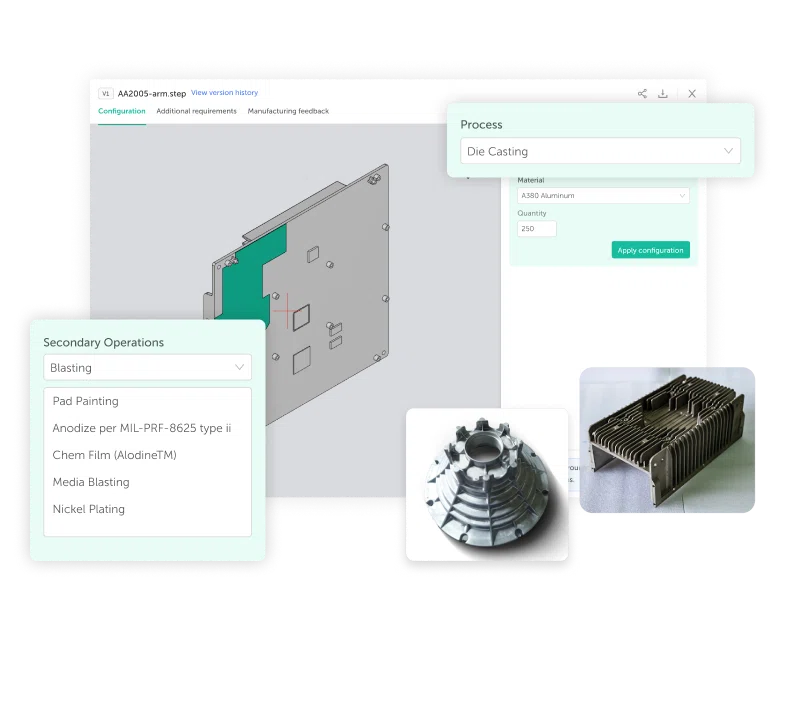
Magnesium Alloy Die Casting Services By IEC
Looking for high-performance Magnesium Die Casting solutions or want to understand Magnesium Die Casting pricing? As a dedicated Magnesium Die Casting supplier and experienced manufacturing partner, IEC MOULD delivers lightweight, high-strength casting technology and cost-optimized production tailored to your application. Whether you need thin-wall housings, precision components, or durable structural parts, our magnesium expertise and scalable capacity ensure reliable support for your project — contact us today!

±0.01mm
Tolearance
20+
Years Experience
20 Day
Die Casting Samples Delivered
Certifications
ISO 9001 & IATF 16949
Our Magnesium Die Casting Services
IEC MOULD provides full-service magnesium die casting solutions designed to transform your product ideas into lightweight, high-performance components. From early-stage concept to final assembly, we help customers streamline production while leveraging magnesium’s unique advantages.
- Custom Component Design – We develop magnesium parts with complex geometries, thin-wall structures, and integrated functions. Our team collaborates early in the design phase to optimize weight, strength, and manufacturability.
- Engineering & Simulation – Using advanced DFM, mold flow, and thermal simulations, we minimize porosity, optimize fill patterns, and ensure stable casting performance for magnesium alloys.
- Precision Tooling & Mold Fabrication – Our in-house tooling workshop designs durable magnesium die casting molds with precise gating, venting, and thermal control to maintain consistent quality and repeatable production.
- High-Accuracy Machining – Multi-axis CNC milling, drilling, tapping, and surface finishing allow tight tolerances and parts ready for assembly with minimal post-processing.
