Introduction: Unleashing the Power of the Lightweight Champion
In today’s world, where efficiency, energy savings, and miniaturization are paramount, weight reduction is a core mission for engineers and designers. Magnesium die-cast is the key to achieving this goal. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth overview of magnesium die casting, from the basic process to selecting the best option for your project.
What is Magnesium Die Casting?
The core of its appeal lies in the inherent property of the magnesium material itself: an unparalleled strength-to-weight ratio. With a density of just 1.738 g/cm³, magnesium alloys are approximately 33% lighter than aluminum and 75% lighter than steel, making them the preferred choice for weight-sensitive applications without compromising on magnesium’s strength.
The Magnesium Die Casting Process Explained
Hot Chamber vs. Cold Chamber Die Casting: A Quick Guide
| Feature | Hot Chamber Die Casting | Cold Chamber Die Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Process |
Hot Chamber Die Casting
The magnesium alloy is melted in a crucible attached to the injection mechanism. |
Cold Chamber Die Casting
The alloy is melted in a separate furnace, then ladled into the injection sleeve. |
| Best For |
Small, thin-walled, high-volume parts
|
Larger, structural, high-integrity parts
|
| Production Efficiency |
Very High
Shorter cycle times, high automation, suitable for high-volume production. |
High
Relatively longer cycle times, but capable of larger and more complex parts. |
| Equipment Cost |
Higher
More complex equipment, higher maintenance costs. |
Relatively Lower
Simpler equipment structure, higher flexibility. |
| Common Mg Alloys |
Primarily low-iron magnesium alloys:
|
All commercial magnesium alloys:
|
The Step-by-Step Workflow at IEC MOLD:
Alloy Melting & Die Preparation: Magnesium ingots are melted in a protective atmosphere to prevent oxidation. The steel die is preheated and coated with a release agent. High-Pressure Injection: Molten magnesium is injected into the die cavity at high speed. Solidification: The alloy cools and solidifies rapidly into the shape of the part. Ejection: The die opens, and ejector pins push the solidified part out. Trimming & Finishing: Excess material is removed. Secondary operations like CNC machining or surface treatments are applied for precision and protection.
Discover IEC MOLD’s full-range magnesium die casting capabilities and see how we manage this process for optimal results.
Why Choose Magnesium Die Casting? The Unbeatable Advantages
Ultra-Lightweight
The foremost benefit, critical for magnesium auto parts and aerospace applications, leading to improved fuel efficiency and performance.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Components made from die cast magnesium offer exceptional strength and rigidity, making them suitable for structural applications.
Excellent Castability
The high fluidity of molten magnesium material allows for the production of complex geometries and thin walls, which are often challenging with other alloy die casting methods.
Superior EMI/RFI Shielding
Naturally protects sensitive electronic components, making it perfect for enclosures.
Good Thermal Conductivity
Efficiently dissipates heat, enhancing the reliability of electronic products.
Cost-Effective for High Volumes
Despite a higher raw material cost, the rapid cycle times and excellent castability make magnesium die casting highly economical for large production runs.
A Balanced View: Considerations for Magnesium Die Casting
No process is perfect. Understanding the challenges leads to better decision-making.
Corrosion Resistance: Pure magnesium is reactive, but using high-purity alloys (like AZ91D) and appropriate surface treatments (e.g., chromating, painting) makes it suitable for most applications. Cost: Raw material cost can be higher than aluminum, and production requires strict safety measures. However, for high-volume production, the benefits of light weighting and efficiency often offset the cost. High-Temperature Performance: Standard alloys (e.g., AZ91D) have a limited operating temperature. For high-heat applications, special alloys (like AE44) are required.
A Closer Look at Common Magnesium Grades
AZ91D: The most widely used magnesium alloy for die casting, offering an excellent combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and castability. Ideal for a wide range of magnesium alloy products. AM60B: Known for its higher ductility and impact resistance, making it a preferred choice for automotive components like seat frames that require good energy absorption. AM50A: Similar to AM60B, with good strength and ductility, often used in automotive applications. AS41B: Offers better creep resistance at elevated temperatures, suitable for engine-adjacent components.
Explore our in-depth guide to selecting the right magnesium grades for your specific needs.
Magnesium vs. Aluminum Die Casting: A Detailed Comparison
Many clients consider both magnesium and aluminum die casting services. Here’s a quick comparison to guide your decision:
| Parameter | Magnesium | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Density |
1.738 g/cm³
Lighter
36% lighter than aluminum
|
~2.68 g/cm³
Standard density for most aluminum alloys
|
| Castability |
Excellent
Thinner walls possible
|
Very Good
|
| Strength-to-Weight |
Excellent
|
Very Good
|
| Machinability |
Excellent
|
Good
|
| Cost (Raw Material) |
Higher
|
Lower
|
The choice boils down to your priority: if maximum weight reduction is critical, magnesium is superior. If cost is the primary driver and the weight of aluminum is acceptable, it remains an excellent choice.
