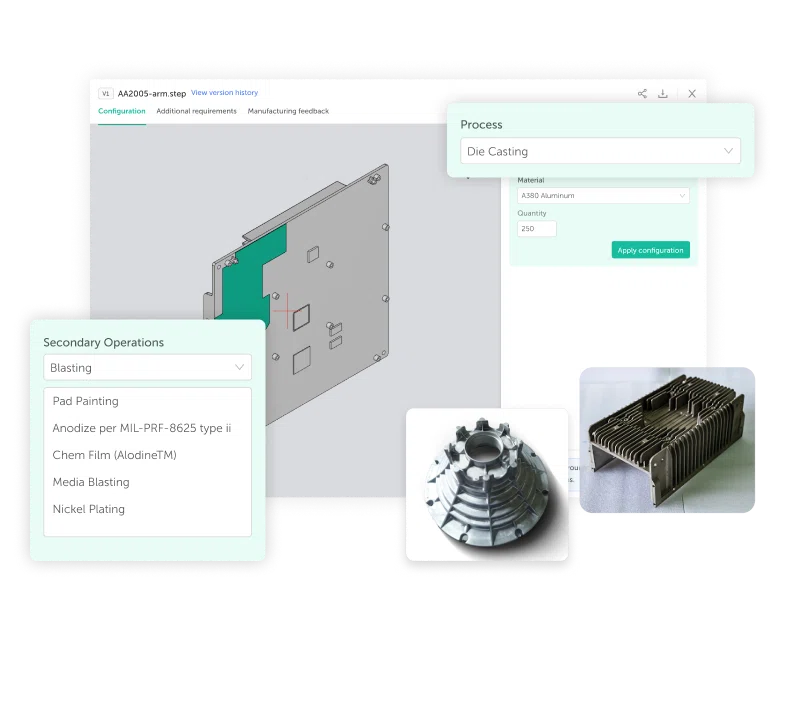
Gravity Die Casting Manufacturer
Precision Casting – Achieve excellent dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finish for reliable parts.
Low Defects – Minimize porosity and shrinkage for zero-rework production.
Cost-Efficient – Ideal for medium-to-high volume production with lower per-unit cost.
Versatile Materials – Supports aluminum and zinc alloys for various components.
- Energy-Efficient – Gravity-driven process reduces energy use and mold wear.
±0.01mm
Tolearance
20+
Years Experience
20 Day
Die Casting Samples Delivered
Certifications
ISO 9001 & IATF 16949
Best Gravity Die Casting Manufacturer and Supplier
IEC MOULD is a trusted Gravity Die Casting manufacturer and supplier specializing in precision aluminum and copper alloy components. Through controlled gravity feeding, molten metal fills the mold cavity smoothly and evenly, achieving superior material density, reduced porosity, and excellent dimensional accuracy compared with conventional casting methods.