- Surface Treatment & Finishing – Chromating alternatives, powder coating, painting, and cosmetic finishing enhance corrosion resistance, thermal performance, and aesthetic quality for demanding applications.
- Assembly & Integration – We provide insert installation, sealing, and multi-part assembly to deliver turnkey magnesium components ready for installation.
- Quality Assurance & Testing – Dimensional inspection, X-ray and porosity evaluation, hardness and thermal testing, and full traceability reporting ensure each component meets exacting standards.
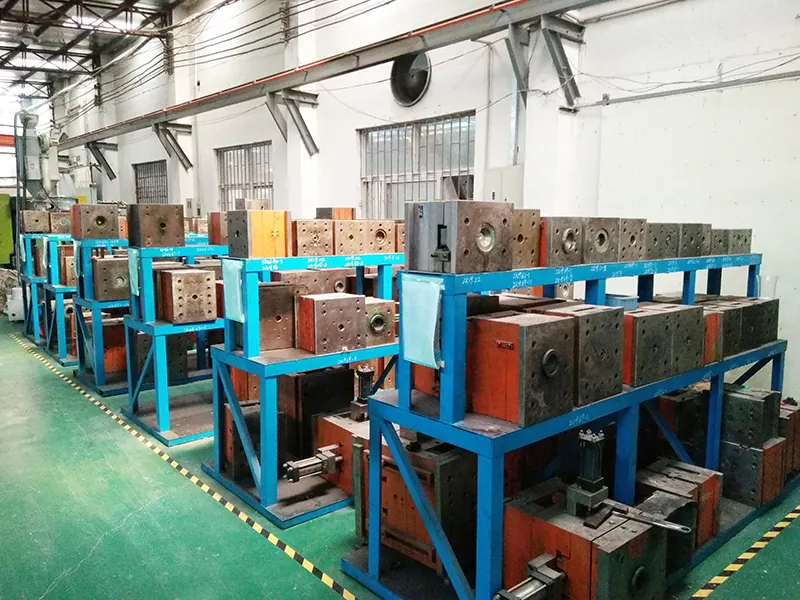
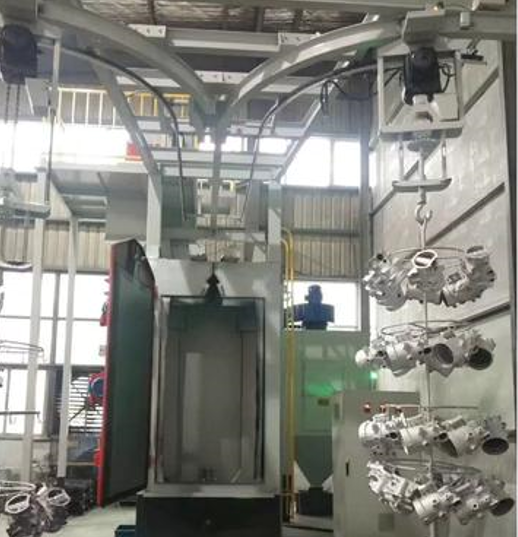
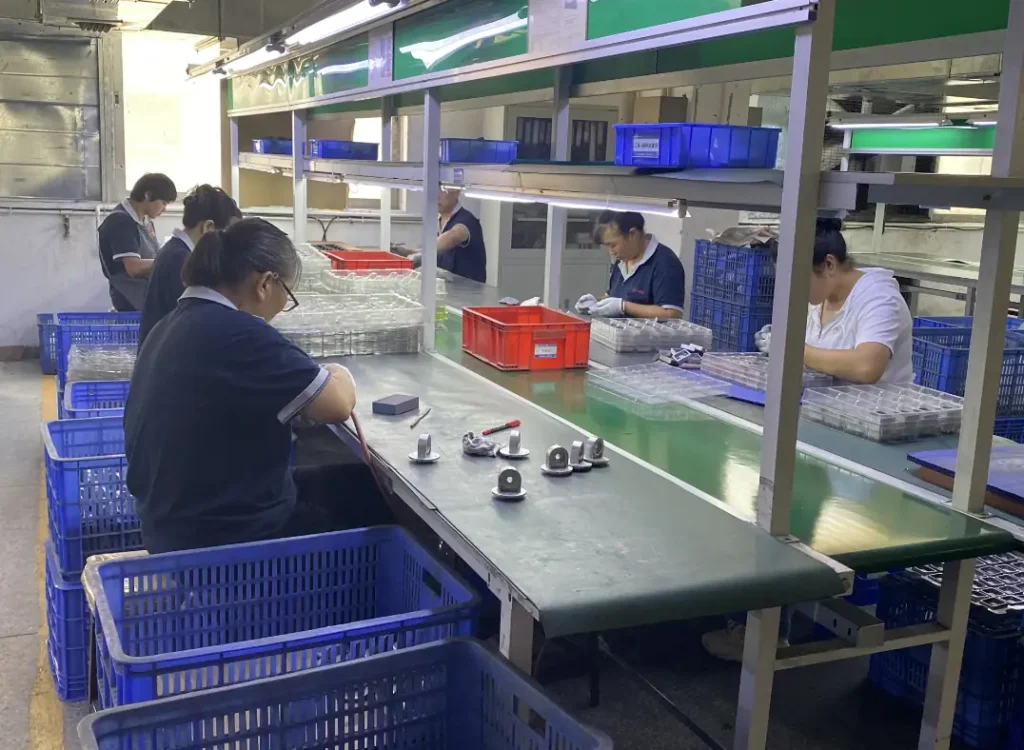
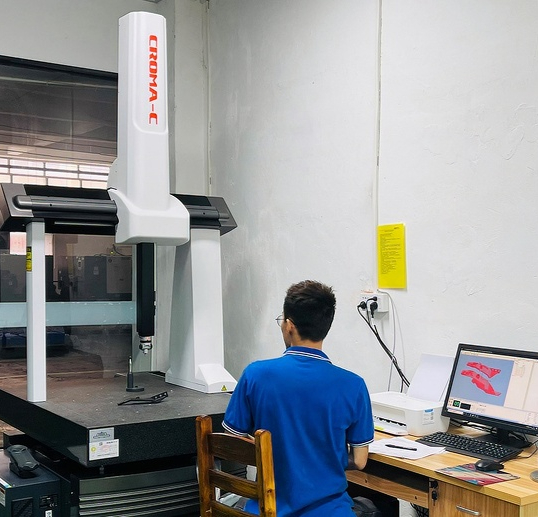




IEC Mould's Magnesium Die Casting Capabilities
| Details | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy for Magnesium Die Casting Components | Our magnesium die cast parts achieve tight tolerances of ±0.02 mm, and up to ±0.01 mm after CNC finishing—perfect for lightweight magnesium components, electronic housings, and high-precision assemblies. |
| Minimum Wall Thickness for Magnesium Parts | Standard thin-wall sections range from 0.8–1.5 mm depending on part geometry and mold design. Magnesium’s high strength-to-weight ratio allows ultra-thin, lightweight structures. |
| Uniform Wall Structure Requirement | To ensure proper magnesium alloy flow and prevent shrinkage or warping, wall thickness ratios between adjoining sections are typically 1:1.5 to 1:2. |
| Fine Details, Threads & Inserts | Small holes (≥1.2 mm), fine threads, and insert features can be cast directly in magnesium die casting components, minimizing secondary machining. |
