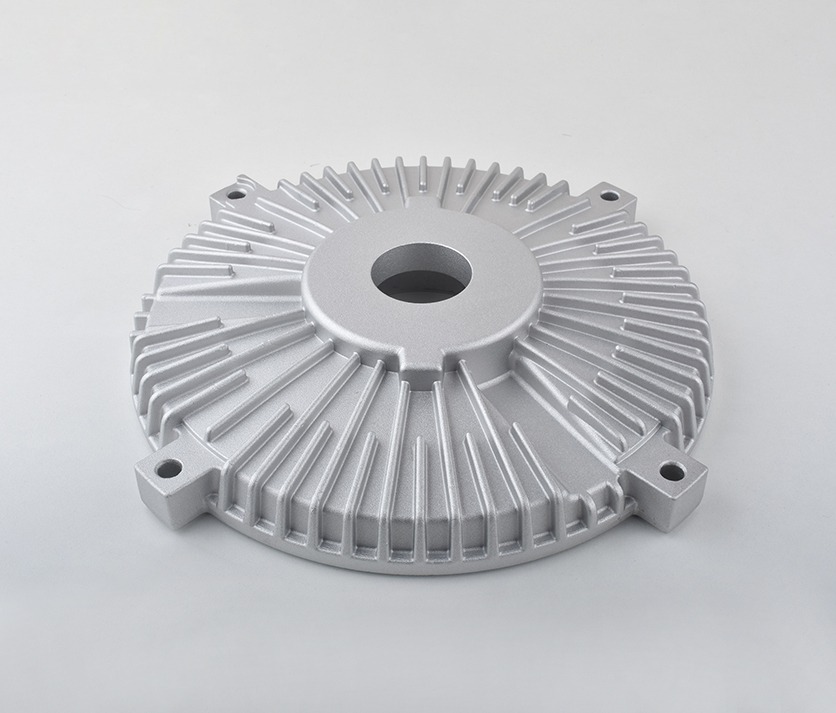
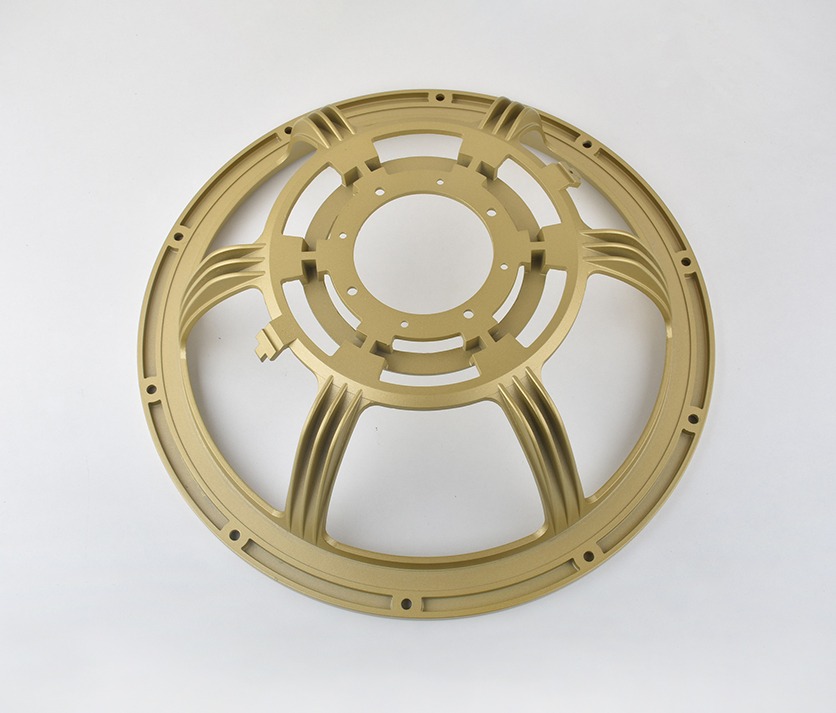
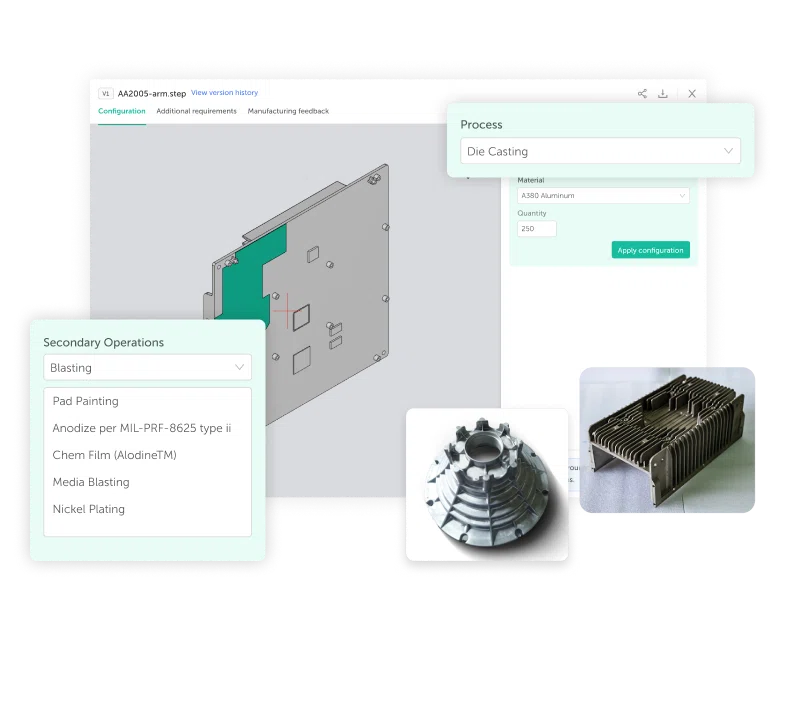
Aluminum Die Casting Services
Looking for reliable Aluminum Die Casting solutions or want to know more about Aluminum Die Casting costs? As a professional Aluminum Die Casting supplier and experienced Aluminum Die Casting manufacturer, IEC MOULD provides high-quality die casting technology and cost-competitive manufacturing services tailored to your needs. Whether you require precision components or large structural castings, we have the expertise and production capacity to fully support your projects — contact us today!