We operate our own tooling workshop and casting facilities, enabling full control from mold design and manufacturing to die casting, CNC machining, and surface finishing. This integrated process ensures stable quality, high repeatability, and cost-effective solutions suitable for low to medium volume production and complex structural parts.
With ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certifications, advanced measuring systems, and an experienced engineering team, IEC MOULD guarantees reliable performance and consistent quality in every project.
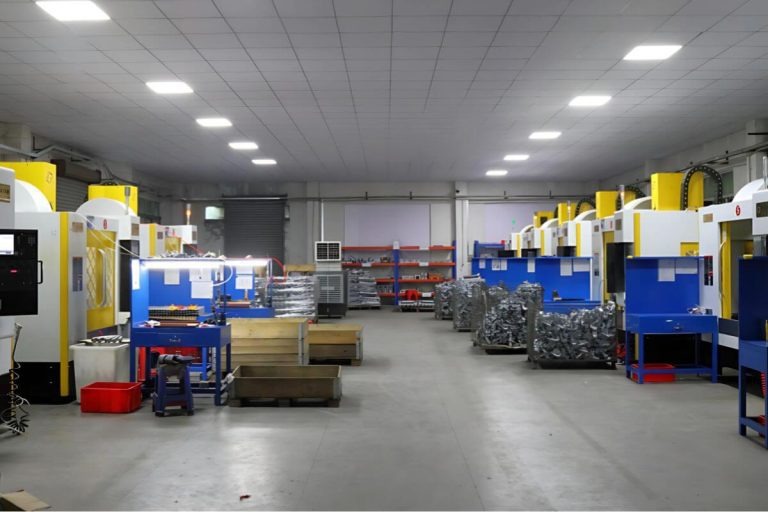
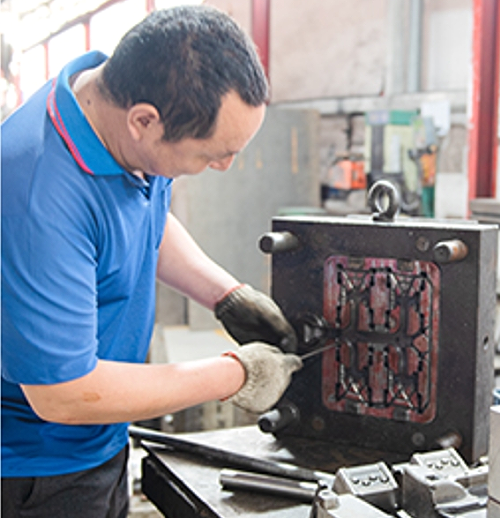
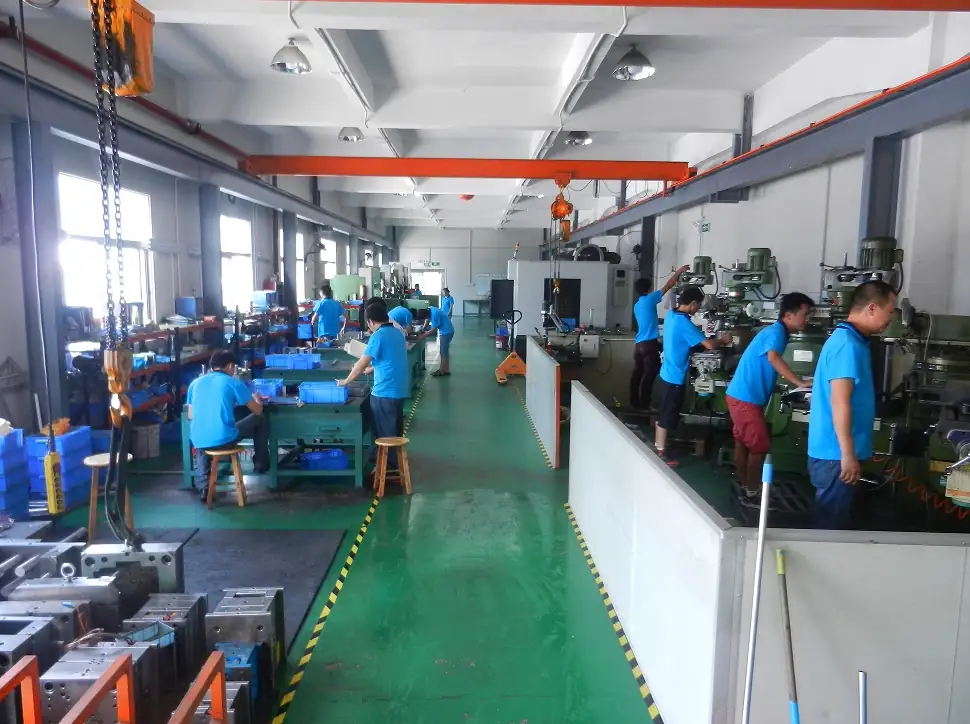
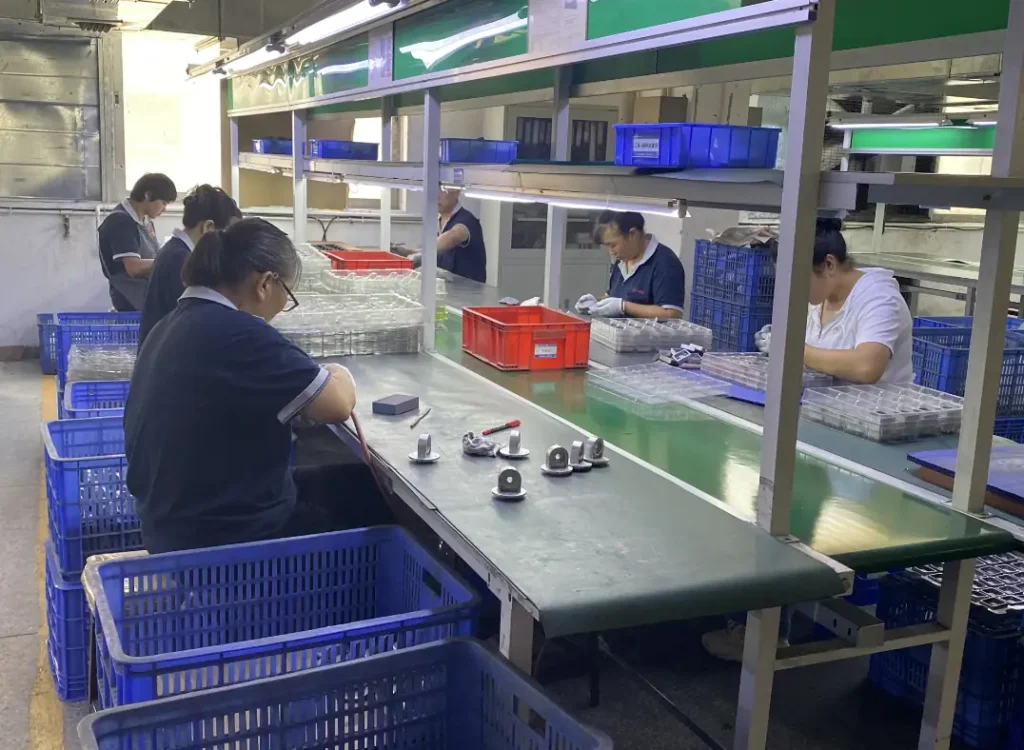
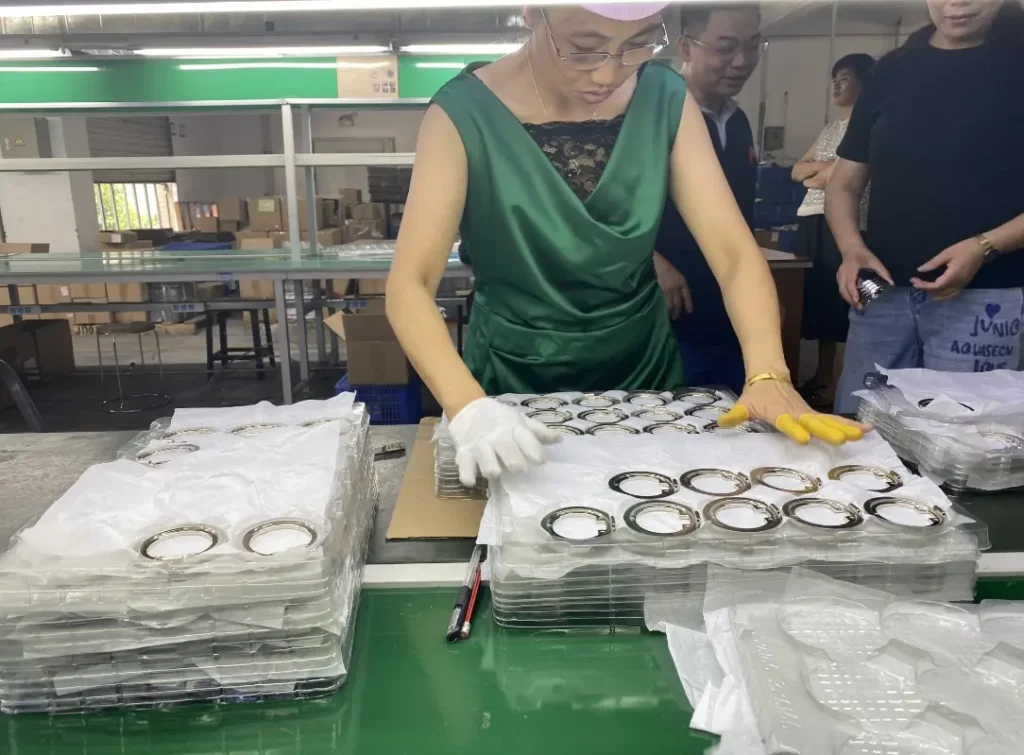





Our Gravity Die Casting Services
We offer professional Gravity Die Casting (GDC) services to support diverse project needs::
- Custom Gravity Die Casting – High-quality aluminum and copper alloy parts with excellent strength and density.
- Tooling Design & Manufacturing – Durable steel molds built for accuracy, smooth metal flow, and long service life.