| Draft Angle for Magnesium Ejection | Typical draft angle: 1°–1.5°, adjustable for high-precision or cosmetic areas. Magnesium’s fluidity and moderate shrinkage support complex shapes. |
| Mold Durability for Magnesium Alloy | Magnesium die casting molds can achieve 100,000–500,000 cycles depending on complexity and thermal control, providing cost-effective production for lightweight magnesium parts. |
| Surface Finish Quality | As-cast magnesium surfaces typically reach Ra 1.0–2.0 µm, suitable for powder coating, painting, or anodizing alternatives with minimal polishing. |
| Minimum Production Volume | Flexible production starting from 300 pcs, ideal for magnesium prototypes, pilot runs, and full-scale lightweight part production. |
| Production Schedule / Lead Time | Mold fabrication and first article sampling: 20–30 days depending on part complexity, thin-wall features, and surface finishing. Fast solidification ensures efficient magnesium die casting cycles. |
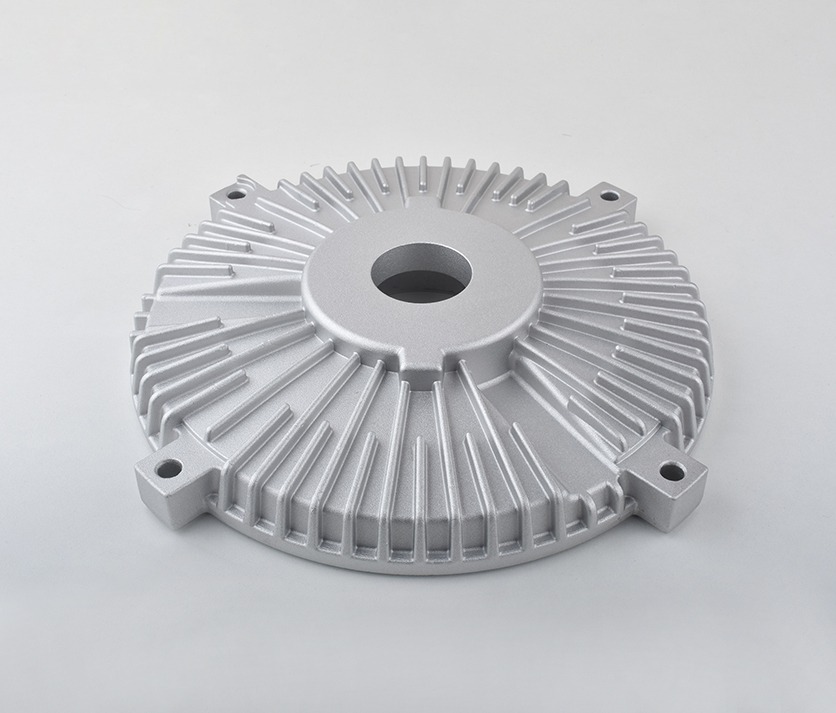
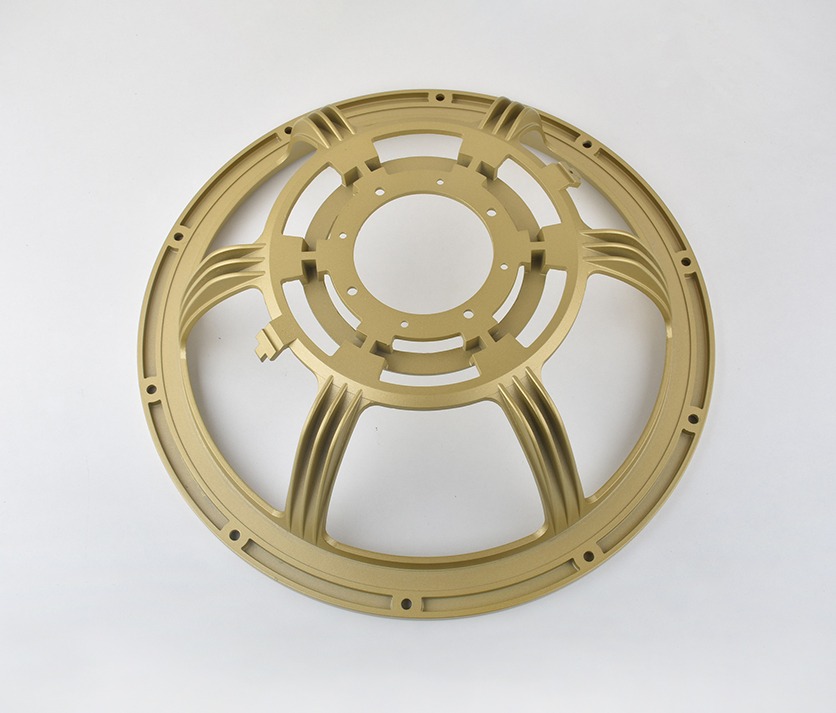
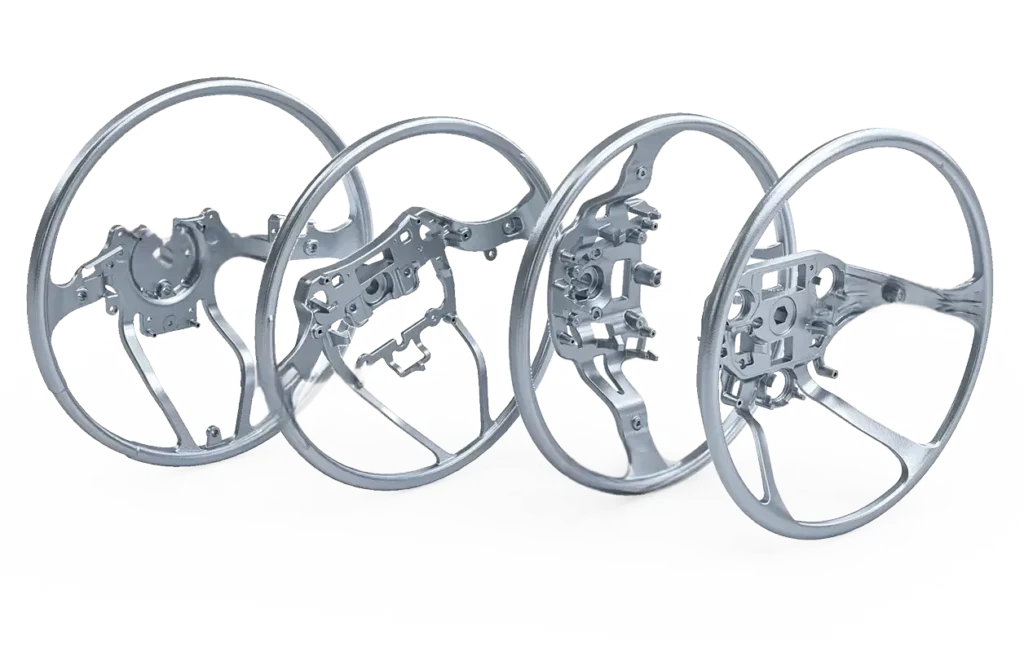
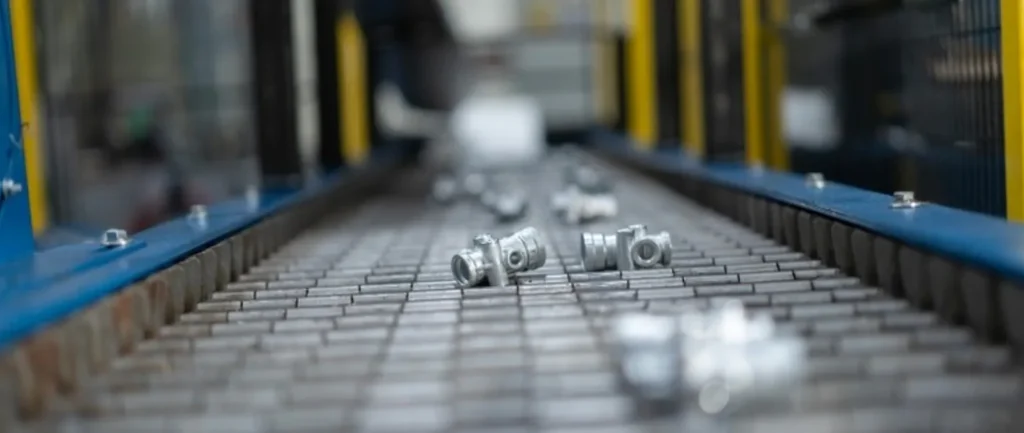
Magnesium Die Casting Parts We Manufactured
These magnesium die cast components demonstrate our expertise in producing lightweight, high-strength parts with intricate geometries and thin-wall sections. From structural housings to precision electronic enclosures, every component showcases our dedication to dimensional accuracy, material performance, and consistent quality in magnesium die casting manufacturing.
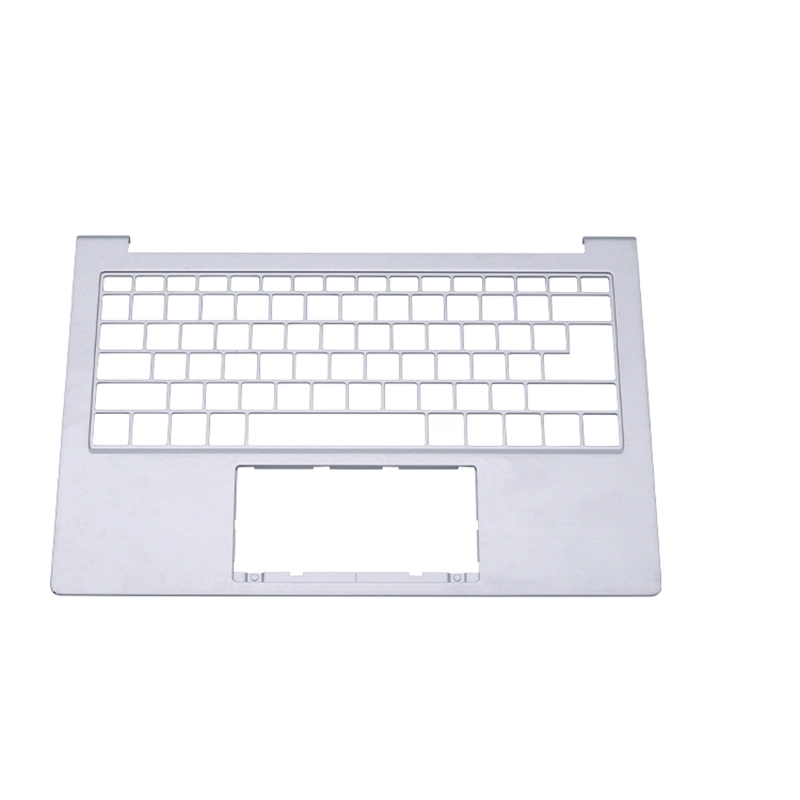

Electronics Part
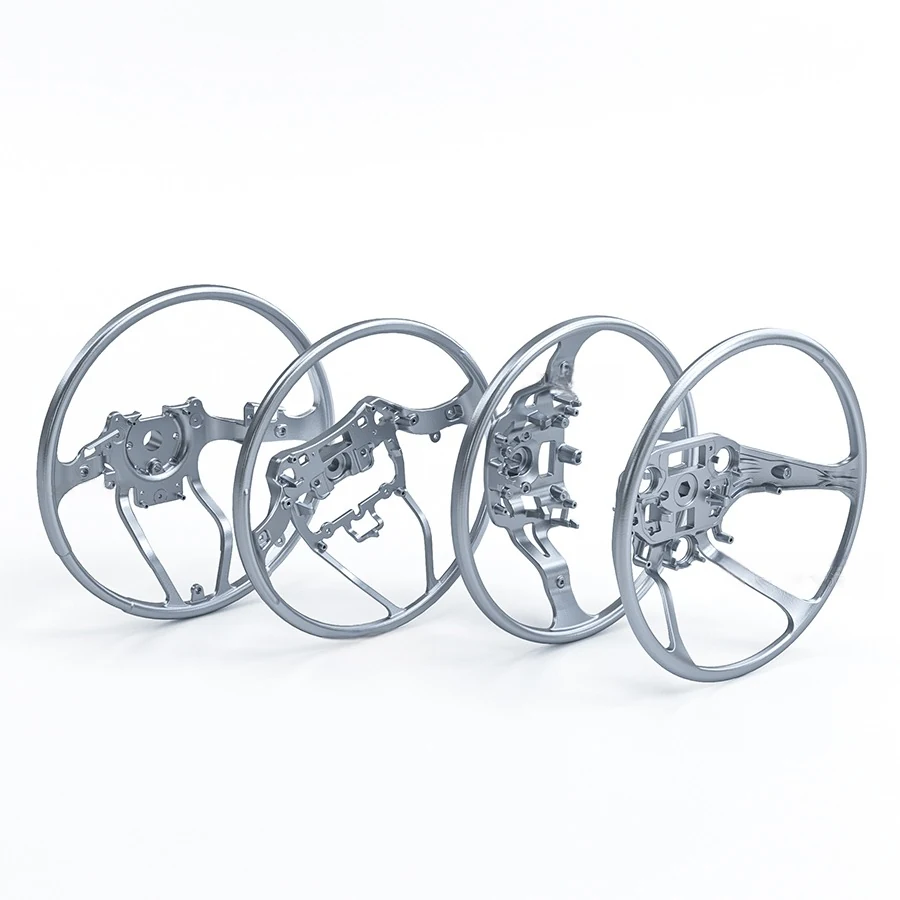

Automotive Part

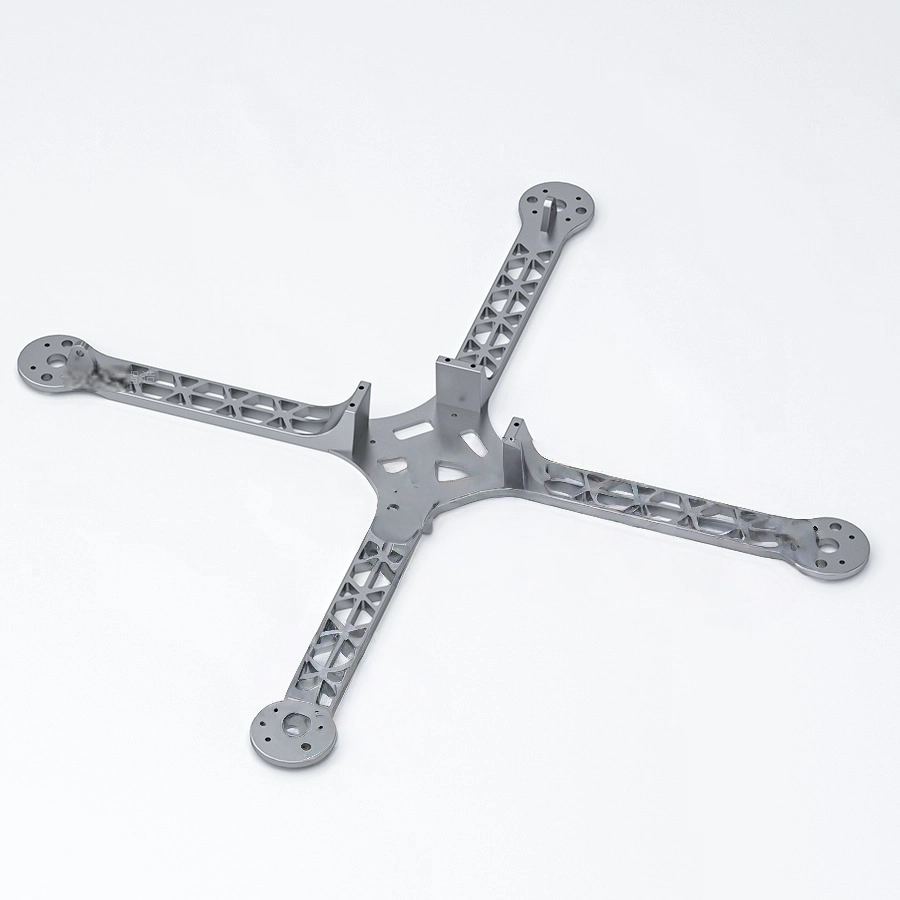
Home Appliances Part

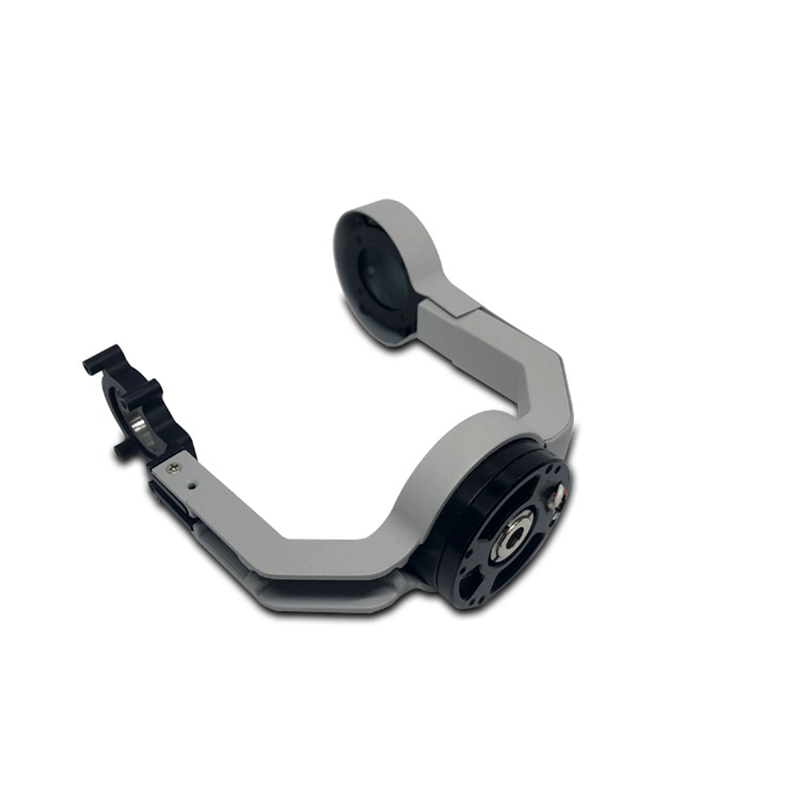
Industrial Machinery Part
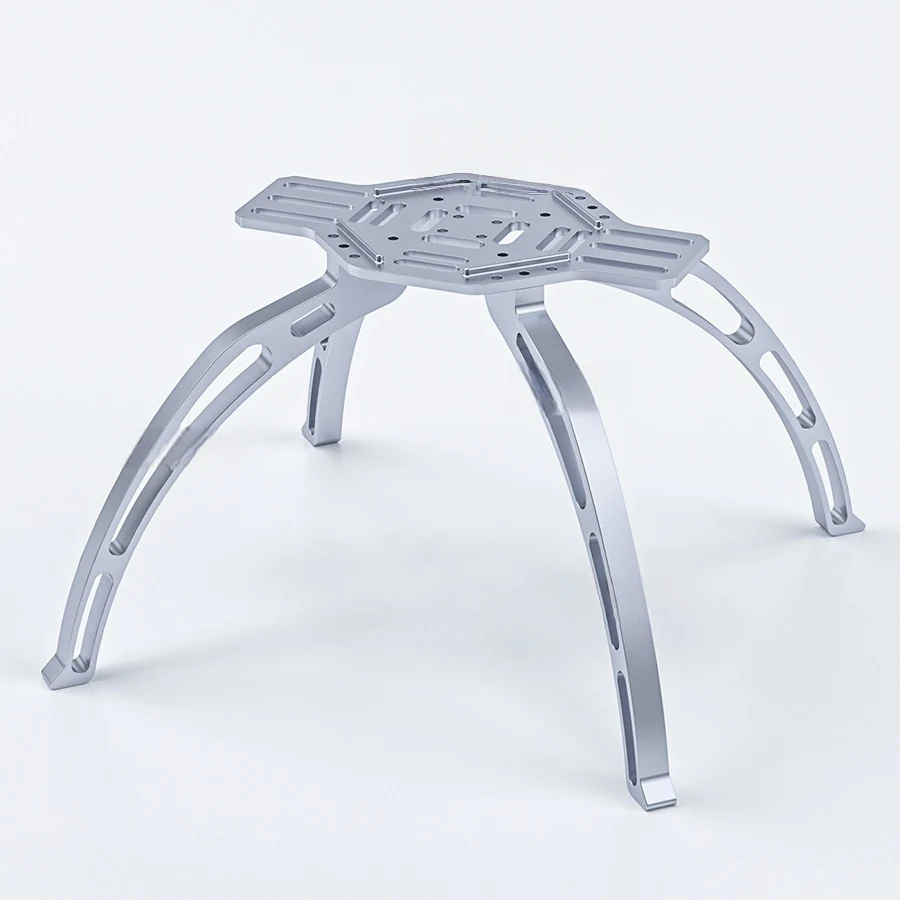