Applications of Magnesium Die Casting Across Industries
Automotive & EV
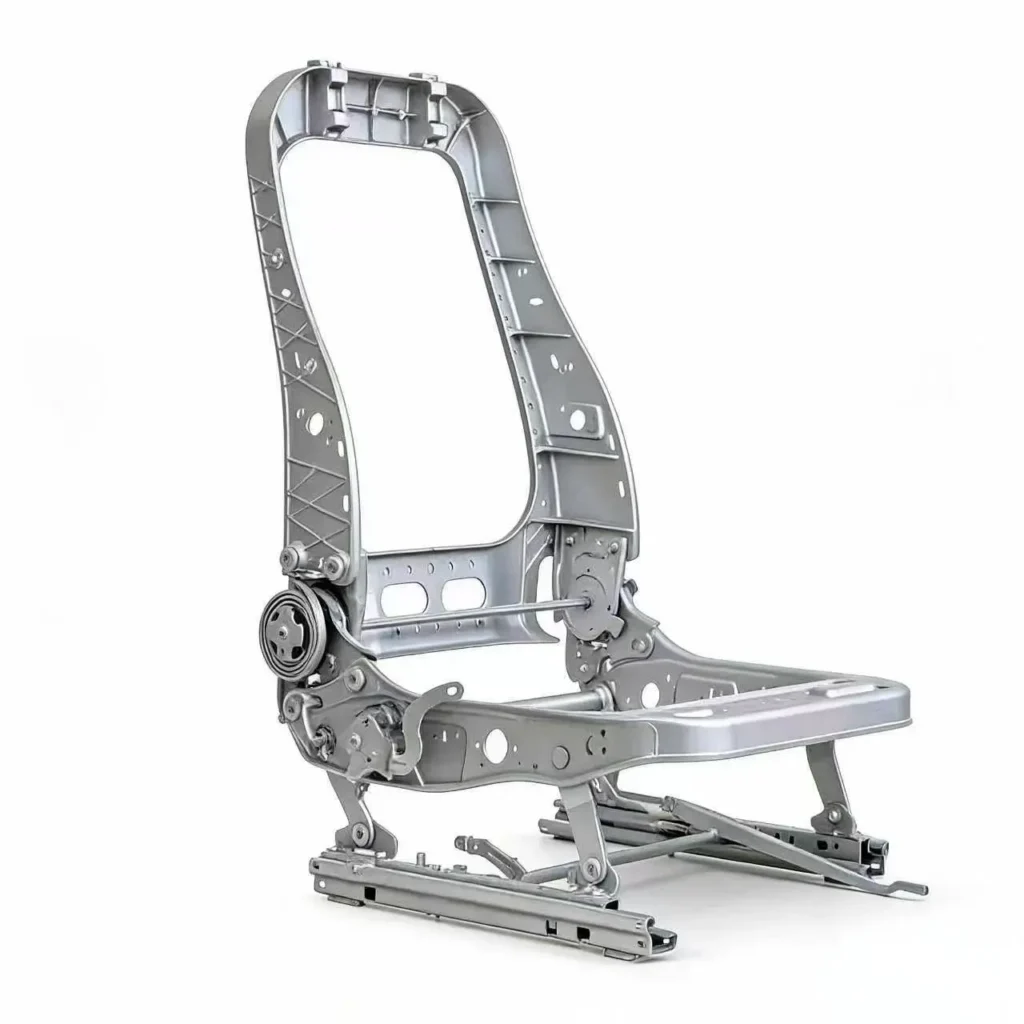
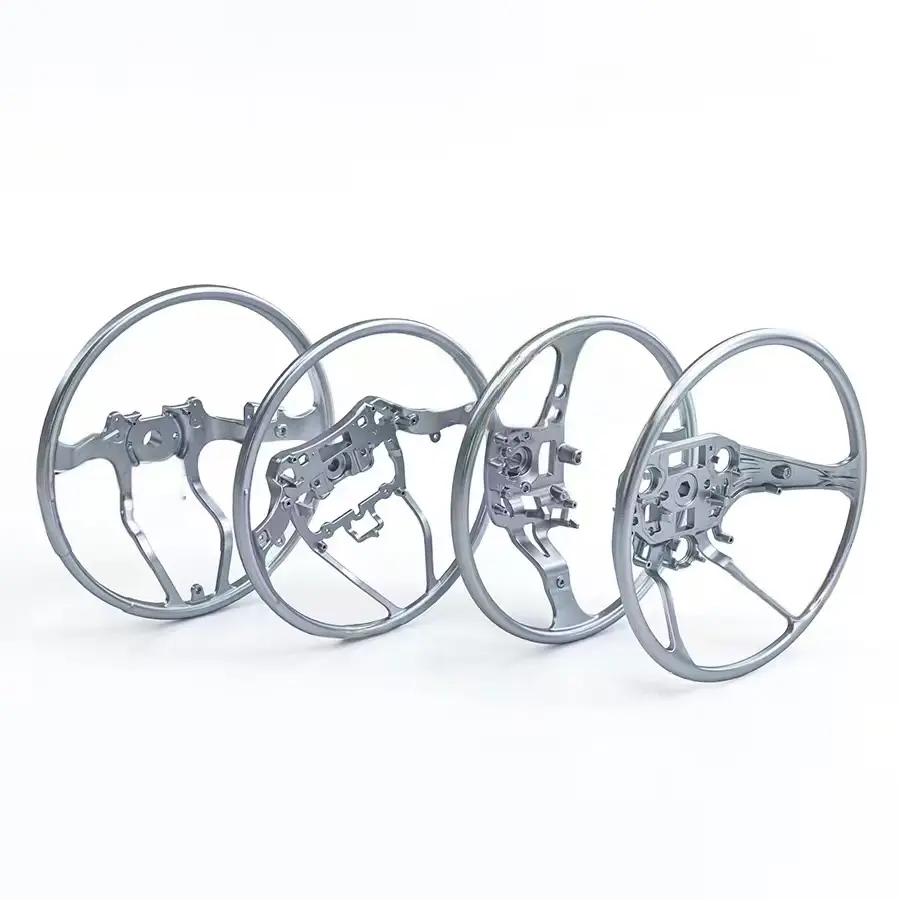
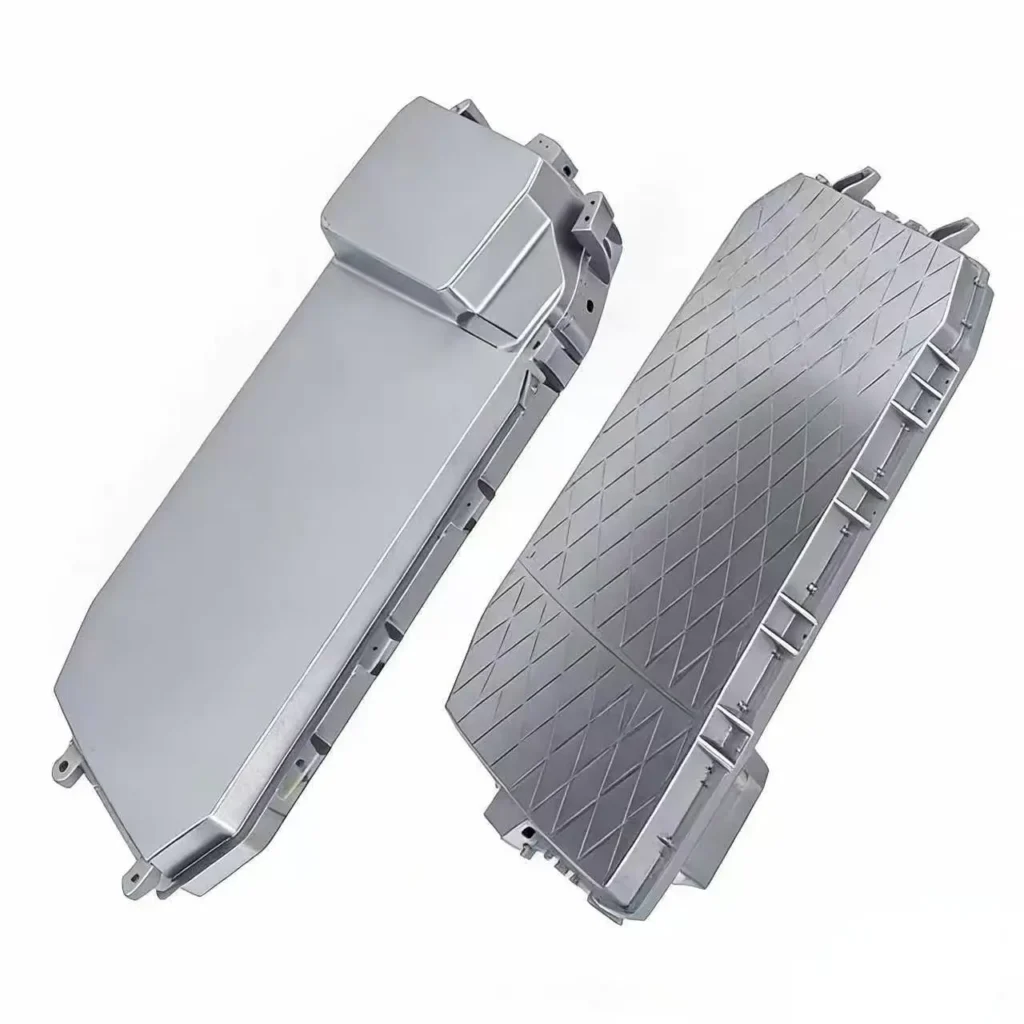



Consumer Electronics
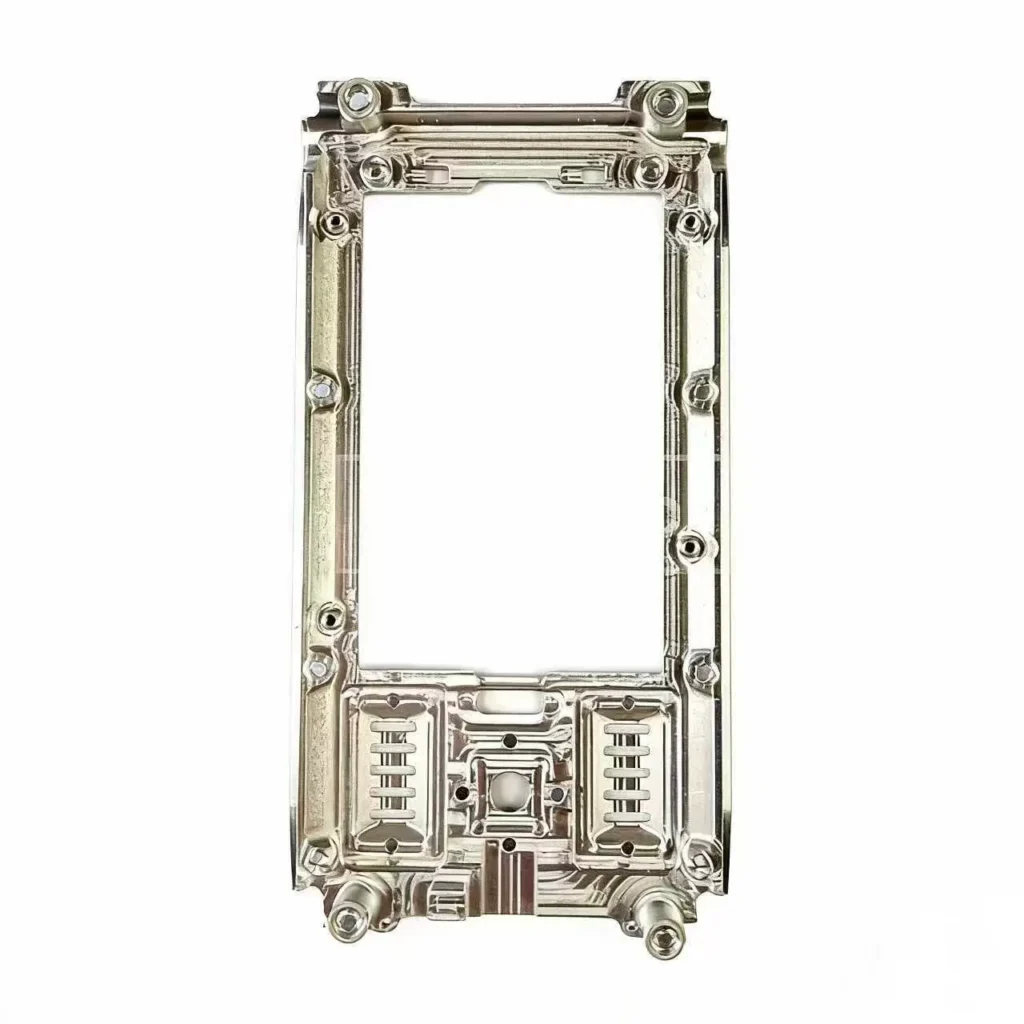



Aerospace



Explore our portfolio of magnesium die casting parts for various industries.
FAQ
Q1: Is magnesium die casting better than aluminum?
It’s not about “better,” but “more suitable.” Choose magnesium when your top priority is maximum weight reduction. Choose magnesium if your project is more cost-sensitive or requires higher natural corrosion resistance.
Q2: How thin can magnesium die casting walls be?
Thanks to excellent fluidity, walls can typically be 0.8mm to 1.2mm, and as low as 0.6mm with optimized design.
Q3: Is the process safe?
Yes. Modern die casting uses protective atmospheres (SF6-free gases) to eliminate ignition risk, adhering to strict safety protocols.
Q4: What are the tolerances achievable?
Standard tolerances range from ±0.05mm to ±0.10mm. With CNC machining, critical dimensions can be held to ±0.005mm.
Conclusion: Partner with IEC MOULD for Your Lightweighting Journey
At IEC MOULD, we combine deep expertise in magnesium alloys with advanced engineering, precision tooling, and stringent quality control to deliver components that meet your most demanding requirements.