- DFM & Flow Simulation – Optimize casting performance, reduce turbulence, and minimize porosity.
- CNC Machining & Surface Finishing- Precision machining with anodizing, painting, or coating options.
- Prototype to Medium Volume Production – Flexible, cost-efficient production starting from small batches.
- Strict Quality Control – CMM measurement, leak testing, and metallurgical inspection to ensure reliability.
- One-Stop Manufacturing – From mold design to finished components — all under one roof.
With IEC MOULD, you gain a single-source partner for tooling, casting, machining, and finishing — delivering high-quality, cost-effective gravity cast components with stable performance and repeatable accuracy.
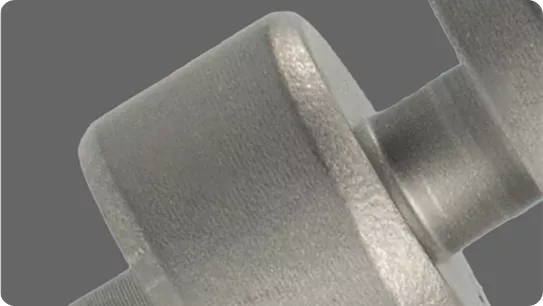



IEC Mould's Gravity Die Casting Capabilities
| Details | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Tolerance | Gravity Die Casting parts can achieve accuracy up to ±0.05mm for typical aluminum and copper alloys. Tighter tolerances can be achieved with secondary machining. |
| Minimum Wall Thickness | Recommended minimum wall thickness is 2.5–3mm for aluminum alloys and 3–4mm for copper alloys, ensuring smooth metal flow and reduced porosity. |
| Wall Thickness Ratio | To maintain casting stability, Gravity Die Casting parts should follow a 1:4 wall thickness ratio to prevent shrinkage and filling defects. |
| Hole Diameter | Round holes smaller than 4mm typically require secondary drilling. Threaded holes are generally machined after casting. |