Medical Devices Part
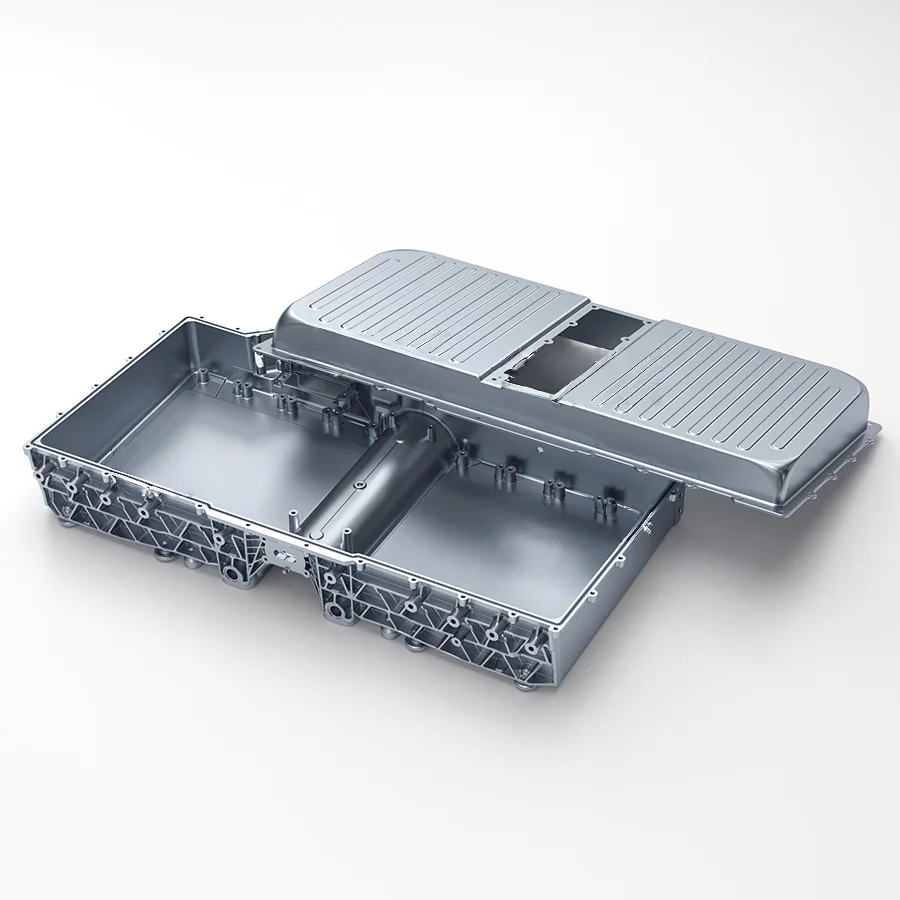

Engineering Part
Selecting the Right Magnesium Alloy for Die Casting.
Choosing the right magnesium alloy is critical to achieving the optimal combination of mechanical performance, weight reduction, surface finish, and production efficiency. IEC MOULD’s engineering team evaluates your project’s functional requirements, environmental conditions, and production volume to recommend the most suitable magnesium alloy.
| Alloy Grade | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications | Why It Excels in Magnesium Die Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| AZ91D | Most widely used magnesium die casting alloy; excellent strength-to-weight ratio, good corrosion resistance, high castability, and good surface finish. | Electronic housings, automotive interior parts, lightweight enclosures | Offers a strong balance of light weight, mechanical performance, and economical high-volume production. |
| AM60B | Superior ductility with moderate strength; better impact resistance than AZ91D; easy to machine and cast. | Automotive structural brackets, gears, and load-bearing components | Ideal for parts requiring higher toughness while retaining thin-wall castability and lightweight design. |
| AZ31B | Good corrosion resistance, moderate strength, and excellent formability; suited for thin-wall complex geometries. | Laptop frames, handheld device housings, precision electronics | Best choice for intricate, lightweight magnesium components with tight tolerances. |
| WE43 | High strength and excellent creep resistance at elevated temperatures; good corrosion protection with coatings. | Aerospace structural components, heat-sensitive brackets, high-performance enclosures | Excels in high-performance and high-temperature applications where lightweight durability is critical. |
