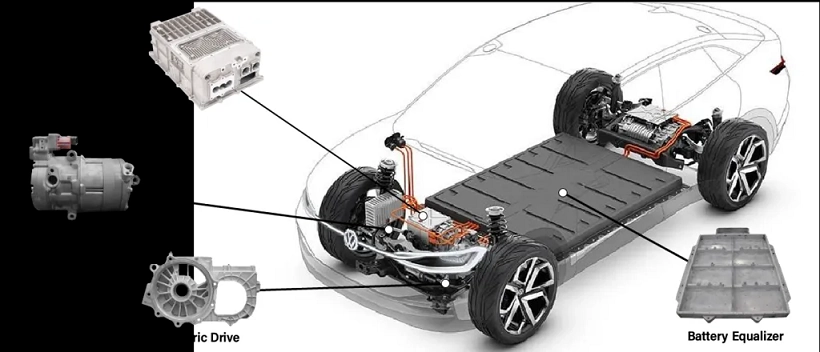
Automotive Industry:
HPDC is used extensively in automotive manufacturing, producing components like: Engine blocks, Transmission housings, Brackets, Suspension parts.
These components must be lightweight, highly durable, and capable of withstanding harsh conditions, making HPDC an ideal choice.
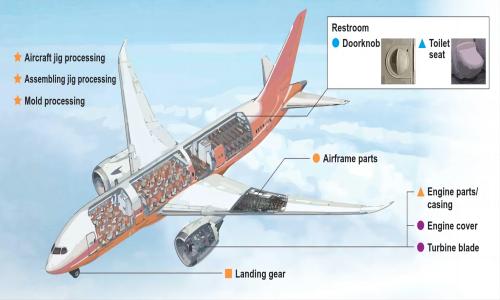
Aerospace Industry:
In aerospace, HPDC is ideal for producing components such as: Airframe parts, Aircraft structural components, Landing gear housings, Engine parts.
HPDC enables aerospace engineers to create lightweight, high-strength parts with complex geometries that meet stringent performance requirements.

Electronics Industry:
For the electronics industry, HPDC is used to produce: Smartphone casings, Laptop housings, TV brackets and frames, Connectors and enclosures.
The smooth surface finishes and tight tolerances make HPDC ideal for parts used in consumer electronics.

Industrial Equipment:
HPDC is also employed in manufacturing parts for industrial machinery such as: Valve bodies, Pumps, Gearboxes, Electrical enclosures.
These parts require precision and strength, making HPDC the go-to process for industrial applications.
High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) Common Technical Specifications
Injection Pressure: HPDC uses high injection pressures between 1,000 and 1,500 bar to ensure rapid and complete filling of the mold.
Cycle Time: Cycle times can range from 30 seconds to several minutes depending on the size and complexity of the part. This allows for high-volume production with consistent results.
Alloy Selection: Common alloys used include A380, ADC12, AZ91D, Zamak and AM60B. Each alloy offers unique strength, corrosion resistance, and performance properties tailored to different applications.
Wall Thickness: HPDC is ideal for thin-walled parts, with wall thicknesses as low as 0.5 mm.
Tolerances: HPDC achieves tight tolerances (±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm), making it perfect for applications requiring high precision.
High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) Common Challenges and Solutions
Mold Wear: Due to the high pressures used in HPDC, mold wear is a common challenge. Regular maintenance and tooling optimization can extend mold life and reduce downtime.
Defects & Porosity: Porosity and shrinkage can occur if cooling rates or injection pressures are not properly controlled. Implementing advanced process controls and non-destructive testing methods, like X-ray, ensures that these defects are minimized.
Tooling Costs: HPDC tooling can be expensive due to the high precision required for the molds. However, this cost is offset by the low per-part cost when producing high volumes
Get in touch with us
Contact our experts and we will provide you quotation, DFM, Moldflow for your High Die Casting Part.
- yoyo@iec-mould.com
- 86 13712993487
- 86 13712993487

*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.