| Draft Angle | Minimum draft angle of 1° is recommended to facilitate smooth part ejection and reduce mold wear. |
| Maximum Die Life (Cycles) | Gravity Die Casting molds can last 50,000–200,000 cycles depending on material and complexity; mold wear is slower than high-pressure processes. |
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | Flexible production: from 50 pcs per batch, suitable for low to medium volume orders. |
| Lead Time | Typical lead time for Gravity Die Casting parts is 25–30 days, depending on mold complexity and batch size. |
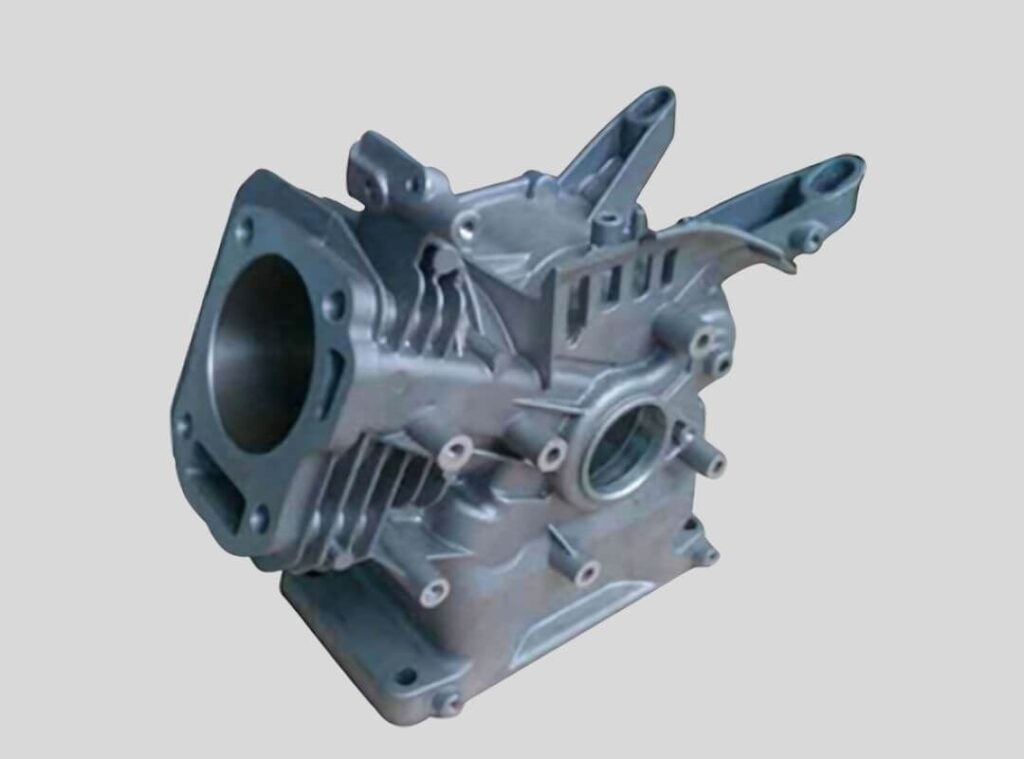
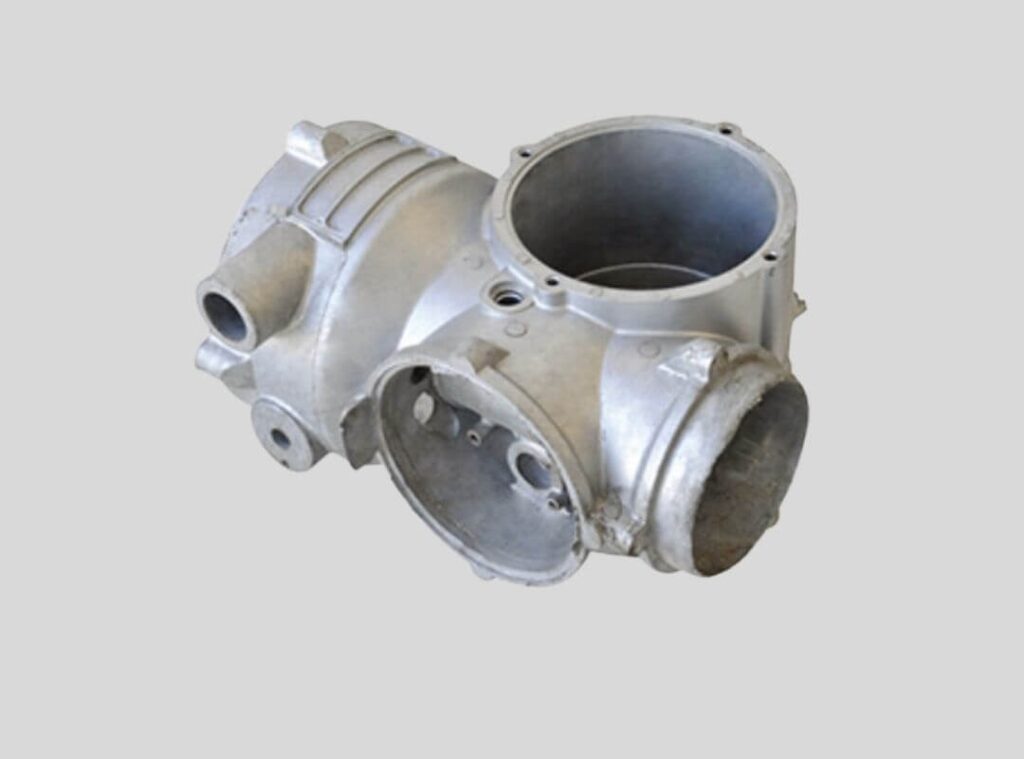
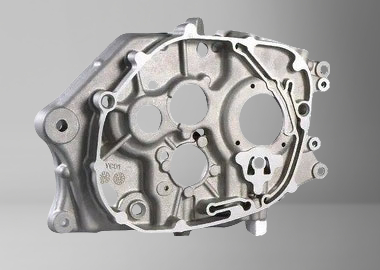
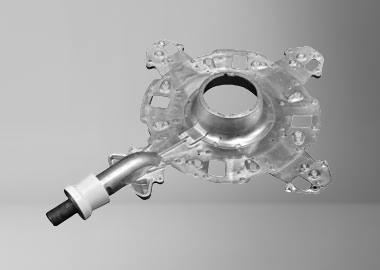
Gravtiy Die Casting Parts We Manufactured
Whether you need medium-to-large structural components or intricate aluminum and copper parts, our Gravity Die Casting (GDC) expertise ensures smooth metal flow, superior material density, and cost-effective production for low to medium volume orders.
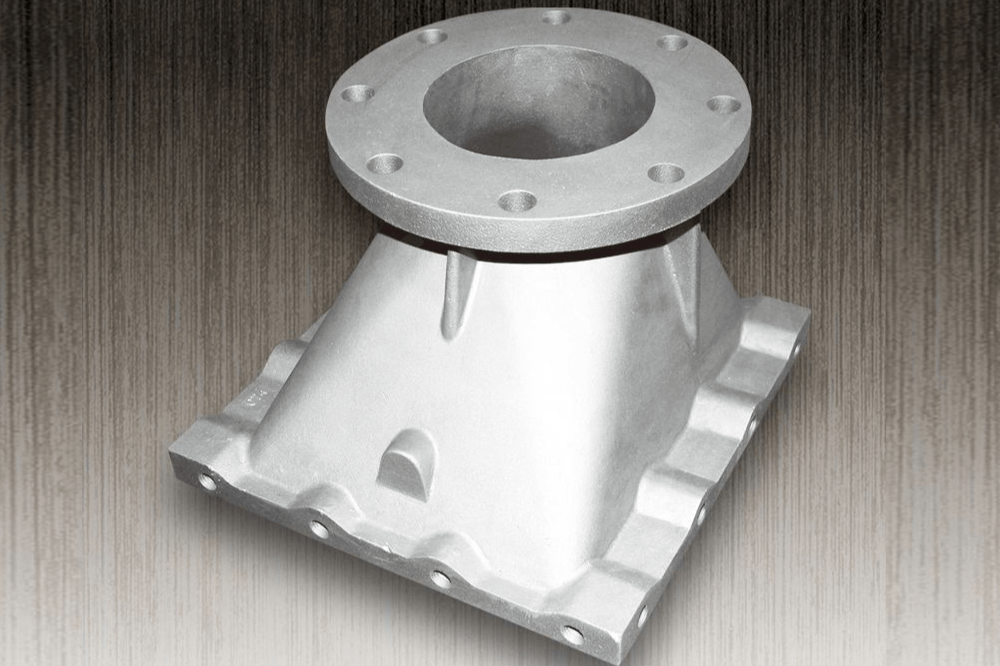
Robot Arm Shaft Housing
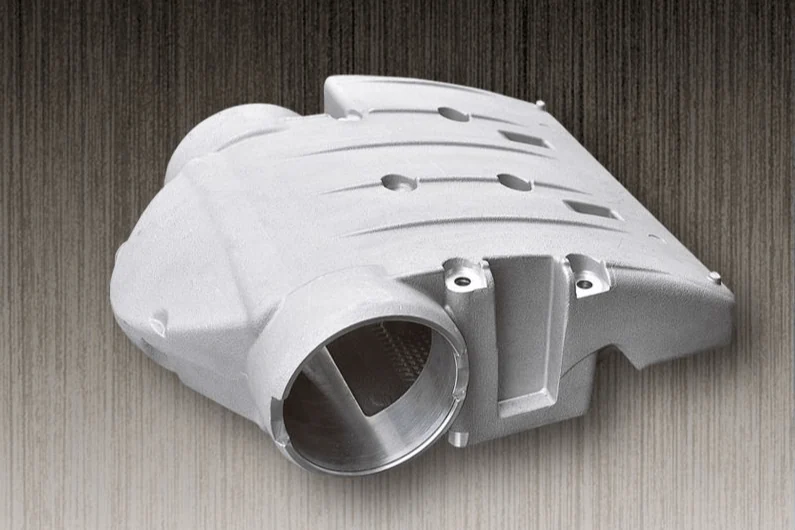

Engine Intake Manifold
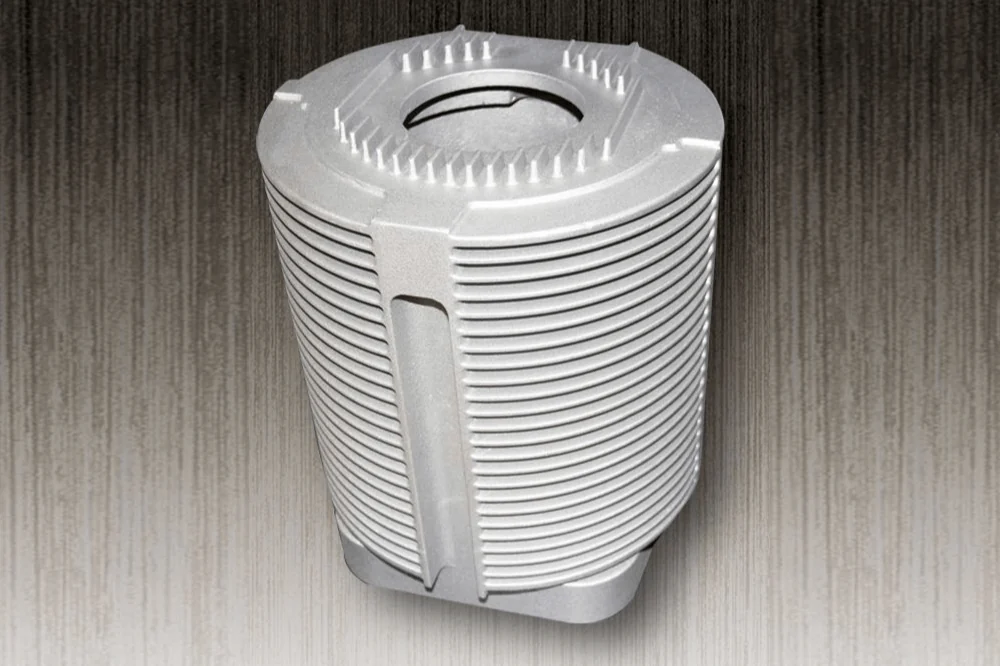

Motor Housing
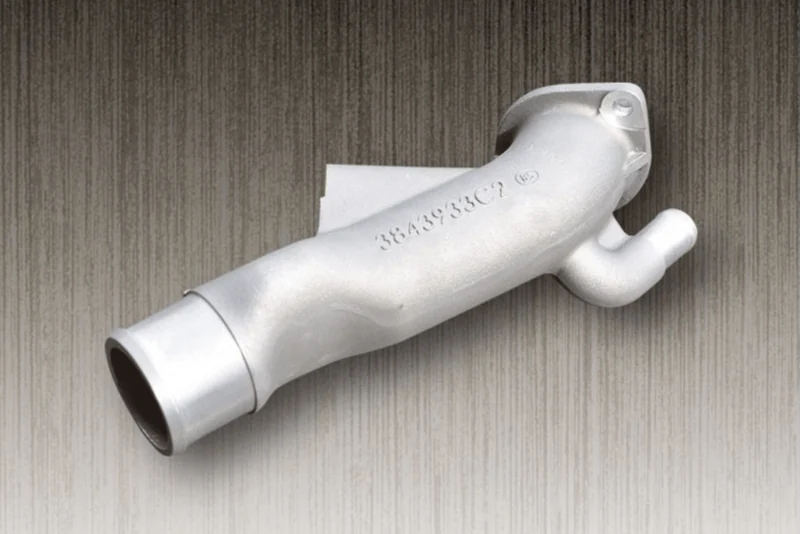

Engine Water Inlet Pipe
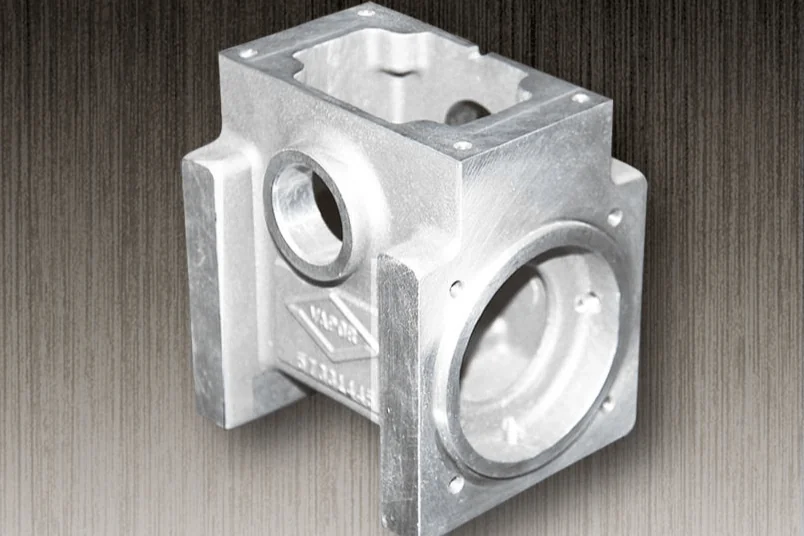

Transmission Housing
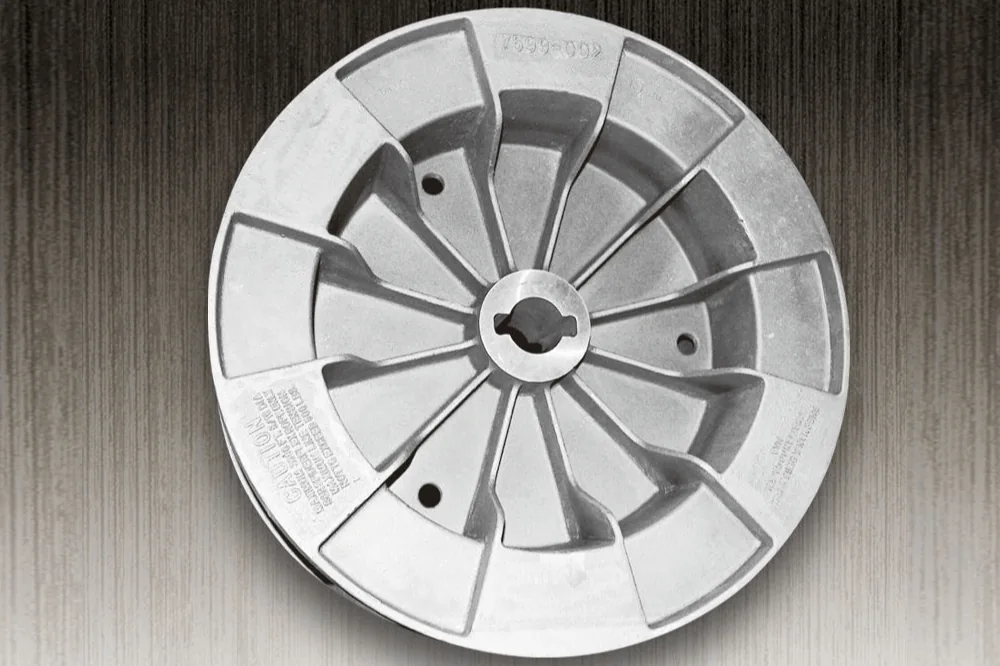

Large Gear
Gravity Die Casting materials we used