| ZE41A | Very high tensile and yield strength, good fatigue resistance; designed for structural load-bearing applications. | Automotive engine covers, structural housings, industrial machinery components | Perfect for semi-structural magnesium parts requiring both strength and dimensional precision. |
Custom Magnesium Die Casting Manufacturers and Suppliers
IEC MOULD is a reliable Magnesium Die Casting manufacturer and supplier, focused on producing ultra-lightweight, high-strength components for automotive, electronics, aerospace, and industrial sectors. With our in-house mold engineering center, dedicated magnesium die casting cells, precision CNC machining, and integrated finishing processes, we offer a complete end-to-end production solution—from 3D design and prototyping to final assemblies. We deliver components with:
- Precision Thin-Wall Forming: Achieving stable dimensions, tight tolerances, and reduced machining requirements.
- High-Strength Magnesium Alloys: Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio for lightweight structures without compromising rigidity.
- Excellent Thermal & EMI Properties: Ideal for heat-dissipating housings, shielding components, and electronic enclosures.
- Efficient Production & Rapid Lead Times: Optimized tooling, flexible volume capability, and streamlined manufacturing efficiency.
Supported by ISO 9001 & IATF 16949 certifications, strict quality control, and advanced inspection systems, IEC MOULD ensures consistent quality, competitive pricing, and dependable delivery worldwide. Choose IEC MOULD for reliable, high-performance magnesium die cast components engineered to meet today’s demanding performance and weight-reduction requirements.