±0.01mm
Tolearance
20+
Years Experience
20 Day
Die Casting Samples Delivered
Certifications
ISO 9001 & IATF 16949
China Aluminum Die Casting Manufacturer and Supplier
IEC MOULD is a professional Aluminum Die Casting manufacturer and supplier, offering engineering-driven solutions for lightweight and high-performance metal parts. With our in-house mold workshop, aluminum die casting lines, CNC machining center, and surface finishing capabilities, we provide full-process manufacturing from design to finished assemblies.
Our aluminum casting expertise covers automotive, new energy, robotics automation, medical devices, communication equipment, and consumer electronics, delivering reliable, durable, and tight-tolerance aluminum components. Supported by ISO 9001 & IATF 16949 certifications, advanced testing equipment, and strict quality control, IEC MOULD ensures stable production quality, cost efficiency, and fast delivery for global customers.
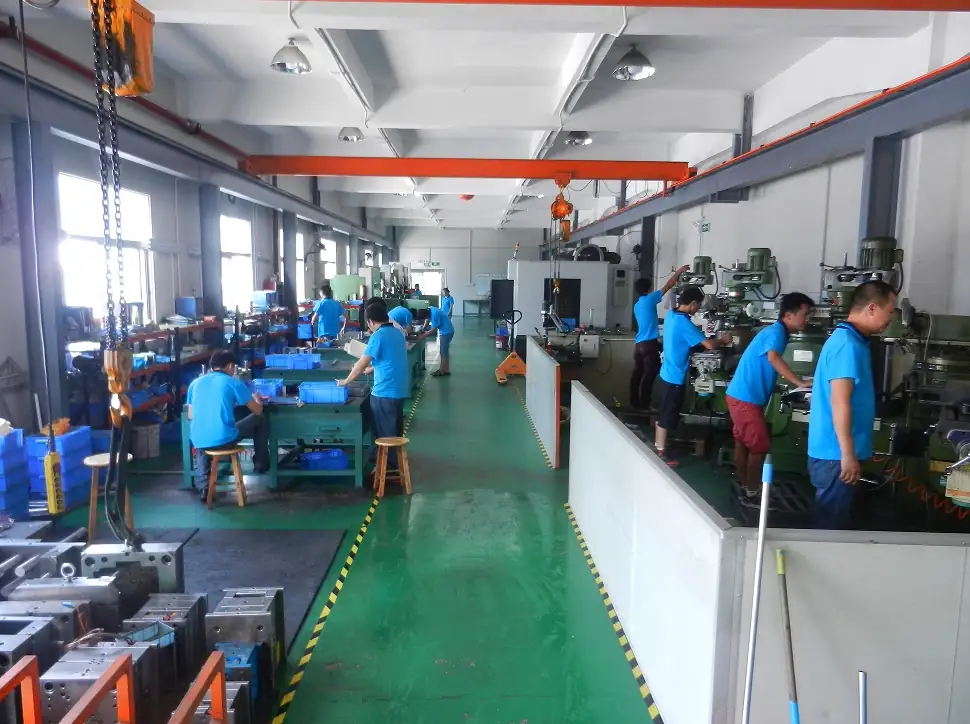
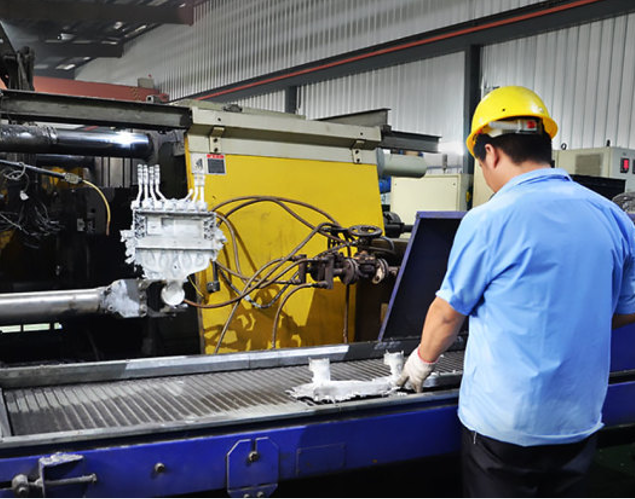
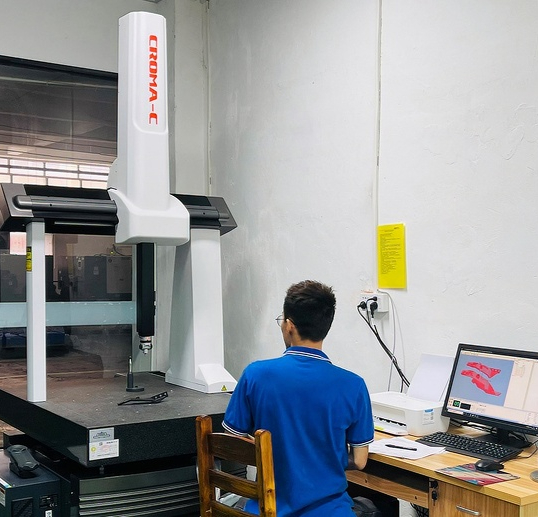





Our Aluminum Die Casting Services
We deliver complete aluminum die casting solutions designed to support projects from concept validation to mass production:
- Custom Aluminum Casting – Specialized in lightweight, high-strength aluminum components with complex geometries and thin-wall structures
- Engineering & Simulation – DFM, fill & cooling analysis, and structural review to ensure stable casting flow and reduce porosity
- Tooling Development – Precision aluminum die design and in-house mold manufacturing for consistent production performance
- High-Accuracy Machining – CNC milling, drilling, tapping, and multi-axis machining to achieve tight tolerances and fine surface finish
- Advanced Surface Finishing – Anodizing, bead-blasting, powder coating, chromate treatment, painting, and custom cosmetic finishes
- Component Integration – Insert installation, sealing features, thread inserts, and part assembly for ready-to-install components