| Material | Key Features | Typical Applications | Why It Fits Gravity Die Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys (ADC12, A380, A383, A360) | Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance, high thermal conductivity, good mechanical strength | Structural housings, pump bodies, automotive brackets, industrial machinery parts | Suitable for medium-to-large components with thicker walls, offering strong material integrity and low porosity |
| Copper Alloys (Brass, Bronze, Cu-based alloys) | High strength, superior corrosion resistance, excellent wear resistance, good thermal conductivity | Plumbing fittings, heat exchangers, electrical connectors | Ideal for medium-sized parts where durability and thermal or electrical conductivity are critical |
| Magnesium Alloys (AZ91D, AM60B, AM50) | Ultra-lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, good machinability | Instrument frames, lightweight structural components | Enables weight reduction for medium-volume production while maintaining structural strength |
| Zinc Alloys (Zamak 3, Zamak 5) | Good corrosion resistance, easy machining, moderate strength | Decorative hardware, housings, enclosures | Works well for small to medium parts with low-to-medium volume, simpler complex geometry |
| Specialized Aluminum-Silicon Alloys (Al-Si series) | Excellent wear resistance, low thermal expansion, good flow for molds | Cylinder housings, industrial equipment, durable structural parts | Supports medium-to-large complex parts with high strength and thermal stability under GDC conditions |
Why Choose IEC MOULD for your Gravity die casting part?