Why Choose IEC MOULD for your Magnesium die casting project?
1. Specialized Expertise in Lightweight Magnesium Components
IEC focuses on high-performance magnesium die casting solutions that help customers reduce overall product weight, improve fuel and energy efficiency, and enhance mechanical performance. Our deep understanding of magnesium alloys, thin-wall structures, and complex geometries enables us to deliver components that maximize strength-to-weight ratio and functional durability.
2. Certified Quality and Strict Process Control
IEC ensures every magnesium component meets rigorous international standards. Our ISO 9001 & IATF 16949 certified system is supported by CMM measurement, X-ray inspection, metallurgical testing, leak and durability testing, and full traceability. This ensures dimensional accuracy, structural integrity, and long-term performance for safety-critical and precision assemblies.

3. Engineering Collaboration That Enhances Manufacturability
IEC works closely with your design and engineering teams to refine part structure, optimize wall thickness, improve thermal flow paths, and enhance moldability. Through DFM reviews, mold flow analysis, and material selection guidance, we help ensure your magnesium parts are both high-performance and cost-effective to manufacture.
4. Cost-Optimized and Efficient Manufacturing Workflow
With in-house mold engineering, magnesium die casting machines, CNC machining centers, and finishing lines, we streamline the entire production process. This reduces tooling cost, shortens lead time, improves casting stability, and provides competitive pricing—especially for medium to high-volume magnesium component production.

Other Die Casting Metals Services You May Looking for
Magnesium Die Casting Frequently Questions & Answers
How thin can magnesium die cast walls be?
Magnesium supports very thin sections thanks to excellent fluidity:
- Typical thin walls: 0.8–1.2 mm
- Advanced thin-wall designs: as low as 0.6 mm, depending on geometry and flow simulation
Our DFM and mold flow analysis help optimize wall thickness for stable filling and structural performance.
Is magnesium die casting safe?
Yes. Modern magnesium die casting equipment includes safety systems that prevent ignition, and the alloys used today (e.g., AZ91D) have very high ignition temperatures. IEC follows strict material-handling protocols and safety standards to ensure safe, stable production.
What surface finishes are available for magnesium die cast parts?
IEC provides a wide range of finishing options:
- Chromate coating / conversion coating
- Powder coating
- Painting
- Anodizing (selective)
- Machining & polishing
Finishing improves corrosion resistance, durability, and cosmetic appearance.
What are common magnesium die casting defects and how do you prevent them?
Typical defects include porosity, incomplete filling, hot cracks, and distortion. IEC prevents these through:
- DFM optimization
- Mold flow simulation
- Proper gating/venting design
- Controlled temperature management
- Vacuum-assisted die casting (optional)
- Strict process monitoring and QA
This ensures stable, repeatable quality.
What is the typical lead time for magnesium die casting production?
- Tooling fabrication: 15–30 days
- First Article Inspection (FAI): 5–10 days after tooling
- Mass production: based on volume and complexity
Our in-house tooling and machining reduce overall lead time significantly.
Can magnesium replace aluminum or plastic parts?
Yes. Magnesium can be an excellent replacement when:
- Weight reduction is a priority
- Higher stiffness or better thermal performance is needed
- Parts require both strength and thin walls
- Structural integrity is critical
IEC’s engineering team can evaluate feasibility based on cost, strength, and performance goals.
What is the typical tolerance for magnesium die cast parts?
Standard tolerances range from ±0.05 mm to ±0.10 mm, depending on part size and geometry. With CNC machining, tolerances can be refined to ±0.005 mm for critical dimensions.
What is Magnesium Die Casting?
Magnesium die casting is the process of injecting molten magnesium alloy into a precision steel mold under high pressure to create parts that are strong, accurate, and unbelievably lightweight. In fact, magnesium is the lightest structural metal we can actually use for real engineering—not counting the “metal” ideas some designers sketch at 2 a.m.
Despite being light enough to make aluminum feel insecure, magnesium delivers impressive stiffness, impact resistance, and thermal performance. When it flows in molten form, it fills thin walls, deep ribs, and complex features with ease, which is why engineers love using it for housings, brackets, electronic enclosures, power tools, and automotive interior structures.
One of the biggest advantages is design freedom: magnesium die casting often allows you to replace multi-piece assemblies with one integrated component. Fewer screws, fewer assembly steps, fewer headaches—everyone wins. And because magnesium cools quickly, cycle times are shorter, making it suitable for medium-to-high-volume production without sacrificing precision.
So what is magnesium die casting?
It’s the ideal solution when you want “strong but light,” “complex but stable,” and “high-performance but cost-sensible.” Think of it as the engineering version of having your cake and eating it too—except here, the cake is a high-quality metal component that truly pulls its weight… which just happens to be very, very little.
Types of Magnesium Die Casting
Magnesium die casting can be produced using two primary die casting processes — Hot Chamber and Cold Chamber. Each method influences part quality, cycle time, and cost structure. Understanding the differences helps engineers and buyers choose the most suitable approach for lightweight structures, thin-walled parts, and high-volume manufacturing.
Hot Chamber Magnesium Die Casting
Hot chamber magnesium die casting integrates the melting and injection system into one machine, allowing extremely fast cycles and excellent repeatability. Because molten magnesium is handled inside a closed system with protective gas, the process minimizes oxidation and delivers consistent flow for thin-wall designs. This method is ideal for small, high-volume components that demand precision and short lead times.
However, hot chamber systems have higher equipment costs and may introduce more gas porosity, making them less suitable for large structural parts.
Cold Chamber Magnesium Die Casting
Cold chamber die casting melts magnesium in a separate furnace and transfers it to the injection chamber before each shot. This method accommodates all commercial magnesium alloys and supports larger, stronger components with lower porosity levels. It is the preferred process for automotive, industrial, and aerospace parts where structural integrity and dimensional stability are essential.
While cycle times are slower than hot chamber casting, cold chamber provides better consistency for medium-to-large frames, brackets, housings, and load-bearing assemblies.
Choosing the Right Method
Engineers typically select hot chamber for compact, thin-wall parts requiring speed and high-volume efficiency, while cold chamber is favored for stronger, larger, or structurally demanding components. At IEC Mould, we evaluate alloy behavior, melt handling, flow simulation, and tooling design to ensure the selected process aligns with performance targets, cost goals, and long-term reliability.
Magnesium Alloy Properties
| Magnesium Alloy | Density | Yield Strength | Elongation | Elastic Modulus | Melting Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
AZ91D | 1.81 g/cm3 | 160 MPa | 3% | 45 GPa | 875-1105 °F |
AZ91HP | 1.81 g/cm3 | 160 MPa | 3% | 45 GPa | 875-1105 °F |
AM60B | 1.80 g/cm3 | 130 MPa | 8% | 45 GPa | 1005-1140 °F |
Why Choose Magnesium Die Casting?
Magnesium die casting stands out when you need parts that are extremely lightweight, structurally strong, and engineered for demanding performance environments. As the lightest structural metal used in die casting, magnesium brings a unique combination of benefits that other alloys simply can’t deliver.
1. Ultra-Lightweight Without Compromising Strength
Magnesium components are up to 33% lighter than aluminum and dramatically lighter than zinc, making them ideal for automotive, aerospace, and handheld electronic applications where every gram matters.
Less weight means lower fuel consumption, easier handling, and improved ergonomics—especially for parts that are frequently moved, held, or assembled.
2. Excellent Stiffness & Structural Integrity
Despite being light, magnesium delivers surprisingly high stiffness and impact resistance. It’s strong enough for steering components, gearbox housings, brackets, seat frames, and load-bearing structures.