- Comprehensive Quality Control – CMM measurement, X-ray inspection, leak testing, material analysis, and dimensional reporting
With IEC MOULD, you don’t need multiple suppliers. We design, cast, machine, finish, and assemble – all under one roof.
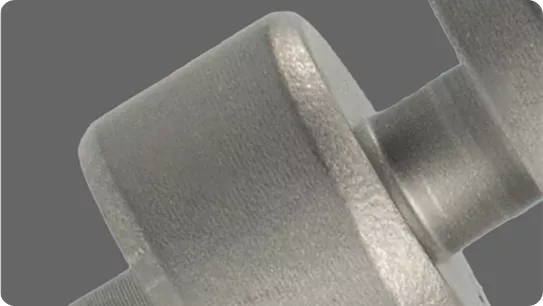



IEC Mould's Aluminum Die Casting Capabilities
| Details | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy for Aluminum Components | Aluminum die cast parts can typically achieve ±0.02mm, and up to ±0.01mm with CNC finishing, meeting precision assembly and sealing requirements. |
| Minimum Aluminum Wall Thickness | Standard thin-wall aluminum structures range 1.5–2.0mm; optimized thin-wall zones can achieve ~1.2mm with proper flow design. |
| Uniform Wall Structure Requirement | To avoid shrinkage and cold shuts, aluminum die castings are recommended to maintain a 1:2 to 1:3 wall thickness ratio between sections. |
| Internal Holes & Boss Features | Holes smaller than 3mm, threaded bosses, and fine threads are machined post-casting for accuracy and thread integrity. |
| Draft Angle for Aluminum Ejection | Typical aluminum draft angle: 1°–2° (can be reduced for cosmetic surfaces or increased for deep cavities). |
| Mold Durability for Aluminum Alloy | Aluminum die casting molds generally achieve 80,000–120,000 cycles, depending on steel grade, heat treatment, and maintenance. |
| Minimum Production Volume | Flexible order support starting from 100 pcs, suitable for prototypes, bridge production, and mass manufacturing. |
| Production Schedule / Lead Time | Mold manufacturing & first article delivery: 20–30 days based on part complexity, machining, and finishing needs. |
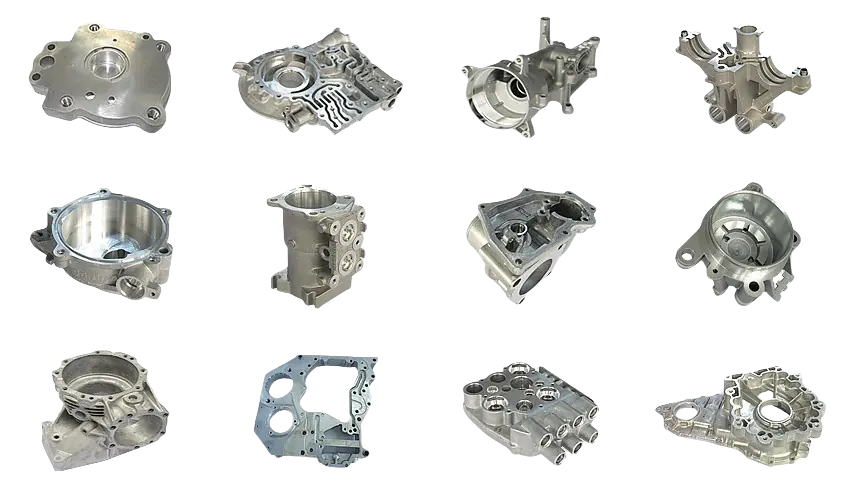
Aluminum Die Casting Parts We Manufactured
Whether you’re developing thin-wall housings or load-bearing structural components, our Aluminum Die Casting design expertise ensures optimal part performance, manufacturability, and cost efficiency from the very beginning.