- Feature: In-house tooling, gravity-fed die casting, CNC machining, and finishing
- Advantage: Ensures smooth metal flow, high material density, and superior structural integrity for medium-to-large components
- Benefit: You gain reliable, low-defect parts with flexible production volumes, reducing costs and risks compared to multi-supplier solutions
- Evidence: ISO 9001 & IATF 16949 certified, advanced CMM and metallurgical inspection equipment, trusted by clients requiring durable, precision-engineered components.
Choosing IEC MOULD means partnering with a team who understands the unique requirements of gravity die casting — delivering strong, dense, and cost-effective components tailored to your gravity die casting project needs.

Gravity Die Casting Frequently Questions & Answers
Can GDC parts be painted or coated?
Yes, surfaces are smooth and can be anodized, powder-coated, or painted to meet aesthetic or protective requirements.
How to choose between Gravity Die Casting and other casting methods?
GDC is ideal for medium-to-large parts with good mechanical strength, smooth surface finish, and medium production volume. High-pressure die casting is better for very thin, intricate, or high-volume parts, while sand casting suits very large, low-volume components.
What are common defects in Gravity Die Casting?
Porosity, cold shuts, surface oxides, and shrinkage are common. Proper mold design and pouring parameters can reduce defects.
How can porosity be minimized in GDC?
Preheating the mold, controlling pouring temperature, and optimizing gating and venting systems can significantly reduce porosity.
What inspection methods are used for GDC parts?
Dimensional inspection (CMM), visual inspection, X-ray or ultrasonic testing for internal defects, and mechanical testing for strength.
What is the typical cost of Gravity Die Casting parts?
Costs depend on material, mold complexity, and production volume. GDC is cost-effective for medium-to-large parts and medium production volumes.
How long does it take to produce a GDC mold?
Permanent steel molds typically take 4–8 weeks to manufacture, depending on complexity.
Other Die Casting Technologies You May Looking for
What is Gravity Die Casting (GDC)?
Gravity Die Casting (GDC) is a permanent mold casting process in which molten metal is poured into a reusable steel or iron mold under the force of gravity, without the use of external pressure. The controlled filling and solidification create castings with excellent density, mechanical strength, and dimensional consistency.
Unlike High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC), which uses fast injection at extremely high pressure, GDC relies on a slower, more natural filling process. This minimizes turbulence during mold filling, significantly reducing porosity, shrinkage, and internal defects. The result is structurally sound castings with improved reliability for critical applications.
Gravity Die Casting is particularly well-suited for aluminum alloys and is commonly applied to medium-to-large components such as housings, brackets, engine parts, and heavy-duty industrial equipment. It offers a balance of mechanical performance, dimensional accuracy, and cost efficiency, making it ideal for applications where both strength and consistency are essential.
Because of its ability to deliver dense, defect-minimized castings with excellent repeatability, GDC is widely used in the automotive, aerospace, energy, and industrial machinery sectors, where safety, durability, and long service life are key requirements.
Why Choose Gravity Die Casting (GDC)?
Engineers
Reliable dimensional accuracy for medium-to-large aluminum parts
Strong mechanical properties from dense, gravity-fed solidification
Suitable for structural components, housings, and heat-resistant parts

- Low porosity and shrinkage through controlled metal flow
- ISO-certified inspection: CMM, X-ray, spectrometry, tensile testing
- Long mold life ensures consistent repeatability over production runs

Cost-efficient for medium-to-high volume production
Lower tooling cost compared to high-pressure processes
Full-service supply chain support: mold design, casting, machining, finishing, and assembly
How Gravity Die Casting Works?
Gravity Die Casting (GDC) is a permanent mold casting process in which molten metal is poured into a reusable steel or iron mold under the force of gravity, rather than being injected under high pressure. This controlled filling method results in dense, mechanically strong castings with low porosity — making GDC ideal for medium-to-large aluminum components that require durability and dimensional reliability. Here is a step-by-step breakdown of how Gravity Die Casting works:
Step 1: Mold Preparation and Preheating
- Clean and preheat the permanent steel or iron die to around 200–300°C.
- Preheating reduces thermal shock, prevents premature wear, and ensures smooth metal flow.
- A refractory coating is applied to improve mold release and extend mold life.
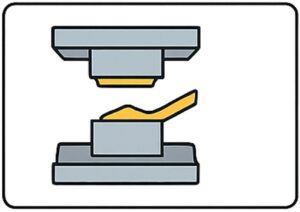
Step 3: Pouring into the Mold
- Molten metal is poured directly into the mold cavity using gravity, without external pressure.
- Controlled pouring minimizes turbulence and reduces the risk of oxide films and air entrapment.
- Runners and risers are designed to ensure complete cavity filling.
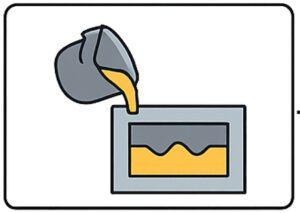
Step 5: Cooling and Solidification
- The casting is allowed to cool naturally inside the permanent mold.
- Mold material extracts heat efficiently, resulting in better dimensional accuracy than sand casting.
