Brass Die Casting Explained: How to Manufacture High-Precision Brass Parts
Brass pressure die casting is an efficient manufacturing process for producing high-precision brass parts with complex shapes and tight tolerances.
What Is Brass Die Casting?
Die casting brass is a metal forming process in which molten brass alloy is injected into a steel mold under high pressure. The mold, also known as a die, is designed to produce precise shapes with minimal variation between parts.
Once the molten metal cools and solidifies, the die opens and the finished brass component is ejected. This process allows manufacturers to produce detailed and dimensionally accurate parts at high production speeds. Compared with other methods, the die casting process offers excellent repeatability and efficiency.
Die Cast Brass is widely used in industrial manufacturing and is recognized for its efficiency and precision, as explained by the American Foundry Society.
How the Brass Die Casting Process Works
The die casting process typically includes the following steps:
Mold preparation
The steel die is cleaned and lubricated to ensure smooth metal flow and easy part release.
Melting the brass alloy
Brass alloys are heated to a controlled temperature suitable for die casting.
High-pressure injection
Molten brass is injected into the die cavity at high pressure, filling even the smallest details.
Cooling and solidification
The brass rapidly cools and solidifies inside the die.
Ejection and finishing
The finished part is ejected, followed by trimming or light machining if required.
This controlled process ensures that Die Cast Brass produces consistent, high-precision brass parts.

In modern industrial manufacturing, achieving consistent quality depends not only on equipment but also on process control, tooling accuracy, and inspection standards. Factors such as mold design, material flow behavior, and dimensional verification play a critical role in ensuring reliable production results and long-term product performance.
In addition to process efficiency, factors such as tooling lifespan, production consistency, and inspection standards also play an important role in ensuring reliable manufacturing outcomes for industrial metal components.
Advantages of Brass Die Casting
This method offers offers several important benefits:
Die Cast Brass enables the production of parts with excellent dimensional accuracy, reducing the need for secondary machining.
High Precision and Tight Tolerances