For designers trying to cut weight without weakening critical features, magnesium becomes an elegant solution rather than a compromise.
3. Outstanding Processability for Complex, Thin-Wall Parts
Molten magnesium flows quickly and cools rapidly, allowing molds to fill completely—even with ultra-thin walls, deep ribs, sharp details, and integrated features.
This makes magnesium ideal for consolidating multiple components into a single casting, reducing part count, fasteners, and assembly time.
4. Superior Thermal & EMI Shielding Performance
Magnesium dissipates heat efficiently and offers natural electromagnetic shielding.
This makes it a top choice for electronics housings, communication devices, power tools, EV components, and any application where heat and interference must be controlled.
5. Faster Cycle Times & Production Efficiency
Compared to aluminum, magnesium’s low density and rapid cooling allow:
- Shorter solidification time
- Quicker injection cycles
- Higher output per machine
This translates directly into lower production costs for medium-to-high volume programs.
6. Easier Machining & Reduced Secondary Operations
Magnesium cuts cleanly and requires less tool wear, enabling:
- Lower CNC machining costs
- Faster processing
- Tighter dimensional consistency
For precision features that cannot be cast, magnesium offers a clear machining advantage.
7. Ideal for Lightweighting & Next-Generation Design
From automotive OEMs targeting CO₂ reduction to electronics brands seeking thinner, lighter devices, magnesium die casting is at the center of modern lightweight engineering strategies.
When your design calls for “lighter, but not weaker,” magnesium is often the only material that checks all the boxes.
How Magnesium Die Casting Works?
As a dedicated magnesium die casting manufacturer, IEC Mould understands that working with magnesium is very different from zinc or aluminum. Magnesium’s ultra-lightweight nature, fast solidification, and reactive characteristics require precise process control, specialized equipment, and experienced engineering judgment.
Below is the typical six-step magnesium die casting workflow used by advanced foundries. It highlights what truly matters from the viewpoints of engineers, procurement teams, and quality control departments.
Step 1: Alloy Melting & Preparation
Magnesium ingots (e.g., AZ91D, AM60B) are melted in a protective atmosphere—typically SF₆-free environmentally friendly gas mixtures—to prevent oxidation and burning. Alloy composition must remain stable to achieve target strength and ductility.

Step 2: Die & Mold Preparation
The steel die is preheated to prevent thermal shock and coated with a specialized release agent formulated for magnesium. Proper venting and gating design are essential due to magnesium’s extremely fast filling speed.
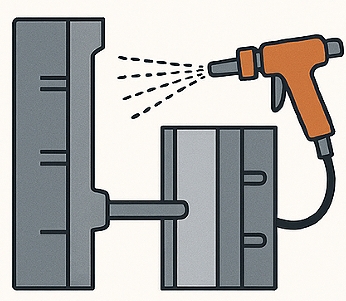
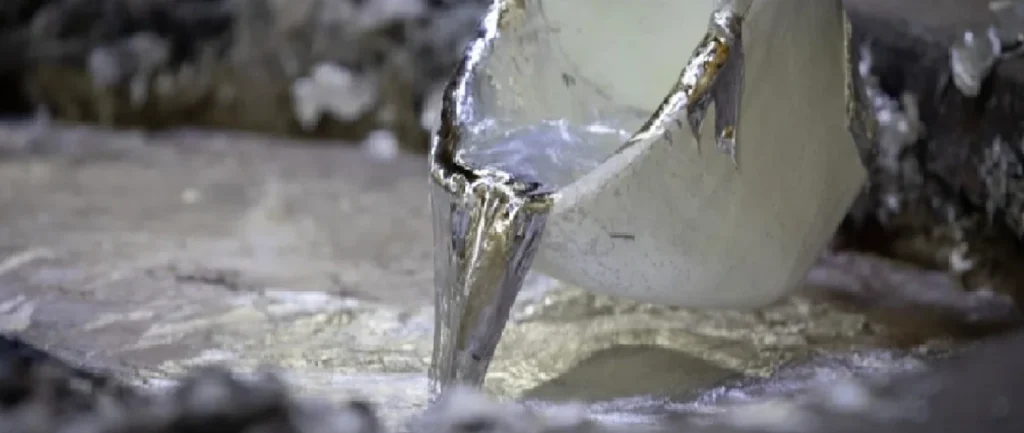
Step 3: High-Pressure Injection Casting
Molten magnesium is injected into the die cavity at high speed. Because magnesium solidifies faster than aluminum, injection timing and pressure must be finely controlled.
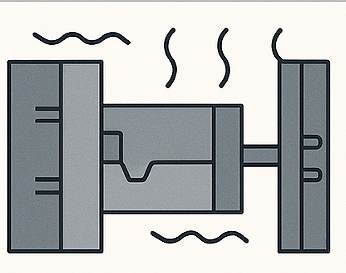
Step 4: Cooling & Solidification
Magnesium cools extremely quickly, which is why advanced cooling channel design is critical. Once solidified, ejector pins release the component from the die.
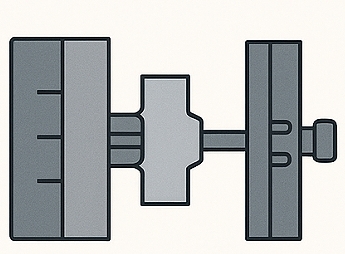
Step 5: Trimming & Surface Finishing
After ejection, runners, gates, and flash are removed. Magnesium’s excellent machinability allows for smooth and efficient secondary processing. Common finishing options include:
- CNC machining for ultra-precise features
- Shot blasting or tumbling for uniform surface texture
- Chromate conversion coating, anodizing, or painting for corrosion resistance
- Final assembly of magnesium housings or mechanical components
Step 6: Quality Inspection & Testing
Because magnesium parts are often structural, every batch undergoes strict inspection to ensure mechanical reliability and dimensional accuracy. Typical tests include:
- X-ray / CT scanning for internal porosity and structural integrity
- CMM measurement for dimensional and geometric accuracy
- Mechanical testing for tensile strength, elongation, impact resistance
- Corrosion resistance testing for coatings or protective treatments
- Surface inspection for cosmetic or functional requirements
Advantages of Magnesium Die Casting
Magnesium Die Casting (MgDC) is prized for its ultra-lightweight properties, high strength-to-weight ratio, and fast cooling characteristics, making it ideal for automotive, aerospace, electronics, and industrial applications where weight reduction, structural integrity, and precision are critical. Below are the key advantages of magnesium die casting.
| Advantage | For Engineers | For Procurement Teams | For Quality Control (QC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultra-Lightweight Components | Enables weight reduction while maintaining structural performance; perfect for thin-wall, load-bearing parts | Reduces shipping costs and supports lightweight product design targets | Easier to handle and inspect due to lower part mass |
| High Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Provides rigidity and impact resistance in minimal material thickness | Supports durable parts with less material, lowering raw material costs | Consistent mechanical performance across production batches |
| Excellent Thermal & EMI Performance | Ideal for heat-dissipating housings and shielding components in electronics | Reduces need for secondary thermal or EMI treatments | Simplifies QC testing for thermal and electrical properties |
| Fast Solidification & High Productivity | Rapid cooling allows thin-wall features and fast cycle times | Shorter production cycles increase throughput and lower unit cost | Stable and repeatable process ensures consistent part quality |
| Good Machinability & Secondary Processing | Can be machined easily for threads, holes, or tight tolerances after casting | Minimizes additional processing costs | Allows precise measurement and defect-free finishing |
| Design Flexibility & Part Consolidation | Supports complex geometries, integrated ribs, and multi-feature designs | Reduces assembly steps and total part count, improving supply chain efficiency | Fewer assembly steps mean fewer potential quality issues |
| Corrosion-Resistant with Surface Treatments | Supports protective coatings like chromate conversion, anodizing, or painting | Enhances product durability, lowering warranty risks | Consistent surface quality and coating adhesion verification |
| Sustainability & Recyclability | Magnesium scrap can be re-melted with minimal performance loss | Supports environmentally friendly sourcing and corporate sustainability goals | Alloy consistency ensures repeatable quality across recycled material |
Disadvantages of Zinc Die Casting
Magnesium die casting excels in lightweight, high-strength, and complex components, but like any material, it comes with certain constraints. Understanding these early helps engineers, procurement, and quality teams make informed design and production decisions.