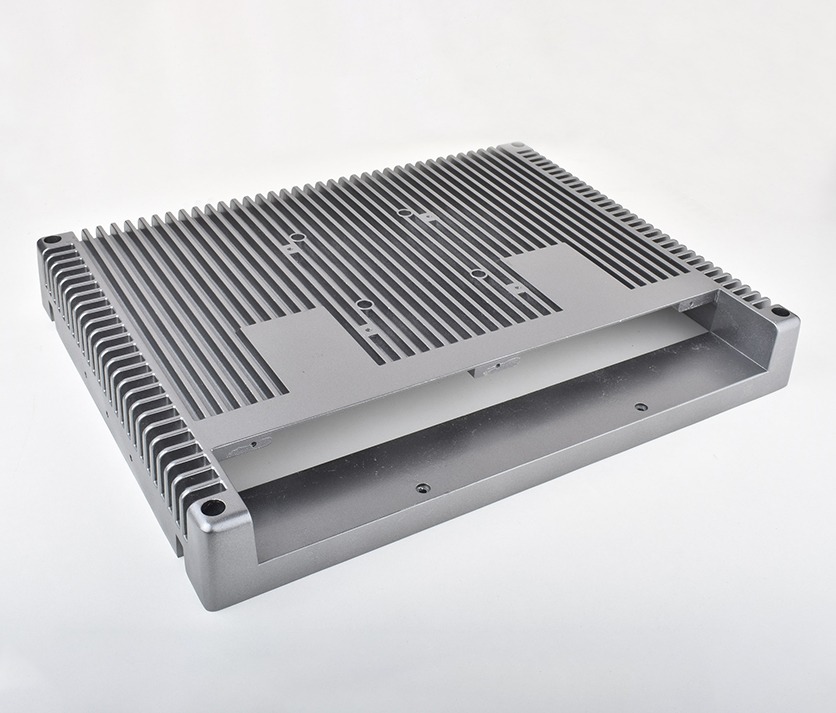

Electronics Part

Automotive Part
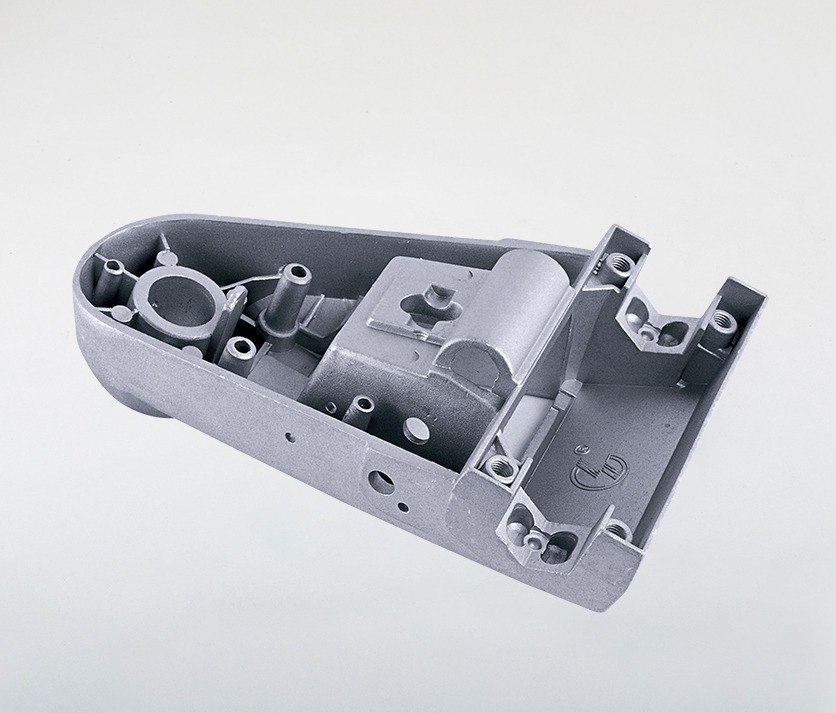
Home Appliances Part

Industrial Machinery Part
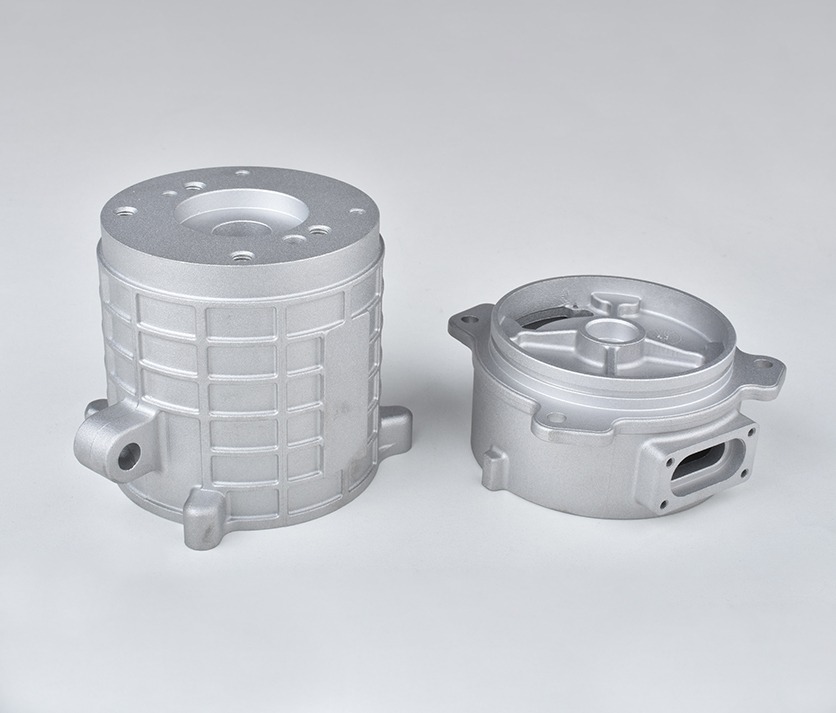

Medical Devices Part
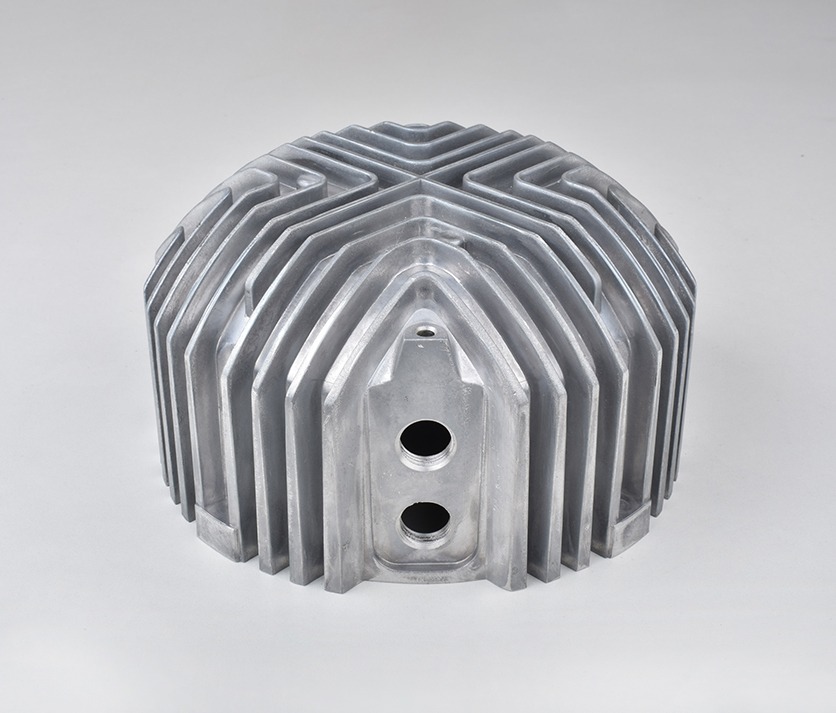

Engineering Part
Aluminum Die Casting Alloys and materials we used
Our engineering team selects the most suitable alloy based on mechanical strength, thermal performance, surface requirements, and cost efficiency:
| Alloy Grade | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications | Why It Excels in Aluminum Die Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADC12 / A380 (Most common Aluminum Die Casting alloy) | Excellent fluidity, high strength, good thermal conductivity, strong corrosion resistance, stable mechanical properties | Motor housings, automotive brackets, gearbox covers, electronic enclosures, lighting housings | Ideal for thin-wall complex structures, reliable strength, excellent cost-to-performance balance |
| A383 / ADC10 | Better corrosion resistance and flow filling than ADC12, suitable for intricate mold designs | Heat sinks, communication housings, automotive interior structures, precision casings | Enhanced fluidity for complex geometries and fine cosmetic surfaces |
| A360 / ADC3 | High ductility, excellent pressure tightness and corrosion resistance, good impact resistance | EV battery housings, pump bodies, structural brackets, sealing parts | Suitable for parts requiring higher toughness and air-tightness |
| A356 / AlSi7Mg (for heat-treatable high-strength parts) | High tensile strength after T6 treatment, good fatigue resistance, excellent casting performance | Suspension housings, aerospace components, medical structures, industrial robotics | Higher structural strength for load-bearing or safety-critical parts |
| AlSi10Mg (Additive + Casting grade for lightweight, high-strength parts) | Excellent fatigue strength, dimensional stability, low density, heat-treatable | EV battery trays, aerospace housings, high-precision mechanical parts | Ideal for lightweight and high-strength parts requiring stability and rigidity |
Why Choose IEC MOULD for Your Aluminum Die Casting Parts?