Precision brass production enables the production of parts with excellent dimensional accuracy, reducing the need for secondary machining.
Superior Surface Finish
Parts made through brass die casting typically have smooth surfaces, which improves appearance and functional performance.
High Production Efficiency
Because the molds are reusable, precision brass production is ideal for medium to high-volume production.
Excellent Material Properties
Brass alloys provide good strength, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity, making brass die casting suitable for demanding applications.
Applications of Brass Die Casting
Brass die casting is widely used in many industries that require durable and precise components, including:
Automotive industry: fittings, connectors, sensor housings
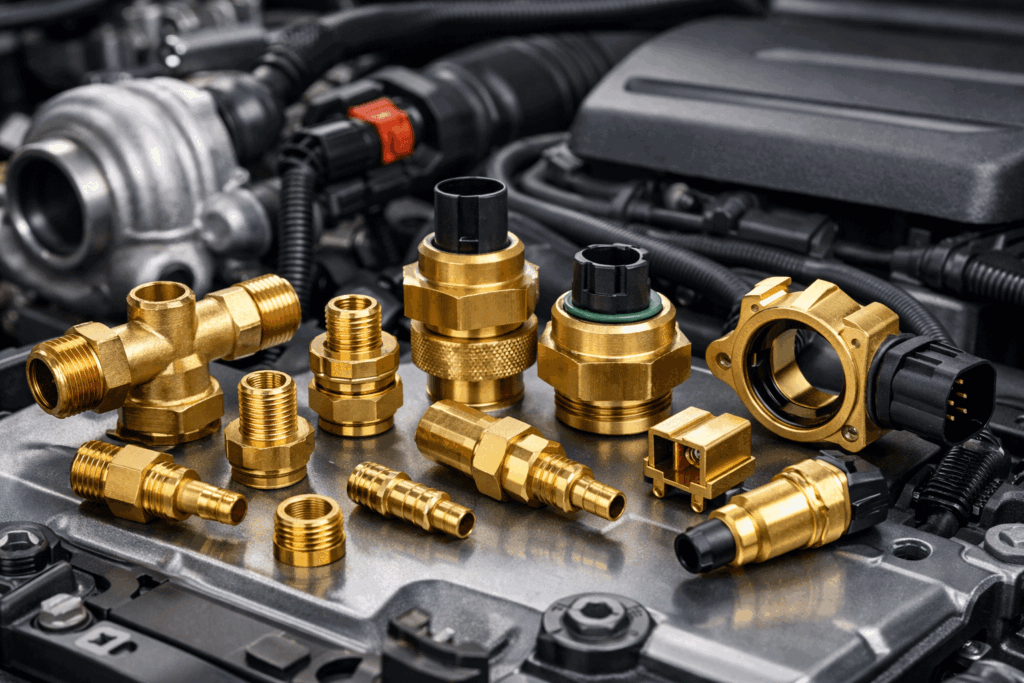
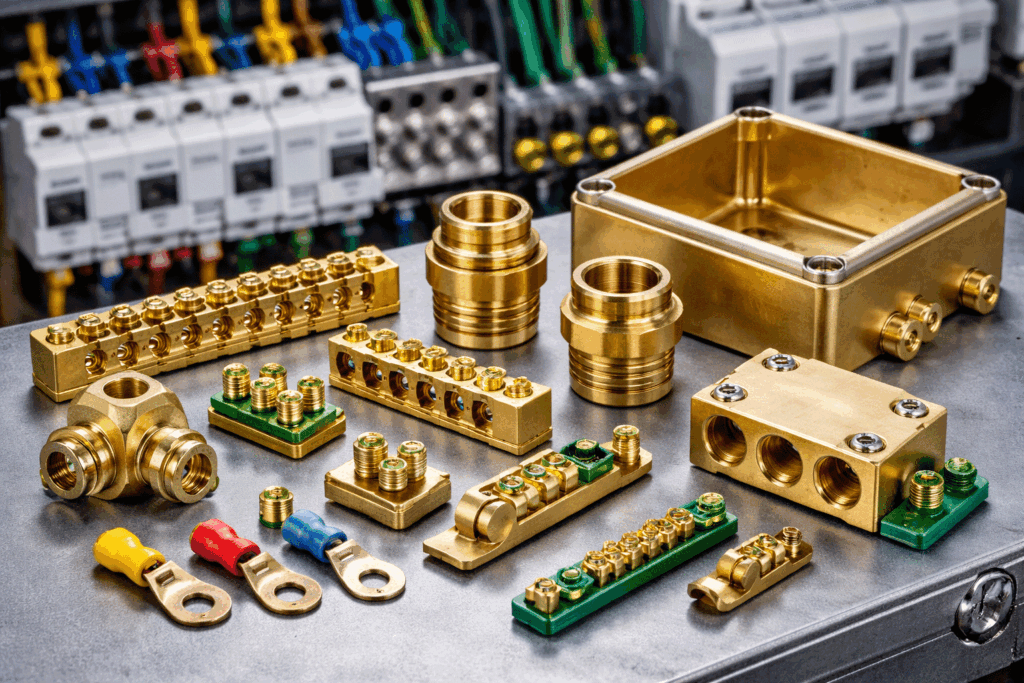
Electrical and electronics: terminals, grounding components, enclosures
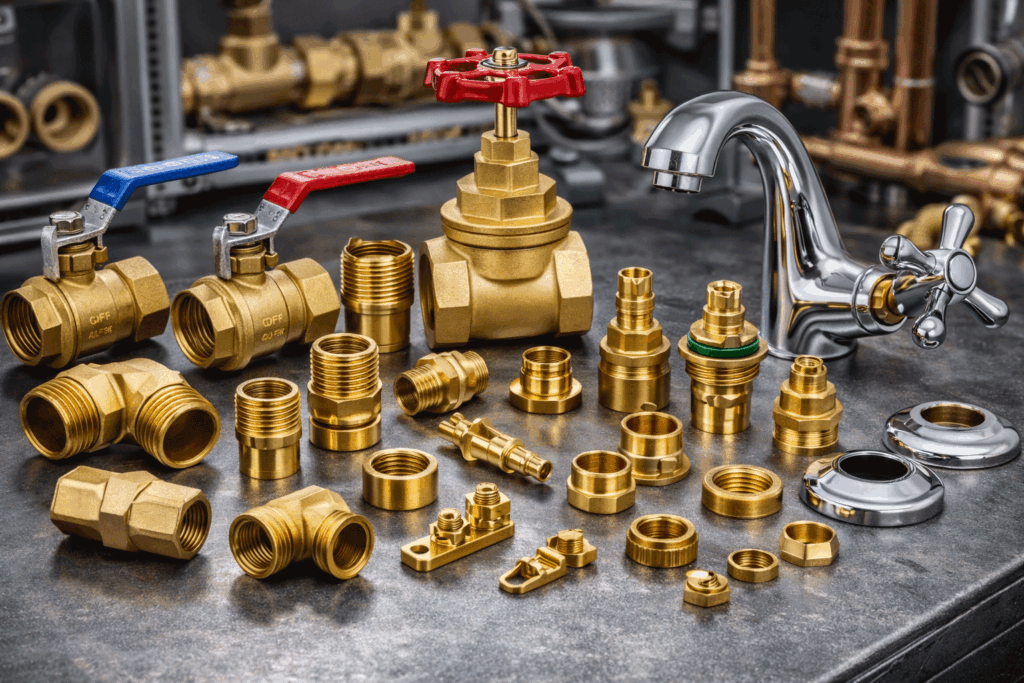
Plumbing systems: valves, pipe fittings, faucet components
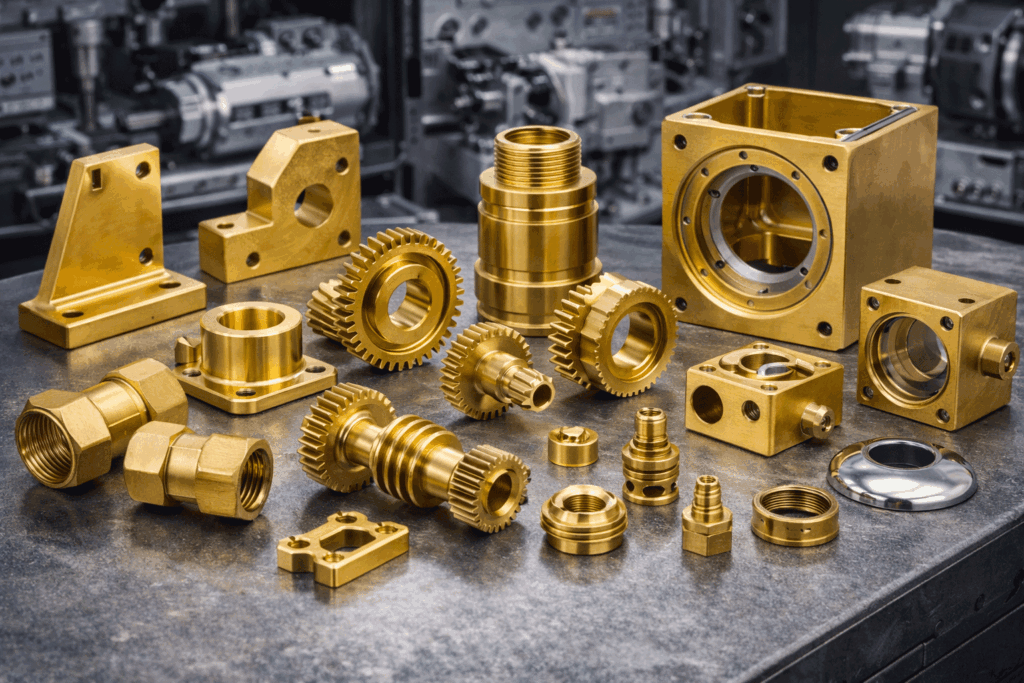
Industrial equipment: gears, brackets, precision housings
In applications where accuracy, durability, and corrosion resistance are critical, brass die casting is often the optimal manufacturing choice.