| Disadvantage | For Engineers | For Procurement / QC Teams |
|---|---|---|
| Flammability Risk During Melting | Magnesium is highly reactive at molten temperatures; careful atmosphere control is required to prevent ignition | Requires specialized equipment and safety protocols, which may increase upfront costs |
| Lower Corrosion Resistance in Untreated Parts | Raw magnesium can corrode in humid or salty environments if not coated or treated | Additional surface treatments (chromate, painting, or anodizing) may be required, adding to material cost |
| Limited High-Temperature Strength | Magnesium alloys (e.g., AZ91D) can lose mechanical performance above 120–150°C, making them less suitable for high-heat applications | May require alternative alloys, thermal barriers, or design modifications for heat-exposed parts |
| Size Constraints for Large Parts | Ultra-large castings may experience distortion or uneven cooling due to magnesium’s rapid solidification | Large tooling and multiple cavity setups increase mold cost and production complexity |
| Thin-Wall Warping Risk in Complex Geometry | Very thin sections with long unsupported spans may deform during ejection or handling | QC must check dimensional stability, especially in weight-critical or load-bearing parts |
| Oxidation During Handling or Storage | Magnesium surfaces can oxidize quickly if left untreated | Requires controlled storage, protective coatings, or timely finishing before shipment |
| Higher Cost for Small Batches | Specialized handling and tooling requirements may make low-volume runs less economical | Procurement must consider total cost per part, balancing lightweight benefits against tooling and safety overhead |
Magnesium vs Other Die Casting Metals
Magnesium die casting gives engineers remarkable flexibility for creating lightweight, high-performance components. Its unique material properties enable ultra-thin walls, intricate geometries, and functional features—such as ribs, bosses, and heat-dissipating fins—directly molded into the part. This minimizes secondary machining and assembly, helping streamline production while preserving structural integrity and dimensional accuracy.
Compared to other die casting metals, magnesium offers an outstanding strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for automotive, aerospace, electronics, and portable applications where every gram matters. Its fast solidification allows for high-volume production with thin-walled designs, while its machinability and corrosion resistance (with appropriate coatings) ensure reliable long-term performance. Designers can consolidate multiple functions into a single casting, reducing part count, assembly complexity, and overall system weight.
At IEC MOULD, we support magnesium die casting with thorough DFM reviews, mold flow analysis, and alloy selection, ensuring each component achieves repeatable precision, structural reliability, and manufacturability. By understanding magnesium’s advantages relative to zinc, aluminum, and copper alloys, engineers can make informed material choices that optimize performance, aesthetics, and cost efficiency.
| Property | Magnesium (Mg) | Zinc (Zn) | Aluminum (Al) | Brass / Copper Alloys (Cu-Zn) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Extremely light – perfect for handheld, portable, and weight-sensitive components | Moderate – gives a solid, premium feel | Very light – suitable for larger parts | Heavy – used where mass and stability are required |
| Strength & Toughness | Moderate to high – excellent strength-to-weight ratio; ideal for load-bearing lightweight parts | High – strong and impact-resistant for small mechanisms | High – strong but can be brittle in thin sections | Very high – ideal for heavy-duty or wear-critical applications |
| Dimensional Precision | Very good – stable for thin walls and complex geometries with proper tooling | Excellent – fine detail and high accuracy | Very good – suitable for most precision applications | Good – stable but limited for thin-wall or intricate parts |
| Surface Finish | Good – usually requires chromate, anodizing, or painting for corrosion protection; smooth finish achievable | Superior – can be polished, plated, or coated directly | Good – can be anodized or painted | Excellent – naturally smooth, corrosion-resistant finish |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate – dissipates heat well, but mechanical performance drops above 120–150°C | Limited – loses strength above 150°C | Excellent – performs well in high-heat applications | Excellent – high thermal tolerance and conductivity |
| Production Efficiency | Moderate to high – rapid solidification allows thin-wall features, but oxidation requires careful handling | Outstanding – low melting point enables fast cycles and long tool life | High – efficient for medium-to-large components | Low – high melting temperature increases tooling wear |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate – material cost higher than aluminum, specialized tooling adds expense, but total system weight savings offset cost | Excellent – minimal waste, fast cycles, long tool life | High – good balance between cost and performance | Lower – expensive raw material and high energy consumption |
| Typical Applications | Automotive brackets, EV housings, aerospace structures, handheld electronics, precision casings | Small gears, connectors, locks, hinges, decorative components | Engine covers, structural housings, heat sinks, large frames | Plumbing fittings, valves, decorative or marine hardware |
Magnesium Die Casting Part Applications Across Industries
Magnesium die casting is increasingly favored in applications where weight reduction, thermal management, and functional integration are critical. Its ultra-lightweight properties, fast solidification, and compatibility with thin-wall, intricate designs make it ideal for high-performance, ready-to-use components across multiple industries.
| Industry | Typical Components | Why Magnesium Die Casting Fits |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive & EV | Engine brackets, dashboard frames, pedal assemblies, battery housings | Lightweight components reduce vehicle mass, improving fuel efficiency and EV range; excellent thermal dissipation for electronics and battery modules |
| Aerospace & Aviation | Interior panels, avionics housings, brackets | Strength-to-weight ratio allows structural parts to be lighter without compromising performance; thin-wall features help save space |
| Consumer Electronics | Laptop casings, smartphone frames, camera housings | Ultra-lightweight yet rigid, ideal for portable devices; EMI shielding reduces interference in sensitive electronics |
| Medical Devices | Diagnostic equipment frames, handheld instruments, mounting brackets | Stable dimensional accuracy for precision parts; lightweight design reduces strain for handheld instruments |
| Industrial & Robotics | Motor housings, precision enclosures, sensor brackets | Fast production cycles enable medium-to-large batch manufacturing; good machinability allows post-processing and inserts |
| Lighting & LED Fixtures | Heat sinks, lamp housings, mounting brackets | High thermal conductivity efficiently dissipates heat; thin-walled complex shapes achievable |
| Sports & Recreation Equipment | Bicycle components, portable device frames, protective casings | Ultra-light parts improve portability and user ergonomics; corrosion-resistant with proper surface treatment |
| Telecommunications & Networking | Router housings, server brackets, shielding enclosures | EMI shielding properties and heat dissipation improve performance and reliability; lightweight for modular equipment- |
Ready to Start Your Magnesium Die Casting project?
Our experienced engineers are here to guide you through Magnesium alloy selection, mold design, production optimization. Discover how advanced magnesium die casting technologies can deliver high quality, and cost efficient components for your next magnesium casting project.
- yoyo@iec-mould.com
- 86 13712993487
- 86 13712993487

*Our team will answer your inquiries within 24 hours.
*Your information will be kept strictly confidential.