Choosing the right aluminum die casting supplier is critical to your aluminum product performance, manufacturing cost, and time-to-market. At IEC MOULD, we focus not only on producing high-quality aluminum die cast parts, but also on delivering real business value for our customers.
Faster Time-to-Market: quicker development → faster launch → faster revenue.
Stable Quality, No Surprises: consistent quality → fewer issues → reliable production flow.
Cost-Efficient Manufacturing: lower unit cost → stronger price competitiveness → better margins.
Lightweight & High-Strength Design Expertise: lighter, stronger products → improved performance → long-term value.
Precision for Complex & Tight-Tolerance Parts: accuracy fit-up → assembly-ready parts → reduced rework.
One Supplier, Full Accountability: simplified supply chain → less risk → seamless communication.
Fast Engineering Feedback: fast decision-making → quick problem-solving → stress-free execution.
Flexible Production Volumes: low entry barrier → scalable supply → ideal for new product launches.

Aluminum Die Casting Frequently Questions & Answers
What wall thickness is achievable in aluminum die casting?
Typical walls are 1.5–4.5 mm, but advanced process control allows as thin as 0.8 mm in specific cases.
What tolerance levels can be achieved?
With optimized tooling, aluminum die casting can achieve ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm tolerances.
How long does it take to make alumium die casting tool?
Tooling lead time is typically 4–8 weeks, depending on complexity.
How does aluminum die casting compare with machining costs?
Die casting drastically reduces material waste and machining time, making it more economical for large production runs.
What factors influence die casting cost the most?
Tooling complexity, part size, alloy choice, finishing requirements, and order quantity are key cost drivers.
What testing methods are used to ensure aluminum die casting part quality?
Common methods include X-ray inspection, CMM measurement, tensile testing, hardness testing, and leak testing.
Can aluminum die castings be welded or heat-treated?
Most alloys can be machined, welded, and heat-treated, but properties vary by alloy selection.
Other Die Casting Metals Services You May Looking for
What is Aluminum Die Casting?
Aluminum die casting is a manufacturing process that shapes molten aluminum into precise metal parts using high pressure. In simple terms, it’s like injecting liquid metal into a perfectly designed mold—once it cools and solidifies, you get a strong, accurate, and ready-to-use component.
But aluminum die casting is more than just “making parts.” It’s a process that blends engineering, creativity, and experience. The real challenge lies not only in injecting metal, but in controlling every detail: the mold temperature, the pressure curve, the cooling rate, and even the smallest feature in the cavity. When everything works in harmony, the result is a part that’s light, durable, and dimensionally stable.
That’s why aluminum die casting is the preferred choice for industries that demand performance and precision—like automotive, electronics, and industrial equipment. It allows engineers to design parts that are both lightweight and strong, complex yet consistent, and cost-effective at scale.
At IEC MOULD, we see aluminum die casting as more than a process — it’s a partnership of design and manufacturing. Every project starts with understanding what our customer truly needs: strength or lightness? aesthetics or tolerance? Then we turn those requirements into reality through careful engineering and decades of die casting experience. In short, aluminum die casting is not just about producing parts — it’s about turning ideas into durable, functional, and scalable solutions that support real-world innovation.
Why Choose Aluminum Die Casting?
Aluminum is one of the most versatile and widely used die casting metals. Its unique combination of strength, lightness, and recyclability makes it the material of choice across multiple industries.
Key Benefits of Aluminum Die Casting:
- Weight Reduction: Up to 33% lighter than zinc and 75% lighter than steel.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Suitable for structural and safety-critical applications.
- Corrosion & Weather Resistance: Excellent for outdoor and marine applications.
- Thermal & Electrical Conductivity: Used extensively in electronics and EV battery housings.
- Recyclability: 100% recyclable with minimal property degradation.


How Aluminum Die Casting Works?
As a leading aluminum die casting manufacturer, IEC Mould understand the importance of precision, alloy selection, and process control in delivering high-quality cast components. Whether you need lightweight structures, excellent heat dissipation, or durable and corrosion-resistant parts, a well-defined die casting process is the key to success.
Below, we outline the typical five-step aluminum die casting workflow followed by every reliable foundry. This streamlined approach ensures optimal filling, consistent part performance, and cost-effective scalability across automotive, aerospace, electronics, and industrial applications.
Step 1: Alloy Melting & Preparation
The process begins with melting aluminum ingots or recycled aluminum scrap in a controlled furnace. At this stage, alloying elements such as magnesium, copper, or silicon may be added to enhance strength, corrosion resistance, or thermal conductivity.
- Engineer’s view: Alloy consistency ensures predictable mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy.
- Procurement’s view: Efficient use of recycled aluminum lowers material costs while maintaining sustainability.
- Quality control’s view: Impurity removal and proper temperature monitoring prevent porosity, cracks, and weak points in the final casting.