Brass Die Casting vs Other Manufacturing Methods
When compared with CNC machining or sand casting, brass die casting offers distinct advantages:
Compared to CNC machining
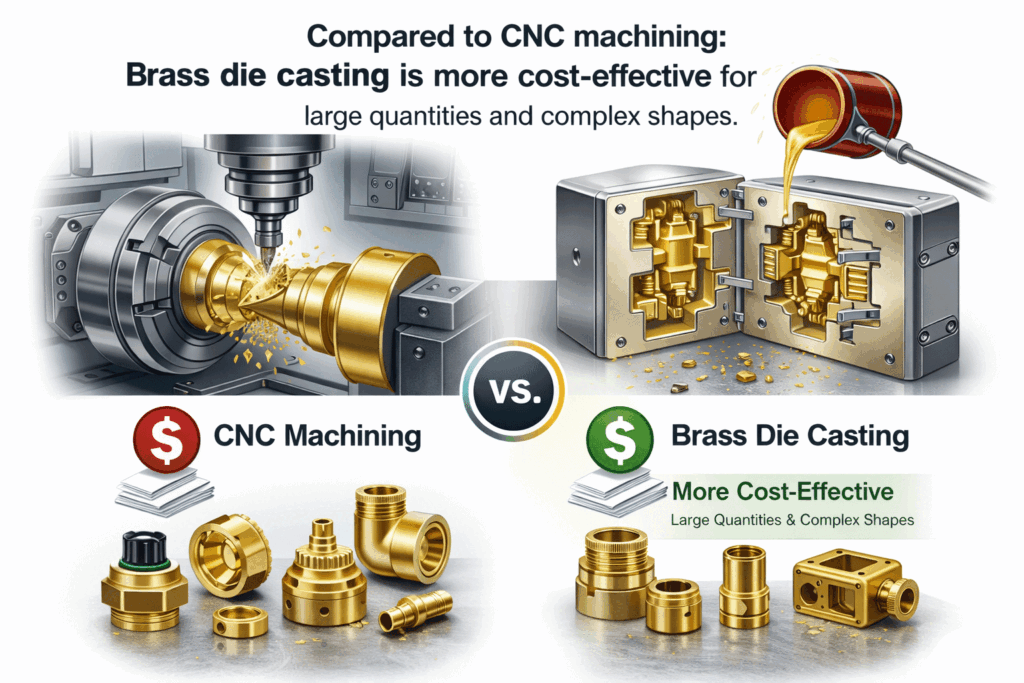
Compared to CNC machining: this manufacturing method is more cost-effective for large quantities and complex shapes.
Compared to sand casting

Compared to sand casting: this manufacturing method provides better surface quality, higher precision, and faster cycle times.
For manufacturers seeking stable quality and scalable production, brass die casting delivers long-term value.
Choosing the Right Brass Alloy
Selecting the correct alloy is essential for successful brass die casting. Common options include:
Standard brass alloys for general-purpose components
Lead-free brass alloys for environmentally regulated markets
High-strength brass alloys for load-bearing applications
The right alloy improves casting performance, mechanical strength, and product lifespan.
Quality Control in Brass Die Casting
Consistent quality in the die casting depends on strict process control, including:
Precision mold design
Controlled melting and injection parameters
Dimensional inspection and surface testing
Continuous process optimization
A reliable brass die casting manufacturer will implement comprehensive quality control systems to ensure every part meets specifications.
Optimized Conclusion (Conversion-Focused)
Brass die casting is a proven and efficient manufacturing solution for producing high-precision brass parts with complex geometries, tight tolerances, and consistent quality at scale. It remains a key process for industries that demand reliability, performance, and cost efficiency.
If you are looking for a trusted partner to manufacture durable, accurate, and cost-effective brass components, our brass die casting solutions are designed to meet your exact requirements.