- Proper cooling control ensures consistent mechanical properties and minimizes defects.
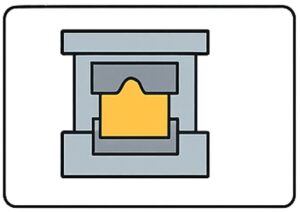
Step 7. Trimming & Flash Removal
- Runners, risers, and excess material are removed.
- Castings typically achieve near-net shape, minimizing the need for heavy machining.
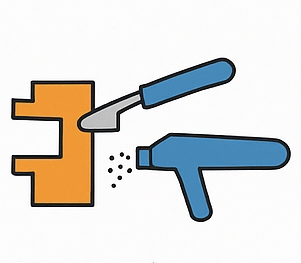
Step 2: Molten Metal Preparation
- Aluminum (or other non-ferrous alloys) is melted in a holding furnace.
- Temperature is carefully controlled to maintain fluidity while avoiding oxidation.
- Degassing and refining may be applied to reduce inclusions and hydrogen porosity.
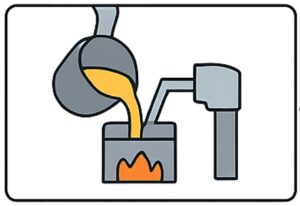
Step 4: Controlled Filling & Solidification
- The cavity fills gradually, allowing uniform distribution of molten metal.
- Slow, steady filling reduces shrinkage and internal voids.
- Faster cooling compared to sand casting leads to denser grain structure and improved strength.
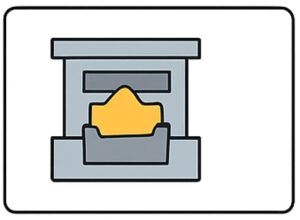
Step 6. Mold Opening & Casting Removal
- Once solidified, the mold is opened, and the casting is removed manually or with ejector pins.
- The permanent mold is then cleaned and prepared for the next cycle.
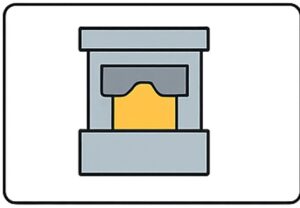
Step 8. CNC Machining, Finishing & Inspection
ritical surfaces may be CNC machined for precision.
- Surface treatments such as shot blasting, powder coating, or anodizing can be applied.
- Final inspection includes CMM measurement, X-ray, and mechanical property testing to ensure compliance with specifications.
Advantages of Gravity Die Casting
Gravity Die Casting (GDC) is ideal for producing medium-to-large structural parts with thick walls, superior material density, and excellent dimensional stability. Unlike high-pressure methods, it offers flexible low-to-medium volume production while maintaining consistent quality and reducing internal defects. Below are the key advantages for engineers, procurement teams, and quality control professionals.
| Advantage | For Engineers | For Procurement Teams | For Quality Control (QC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior Material Density | Produces thick-walled parts with high structural integrity and low porosity | Reduces rework and scrap, improving material cost efficiency | Fewer internal defects make QC more reliable and predictable |
| Low-to-Medium Volume Flexibility | Supports batch sizes from tens to thousands without compromising quality | Reduces inventory risk and allows incremental order fulfillment | Easier to plan inspection schedules for varying batch sizes |
| Excellent Dimensional Stability | Achieves tight tolerances on medium-to-large structural components | Minimizes secondary machining and related costs | Improves repeatability and measurement consistency |
| Durable Tooling & Long Mold Life | Steel molds withstand repeated cycles for consistent part quality | Reduces frequent tooling replacement and associated costs | Stable process reduces QC variability |
| Complex Medium-to-Large Parts | Enables production of intricate geometries with thicker walls | Consolidates parts from multiple suppliers, reducing supply chain complexity | Easier inspection due to lower porosity and predictable dimensions |
| Cost-Efficient for Medium Runs | Lower tooling and setup costs than HPDC for small-to-medium batches | Better cost control for pilot runs or phased production | Predictable quality reduces QC effort on trial batches |
| Controlled Metal Flow | Gravity-fed process reduces turbulence and shrinkage | Less material waste, reducing overall cost | Lower defect rate simplifies QC and inspection processes |
Disadvantages of Gravity Die Casting
Gravity Die Casting is ideal for medium-to-large, thick-walled components, but less suited for ultra-thin walls, extremely high-volume small parts, or applications requiring very fast cycles. Knowing these limitations helps plan production and quality control effectively.
| Disadvantage | For Engineers | For Procurement Teams | For Quality Control (QC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Limited Thin-Wall Capability | Not suitable for ultra-thin walls or very high-volume thin-wall parts | May require alternate suppliers for very thin-walled components | QC must verify tolerances carefully for thinner sections |
| Slower Production Compared to HPDC | Cycle times are longer due to gravity fill | Less efficient for high-volume, small parts | Extended production time may require longer QC monitoring |
| Larger Mold Size Needed | Thick-walled or large parts require bigger tooling | Higher upfront mold investment for large structural parts | Handling and measurement of larger molds/parts may require extra QC resources |
| Secondary Machining Often Required | Some holes or threads must be machined after casting | Adds additional process steps and cost | QC must verify secondary operations for consistency |
| Limited Alloy Selection | Best for aluminum, copper, and some magnesium alloys; high-melting alloys may be challenging | May require sourcing multiple material types if needed | QC standards vary by alloy type, requiring more planning |
Gravity Die Casting vs Other Die Casting Technologies

| Feature | Gravity Die Casting (GDC) | Hot Chamber Die Casting (HCDC) | Cold Chamber Die Casting (CCDC) | Sand Casting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suitable Alloys |  Most non-ferrous alloys (Al, Mg, Cu, Brass) Most non-ferrous alloys (Al, Mg, Cu, Brass) |  Low-melting alloys (Zn, Mg, Pb) Low-melting alloys (Zn, Mg, Pb) |  High-melting alloys (Al, Cu, Brass) High-melting alloys (Al, Cu, Brass) |  Most metals Most metals |
| Filling Pressure | Gravity only (0 bar) | High (up to 1000+ bar) | High (up to 1500+ bar) | Gravity only |
| Porosity |  Moderate (lower than sand) Moderate (lower than sand) |  Moderate Moderate |  Moderate Moderate |  High High |
| Heat Treatment |  Yes (T5/T6 common for Al alloys) Yes (T5/T6 common for Al alloys) |  Often not applicable Often not applicable |  T5/T6 Possible T5/T6 Possible |  Yes Yes |
| Surface Finish |    (Ra 3.2–6.3 μm) (Ra 3.2–6.3 μm) |     (Ra 1.6–3.2 μm) (Ra 1.6–3.2 μm) |     |  |
| Dimensional Accuracy |    (±0.2–0.5 mm) (±0.2–0.5 mm) |     (±0.05–0.1 mm) (±0.05–0.1 mm) |     (±0.1 mm) (±0.1 mm) |  |
| Part Size Capability | Medium to Large | Small to Medium | Medium to Large | Large |
| Ideal for | Medium-volume structural parts, wheels, brackets, manifolds | Small, intricate, high-volume parts | Structural housings, engine components | Large, simple prototypes or low-volume production |
Gravity Die Casting Part Applications Across Industries
Gravity Die Casting (GDC) is primarily used for medium-to-large structural components with thick walls, high material density, and superior dimensional stability. Its ability to produce dense, durable parts with minimal internal defects makes it ideal for industries that require reliable performance, cost-effective low-to-medium volume production, and complex geometries.