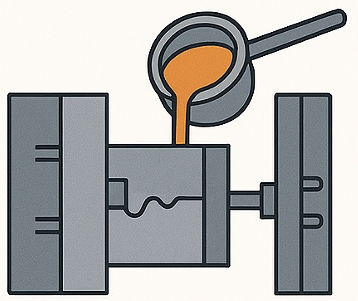
Step 3: High-Pressure Injection Casting
Once prepared, molten aluminum is injected into the die cavity under high pressure (up to 100–150 MPa). This rapid injection ensures complete cavity filling, even for intricate designs and thin walls.
- Engineer’s view: High pressure delivers superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent repeatability across large production volumes.
- Procurement’s view: Short cycle times (often 30–60 seconds) improve productivity and reduce per-unit cost.
- Quality control’s view: Consistent pressure control reduces porosity, ensuring reliability in safety-critical applications such as automotive or aerospace.
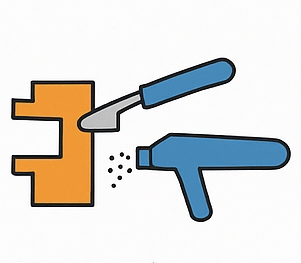
Step 5: Trimming & Surface Finishing
Once the aluminum part is ejected, excess material such as flash, runners, and gates is carefully trimmed. Depending on functional or aesthetic requirements, the components can undergo a variety of surface finishing processes, including:
- CNC machining for tight tolerances
- Shot blasting or tumbling for smoother surfaces
- Anodizing for corrosion resistance
- Powder coating or painting for durability and appearance
- Assembly of multiple die cast components into complete units
- Engineer’s view: Post-processing ensures precise tolerances and enables customized surface finishes for performance and design needs.
- Procurement’s view: Having trimming and finishing in-house shortens lead times and avoids outsourcing costs.
- Quality control’s view: Controlled finishing processes minimize variability and ensure consistent surface quality.
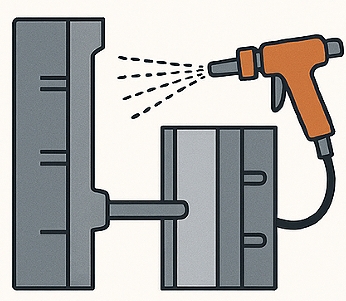
Step 2: Die & Mold Preparation
Before casting, the steel die (mold) is preheated and coated with a release agent. Preheating prevents thermal shock, while coatings extend mold life and improve surface finish.
- Engineer’s view: Proper mold design with cooling channels supports thin walls, complex geometries, and tight tolerances.
- Procurement’s view: A well-maintained die reduces downtime and ensures longer tooling life, optimizing total cost of ownership.
- Quality control’s view: Correct mold preparation minimizes surface defects such as blistering, cold shuts, or flow marks.
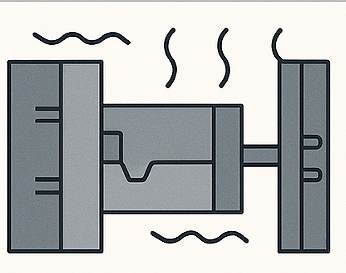
Step 4: Cooling & Solidification
The molten aluminum solidifies quickly inside the die, supported by integrated cooling channels to control shrinkage and dimensional stability. Once solidified, the die opens and ejector pins release the finished part.
- Engineer’s view: Controlled cooling helps achieve dimensional accuracy and predictable mechanical performance.
- Procurement’s view: Optimized cooling reduces cycle time, supporting mass production without sacrificing quality.
- Quality control’s view: Monitoring solidification prevents internal stresses, cracks, or uneven grain structures.
Step 6: Quality Inspection & Testing
Every batch of aluminum die cast parts undergoes strict quality control measures to guarantee compliance with customer and industry standards. Typical testing methods include:
- X-ray inspection for internal porosity or defects
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) for dimensional accuracy
- Leak testing for sealing and pressure integrity
- Mechanical property testing for tensile strength, hardness, and elongation
- Engineer’s view: Testing ensures structural integrity and reliability, especially for safety-critical parts in automotive and aerospace industries.
- Procurement’s view: Verified quality reduces risk of rework, warranty claims, and supply chain disruptions.
- Quality control’s view: Meeting ISO, IATF 16949, or aerospace standards reinforces compliance and customer trust.
Advantages of Aluminum Die Casting
Aluminum Die Casting (ADC) is widely recognized for its ability to produce complex, high-strength, and lightweight parts at scale. It offers exceptional dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and mechanical properties — making it the preferred choice for industries like automotive, electronics, and industrial equipment.
Below are the key advantages of Aluminum Die Casting.
| Advantage | For Engineers | For Procurement Teams | For Quality Control (QC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lightweight with High Strength | Enables lightweight design without compromising mechanical performance | Reduces material costs and improves energy efficiency in final products | Easier to maintain strength consistency across batches |
| Excellent Dimensional Accuracy | Achieves tight tolerances and complex shapes directly from molds | Reduces need for post-machining and lowers total production cost | Stable dimensions simplify measurement and inspection |
| Superior Thermal & Corrosion Resistance | Ideal for heat dissipation and harsh environments | Increases product lifespan, reducing warranty risks | Consistent resistance ensures predictable long-term performance |
| High Production Efficiency | Fast cycle times and automated casting lines support large-scale production | Ensures cost-effective manufacturing for medium-to-high volumes | Consistent process control enhances batch-to-batch reliability |
| Design Flexibility | Supports complex geometries and thin-wall structures | Enables part integration, reducing multi-supplier management | Fewer part variations simplify QC documentation and traceability |
| Excellent Surface Finish | Produces smooth surfaces suitable for anodizing, painting, or plating | Reduces finishing costs and shortens delivery cycles | Easier to inspect and meet cosmetic quality standards |
| Strong Recyclability | Aluminum can be reused without quality loss | Supports sustainable sourcing and lower environmental footprint | Stable alloy quality ensures repeatable QC standards |
| Long Mold Life with Precision Tooling | Durable molds maintain high accuracy over many cycles | Lowers tooling cost per part and improves ROI | Stable tooling condition supports consistent part verification |
Disadvantages of Aluminum Die Casting
Aluminum die casting is excellent for high-precision, lightweight, and complex parts, but it has some limitations, IEC Mould will consider thin-wall limits, tooling cost, alloy choices, and secondary machining when planning production. Understanding these helps plan design, production, and quality control effectively.
| Disadvantage | For Engineers | For Procurement / QC Teams |
|---|---|---|
| Thin-Wall Limitations | Extremely thin sections (<1mm) are challenging and may risk porosity | May need alternative processes or additional supplier support |
| High Tooling Cost for Small Batches | Tooling investment is significant for prototypes or very small runs | Higher upfront cost per part for low-volume production |
| Limited Alloy Selection for Specialized Requirements | High-strength or exotic alloys may be less suitable for standard die casting | Procurement may need to source multiple suppliers for niche materials |
| Secondary Machining Often Required | Fine threads, precise holes, or post-casting tolerances need machining | Adds cost and time for finishing operations |
| Not Ideal for Extremely High Cycle Speed | Very rapid production may be limited by casting and ejection times | May be less competitive than HPDC for massive small parts |
Aluminum vs. Other Die Casting Metals
Aluminum die casting allows you to create durable, high-precision components that meet demanding design and performance requirements. From intricate housings to structural parts, it enables efficient production at scale without compromising quality.
Partner with IEC MOULD to turn your ideas into reliable, ready-to-use aluminum parts for automotive, aerospace, electronics, and industrial applications.
| Property | Aluminum (Al) | Zinc (Zn) | Magnesium (Mg) | Brass / Copper Alloys (Cu-Zn) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Light – ideal for reducing component weight | Moderate – heavier than Al, good “solid feel” | Very light – suitable for ultra-light components | Heavy – adds strength, not suitable for weight-sensitive applications |
| Strength | High – excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Moderate to high (Zamak & ZA alloys) | Moderate – lower than Al | Very high – suitable for load-bearing and wear-resistant parts |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent – naturally forms protective oxide layer; anodizable | Good – usually requires plating or finishing | Good – moderate resistance | Excellent – resistant to corrosion and wear |
| Cost Efficiency | High – cost-effective for medium to high-volume production | High – efficient for small, precise parts | Moderate – less cost-efficient for large-scale production | Higher – more expensive material and tooling |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, aerospace components, electronics housings, industrial equipment | Small precision gears, hardware, connectors, decorative parts | Portable devices, lightweight enclosures | Valves, fittings, plumbing components, marine hardware |
Aluminum Die Casting Part Applications Across Industries
Aluminum die casting is widely used in industries that require efficient manufacturing of functional parts with consistent performance and long service life. It enables production of components that meet thermal, corrosion, and structural demands, while allowing for intricate designs, reduced weight, and scalable volume production.
| Industry | Typical Components | Why Aluminum Die Casting Fits |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive & E-Mobility | Engine housings, transmission brackets, battery supports, structural frames | Supports lightweight structural parts that maintain performance under load and reduce overall vehicle weight |
| Industrial Machinery | Gear housings, pump casings, motor bodies, valve housings | Handles thick and complex parts with consistent mechanical properties for heavy-duty machinery |
| Energy & Electrical Equipment | Transformer cases, heat sinks, electronic enclosures | Provides high thermal conductivity and reliable electrical insulation for critical components |
| Aerospace & Transportation | Seat frames, structural panels, UAV parts | Produces parts that balance reduced weight with mechanical stability and long-term reliability |
| Home Appliances & Consumer Goods | Appliance frames, motor housings, supports | Enables aesthetically clean, robust components that fit together accurately and reduce assembly complexity |
| Marine & Fluid Systems | Pump housings, valve bodies, fittings | Corrosion-resistant and dimensionally stable, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments |
| Medical & Laboratory Equipment | Equipment frames, housings, instrument bases | Meets strict standards for structural integrity and dimensional consistency in precision equipment |
| Lighting & Electrical Fixtures | Fixture bodies, lamp housings, supports | Provides parts with smooth surfaces and precise dimensions suitable for functional and decorative applications |
| Industrial Automation & Robotics | Motor mounts, gearbox housings, brackets | Supports durable, accurately aligned components for machinery with complex geometries and continuous operation |
Ready to Start Your Aluminum Die Casting Project?
- yoyo@iec-mould.com
- 86 13712993487
- 86 13712993487

*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.