| Industry | Typical Components | Why Gravity Die Casting Fits |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive & E-Mobility | Engine brackets, transmission housings, suspension components, structural chassis parts | Ideal for medium-to-large components requiring high strength, thick walls, and durable performance under load |
| Industrial Machinery | Gear housings, pump bodies, motor casings, valve bodies | Supports thick-wall parts with excellent material density and dimensional stability for heavy-duty applications |
| Energy & Electrical Equipment | Transformer housings, heat sink structures, battery enclosures | Provides high thermal conductivity and mechanical strength for durable, load-bearing parts |
| Aerospace & Transportation | Seat frames, structural panels, landing gear components | Enables production of lightweight yet strong components with consistent quality and tight tolerances |
| Home Appliances & Consumer Goods | Appliance frames, structural supports, motor housings | Suitable for medium-to-large components where strength and durability are more critical than ultra-thin walls |
| Marine & Fluid Systems | Pump housings, valve bodies, fittings, heat exchangers | High corrosion resistance and dense casting structure ensure long-term reliability in harsh environments |
| Medical & Laboratory Equipment | Equipment frames, housings, instrument bases | Delivers thick-wall components with high dimensional stability and long-lasting mechanical integrity |
| Lighting & Electrical Fixtures | Fixture bodies, lamp housings, structural supports | Excellent surface finish and dimensional repeatability for medium-to-large structural components |
| Industrial Automation & Robotics | Motor mounts, gearbox housings, mounting brackets | Supports robust, high-strength parts for machinery with complex geometries |
Gravity Die Casting (GDC) Common Technical Specifications
Gravity Die Casting (GDC) is engineered to produce medium-to-large structural components with superior mechanical strength and dimensional stability. Unlike high-pressure methods, GDC uses gravity-fed metal flow to achieve uniform material distribution, resulting in dense, high-quality castings with minimal internal voids.
Mold Materials and Life: Durable steel molds are used to ensure long tool life and consistent casting accuracy over multiple production cycles. Mold maintenance and preheating protocols are essential for preserving surface finish and reducing thermal stress.
Part Size and Geometry: GDC accommodates complex geometries and thick-wall designs, making it ideal for housings, brackets, and structural components. Large sections can be cast without the risk of excessive shrinkage or porosity.
Alloy Compatibility: GDC is suitable for aluminum, copper, and selected magnesium alloys. These alloys provide excellent corrosion resistance, thermal performance, and load-bearing strength, making them reliable for critical applications.
Surface Quality: Gravity Die Cast parts exhibit smooth surfaces suitable for direct machining or finishing. Secondary operations such as CNC machining, anodizing, or plating can further enhance functional and aesthetic properties.
Production Flexibility: GDC supports low-to-medium volume production efficiently, allowing for prototyping, pilot runs, and phased manufacturing while maintaining consistent quality and reducing overall production costs.
Dimensional Tolerance: Typical tolerances range from ±0.05 mm to ±0.2 mm, depending on part size, alloy, and mold design. Critical features can be refined with secondary machining for precision applications.
Key Takeaway: Gravity Die Casting is a cost-effective, reliable solution for producing thick-wall, durable, and structurally critical components, combining material integrity, consistent performance, and design flexibility.
Gravity Die Casting (GDC) Common Challenges and Solutions
Gravity Die Casting (GDC) uses controlled gravity-fed metal flow to produce dense, high-quality castings, offering predictable material properties and minimized internal defects for medium-to-large structural components. While GDC is reliable and versatile, several challenges can arise during design, production, and quality inspection.
Limited Thin-Wall Capability: Ultra-thin sections may not fill completely or could develop porosity. Engineers can reinforce these areas with ribs or thicker sections, procurement should choose suppliers experienced with minimum wall thickness, and QC should monitor for internal defects.
Longer Cycle Times: Gravity-fed casting naturally takes longer than high-pressure methods, especially for larger parts. Optimizing mold design, preheating molds, and sequencing production can help, while procurement aligns schedules and inventory, and QC tracks dimensional consistency across cycles.
Large Mold and Part Handling: Handling medium-to-large molds can be challenging due to weight and thermal stress. Proper mold support, careful handling, and temperature management prevent warping, and QC tools like CMM inspections ensure dimensional accuracy.
Secondary Machining Requirements: Features such as threaded holes or precision surfaces often require post-casting operations. Designing with secondary machining in mind, coordinating production planning, and verifying tolerances after machining ensures finished parts meet specifications.
Alloy Selection Limitations: GDC works best with aluminum, copper, and selected magnesium alloys, which may restrict some designs. Engineers should choose alloys suited for geometry and load requirements, procurement ensures consistent material supply, and QC tests mechanical and thermal properties.
Shrinkage and Porosity in Thick Sections: Improper gating, risers, or cooling channels can lead to defects. Simulation tools help optimize flow, procurement selects suppliers using advanced casting simulations, and QC performs X-ray or ultrasonic inspections to detect internal porosity.
Long Lead Times for Large Parts: Large components require extended cooling and handling times, which can slow production. Planning production schedules, inventory management, and careful QC monitoring help ensure timely delivery without compromising quality.
By understanding and addressing these challenges, Gravity Die Casting delivers structurally sound, high-integrity components with reliable performance, predictable material properties, and cost-effective production.
Get in touch with us
Contact our experts and we will provide you quotation, DFM, Moldflow for your Gravity Die Casting Part.
- yoyo@iec-mould.com
- 86 13712993487
- 86 13712993487

*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.